Dynamic-Tracing Custom Go Programs with Custom Ylang Analyzers (using OpenResty XRay)
In this tutorial, we will demonstrates how to write a simple Ylang analyzer to dynamically trace an aribitrary Go program in OpenResty XRay . This custom analyzer adds a dynamic probe to the entry point of a specified Go function and then dump the content of a Go map-typed variable. Thanks to our dynamic tracing technology, the analyzer can work in a truly noninvasive way with minimal performance overhead. No changes are made to the target Go program and process.
Insert two key-value Pairs into a Go Variable
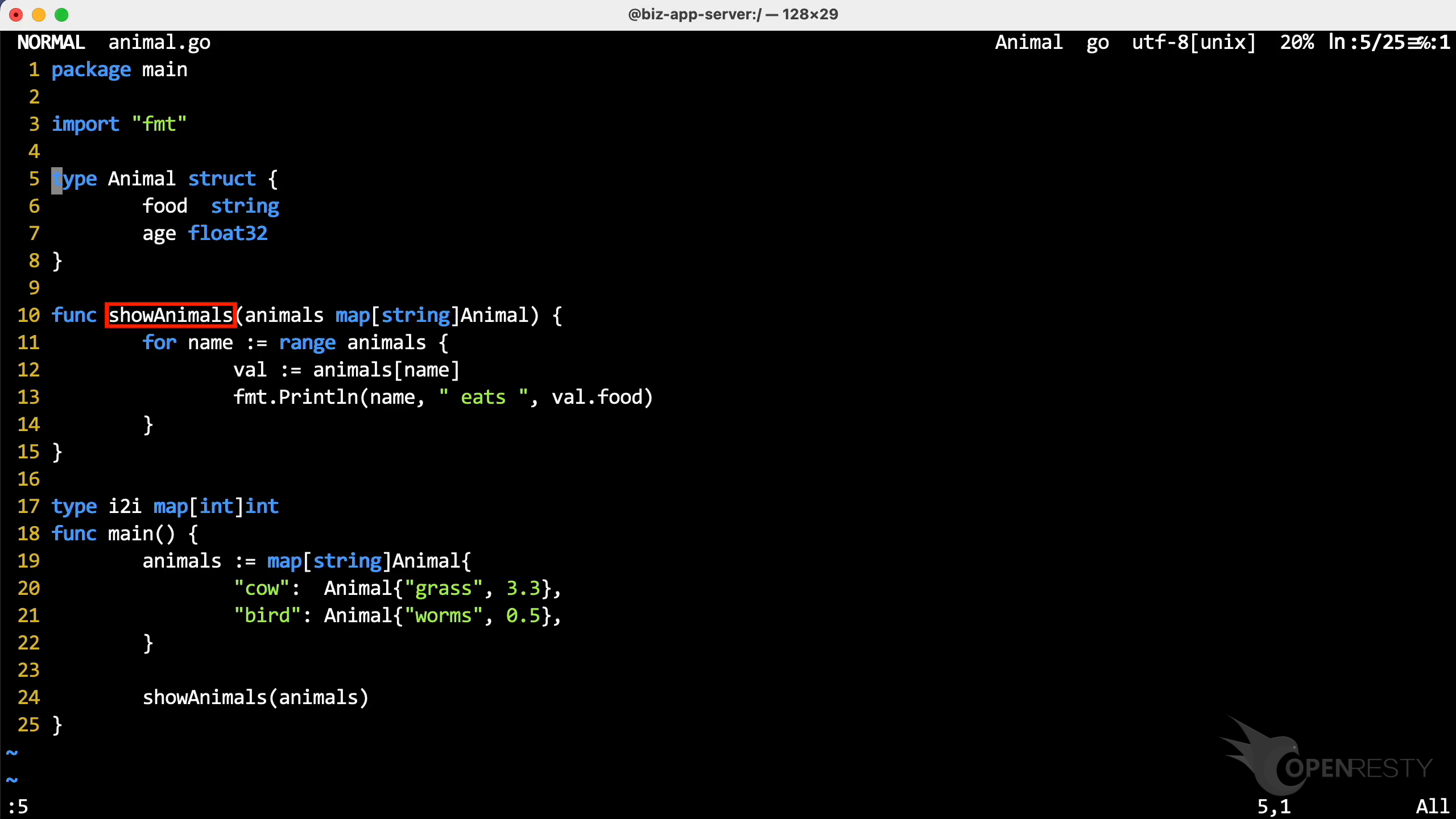
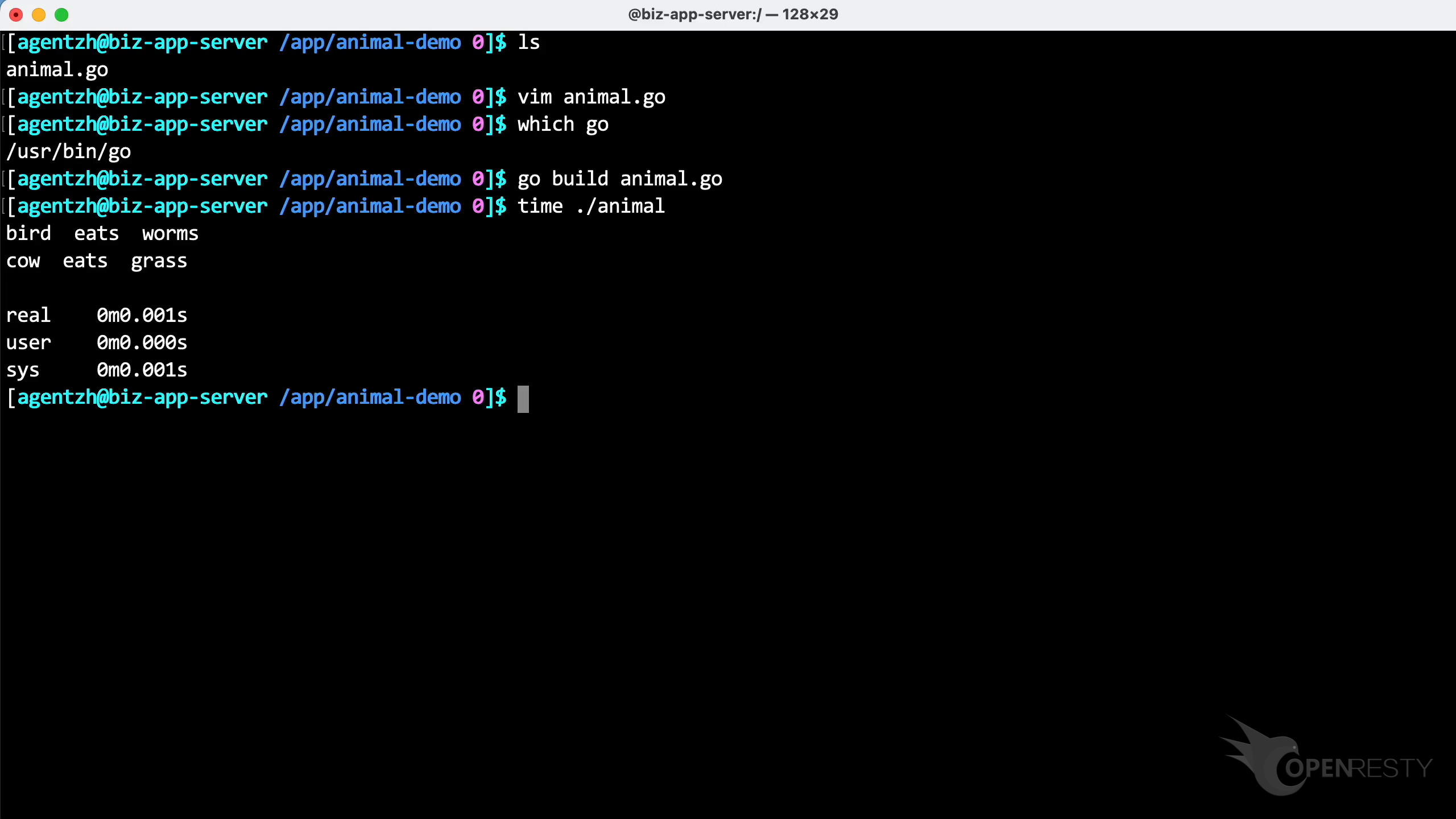
We have a program called animal written in Go.
We use the Vim editor to take a look at the source code of this program.
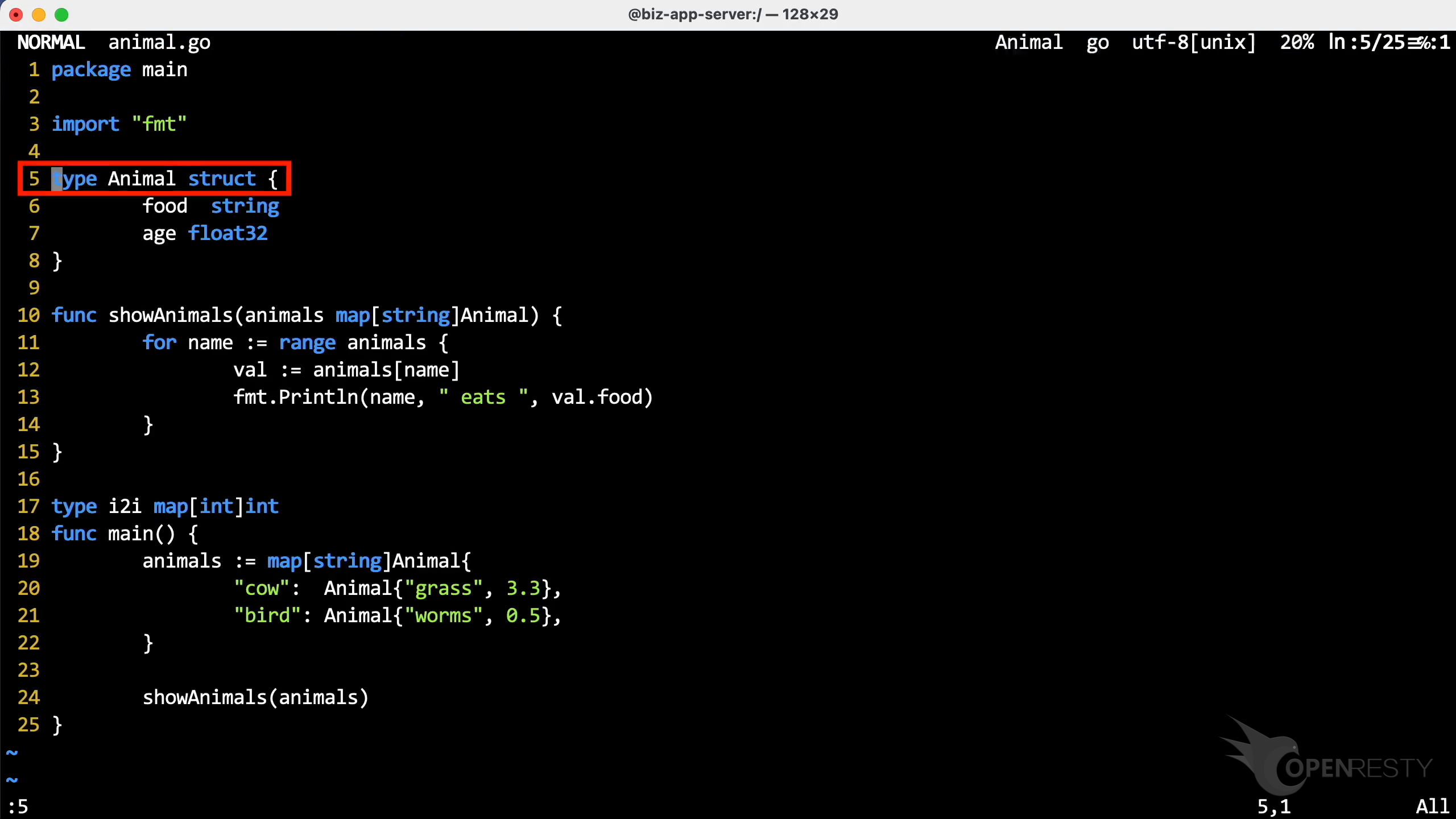
Look at this program, Animal is a struct.
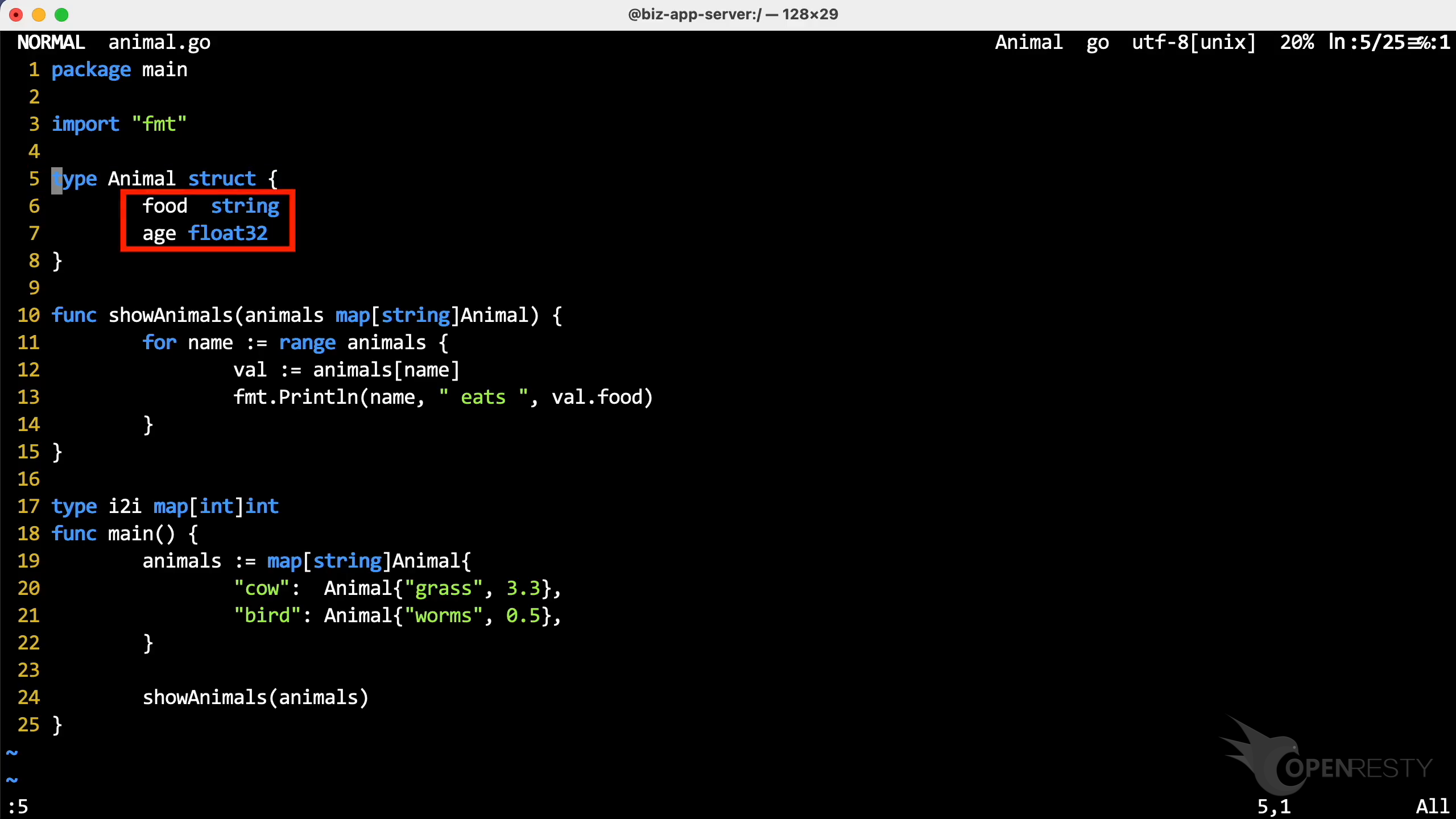
We can see the Animal struct has two members. The food is a string field, and age is a float32 field.
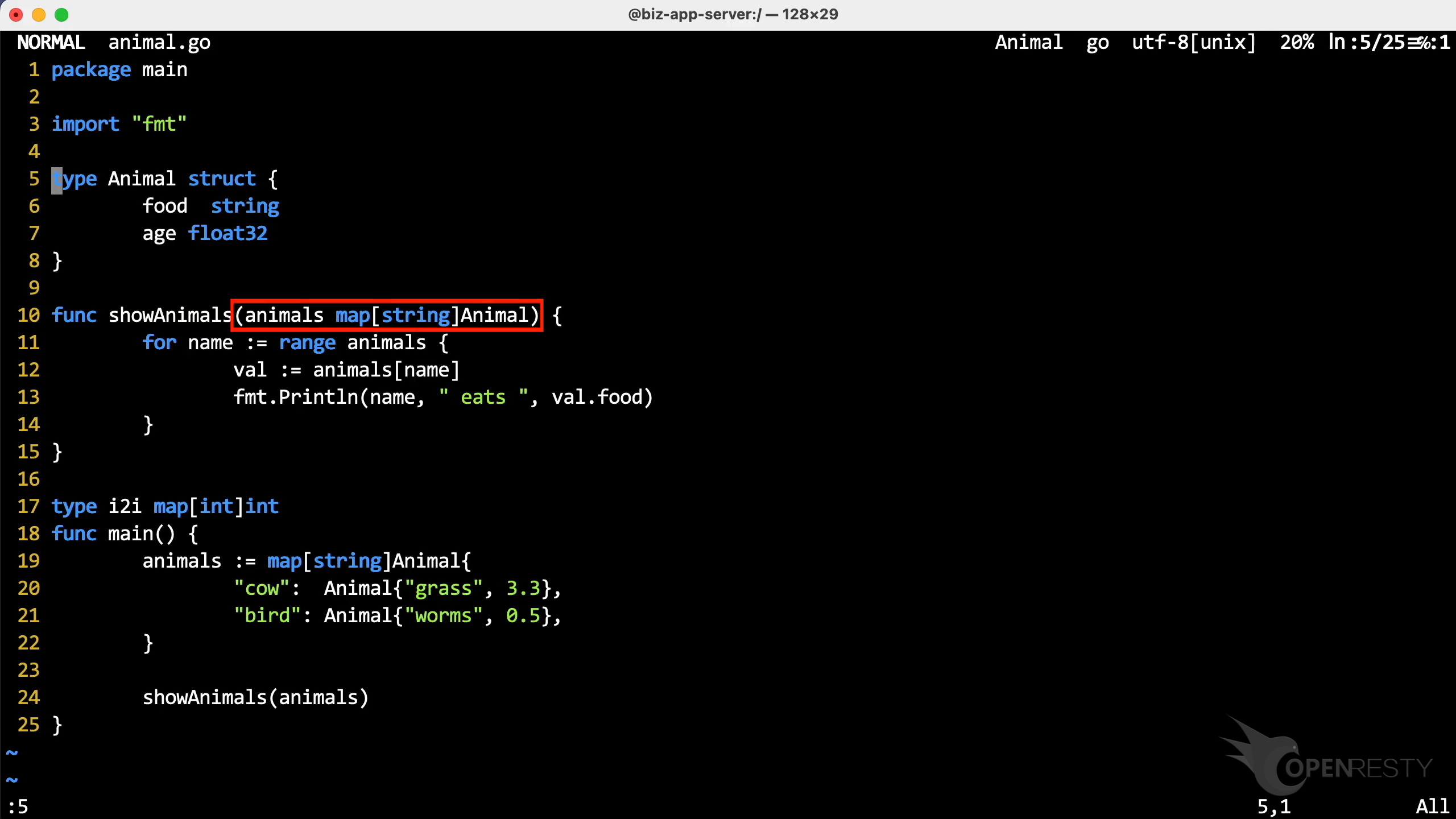
The showAnimals function displays the values in the map variable.
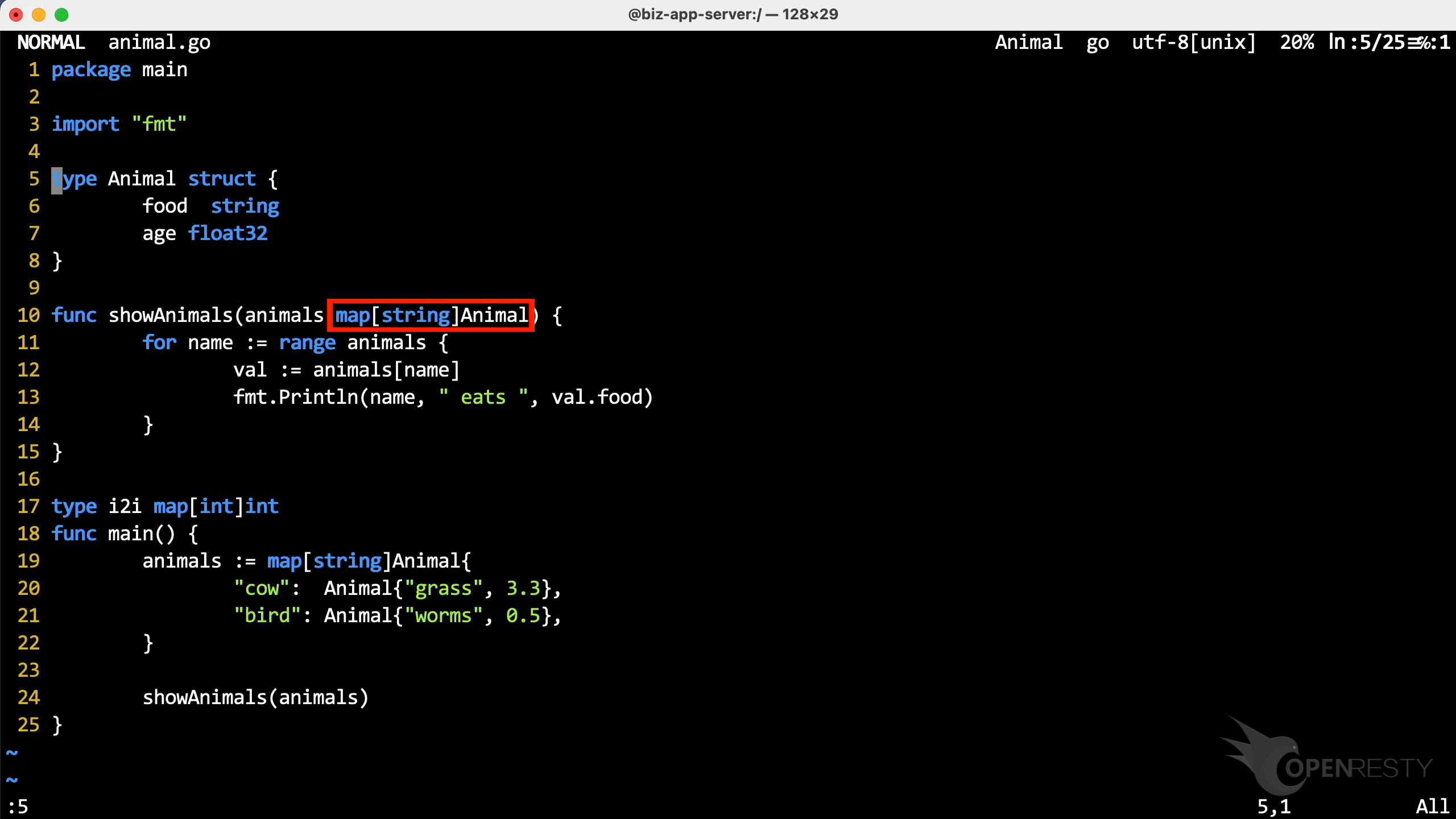
It has a parameter animals of type map[string]Animal.
map[string]Animal is a map aggregation type. The key type is string and the value type is Animal.
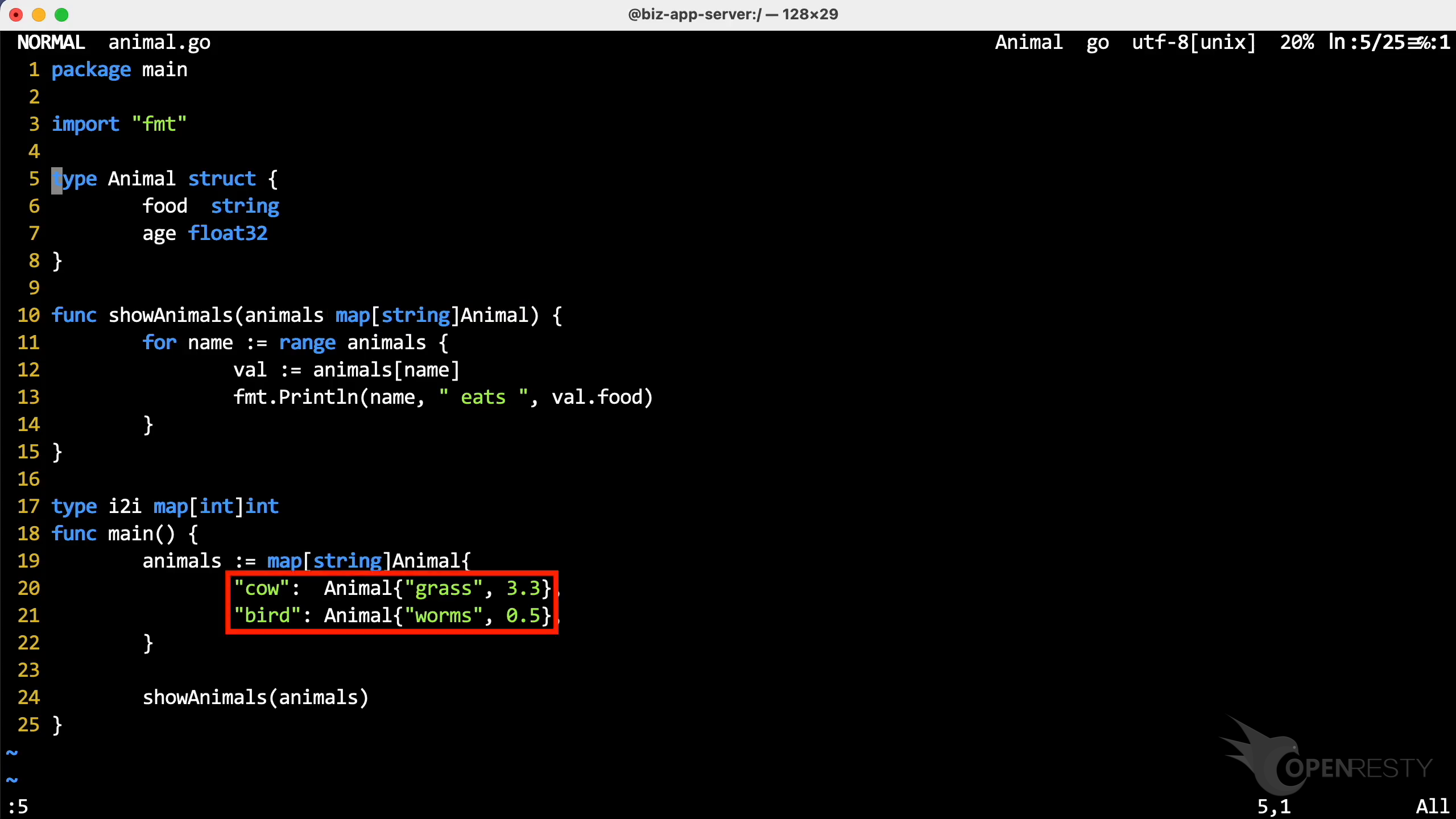
In the main function, insert two key-value pairs into this map variable.
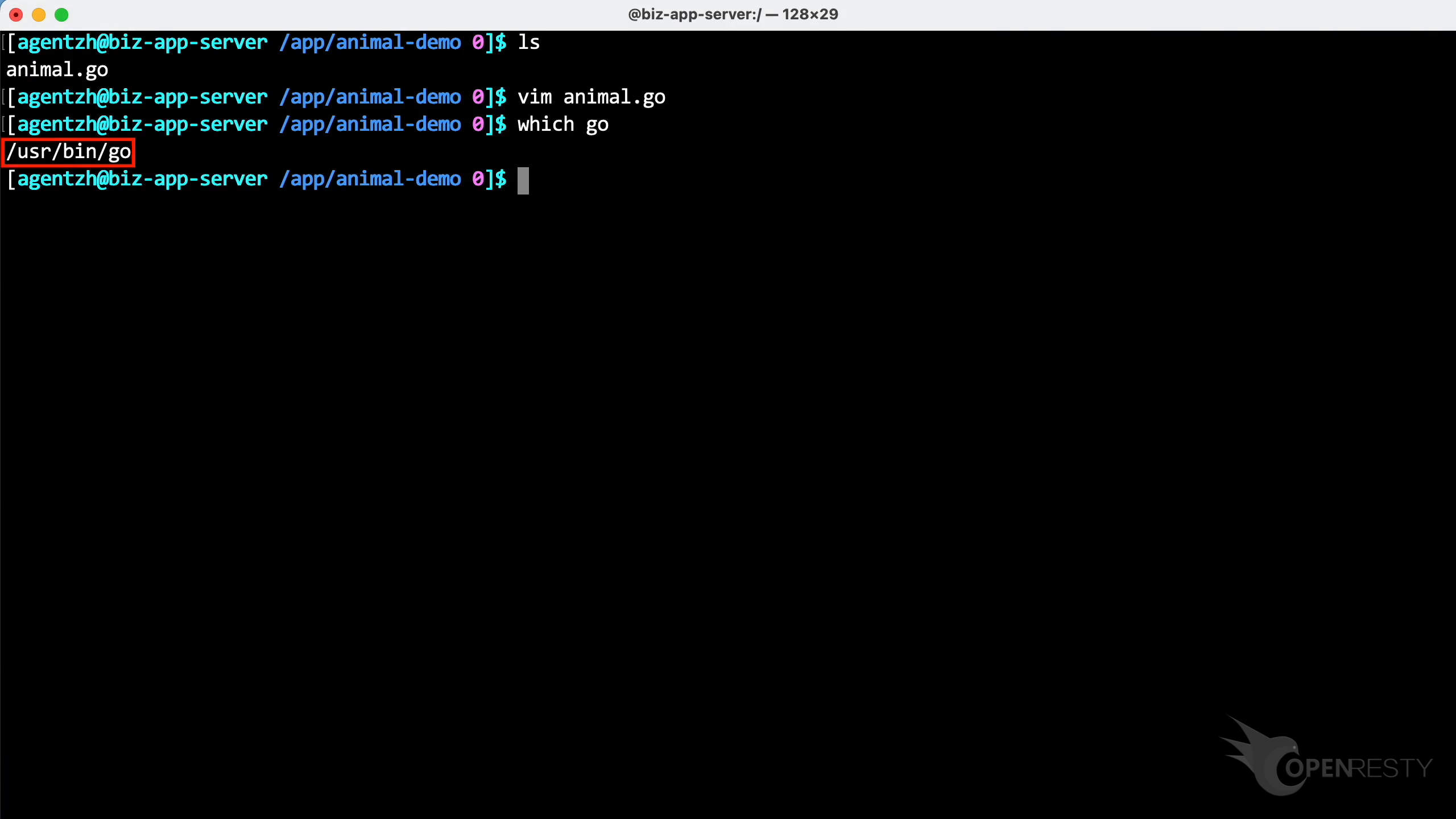
We are using the unmodified Go compiler that comes with the Linux distribution.
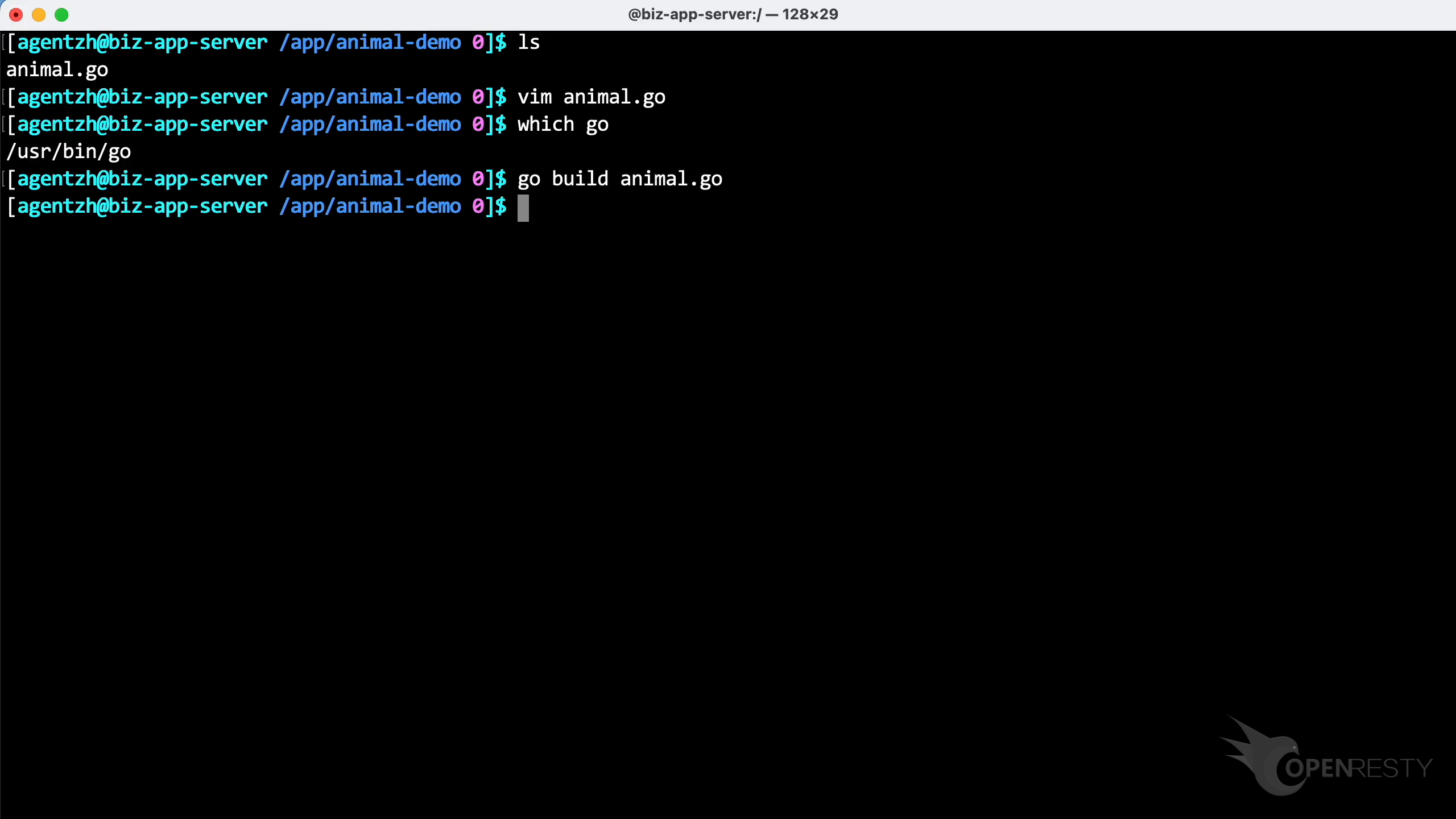
Let’s compile this program. As shown, we don’t need to add any special options.
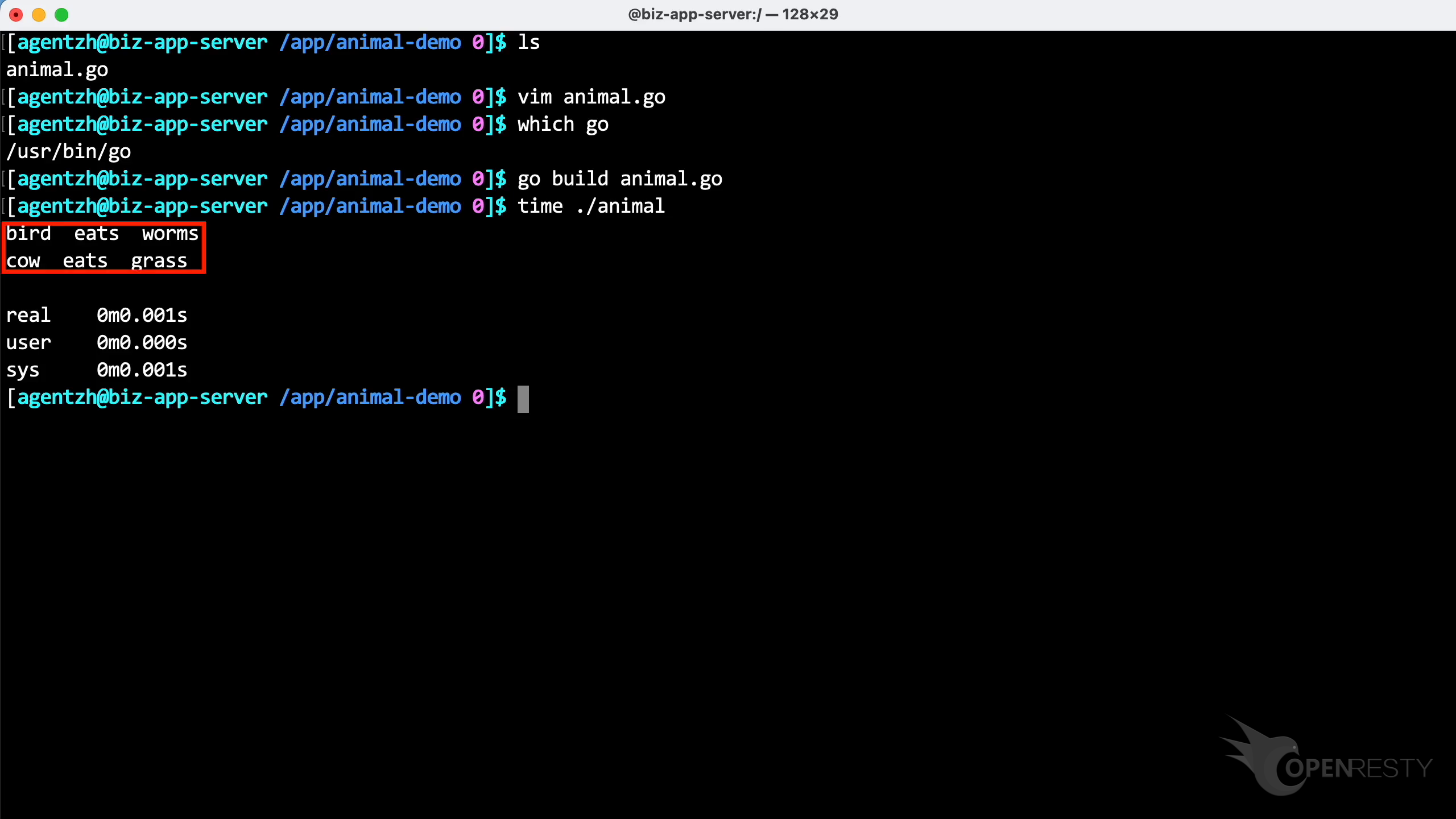
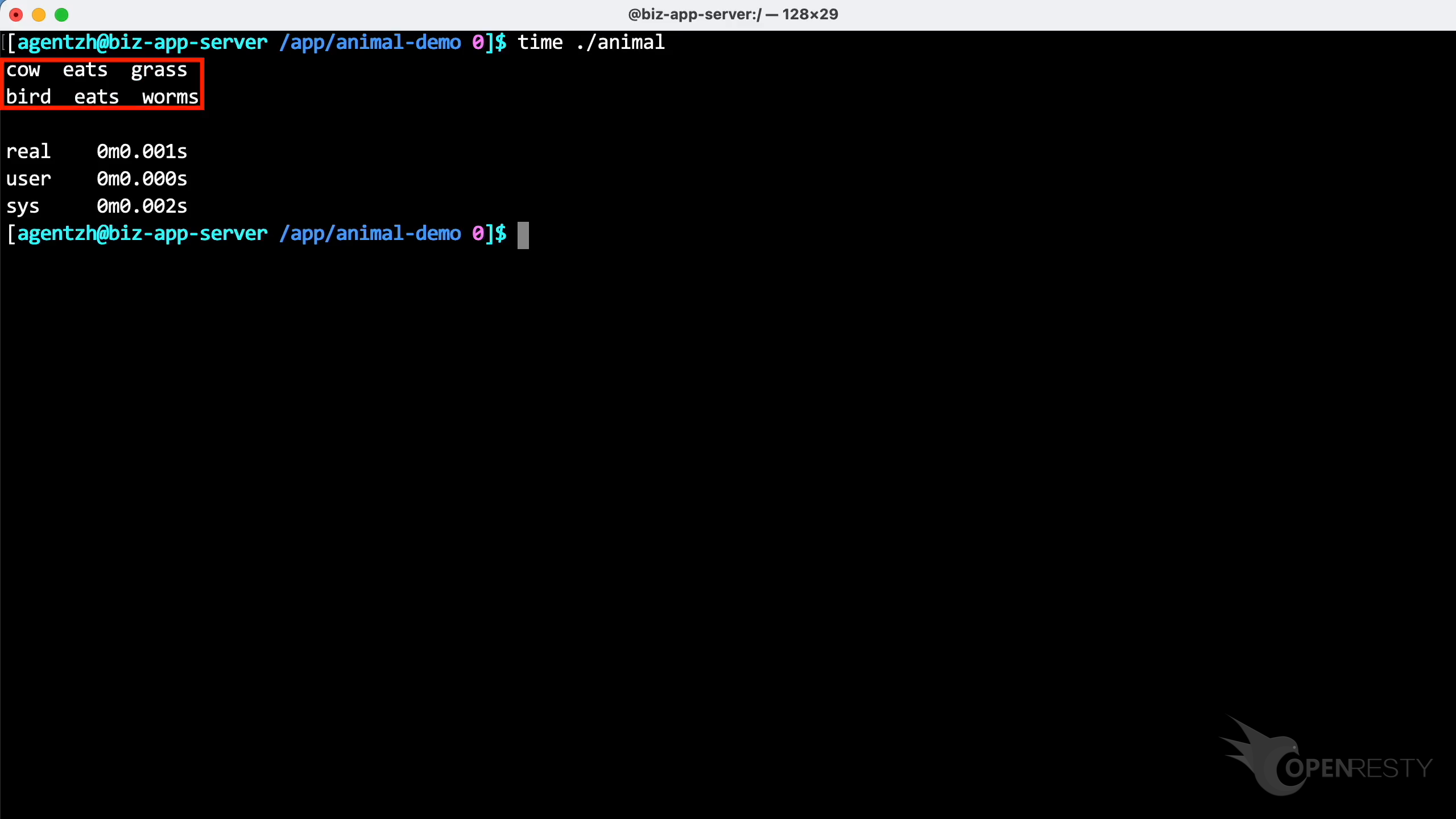
Here is the output of the program.
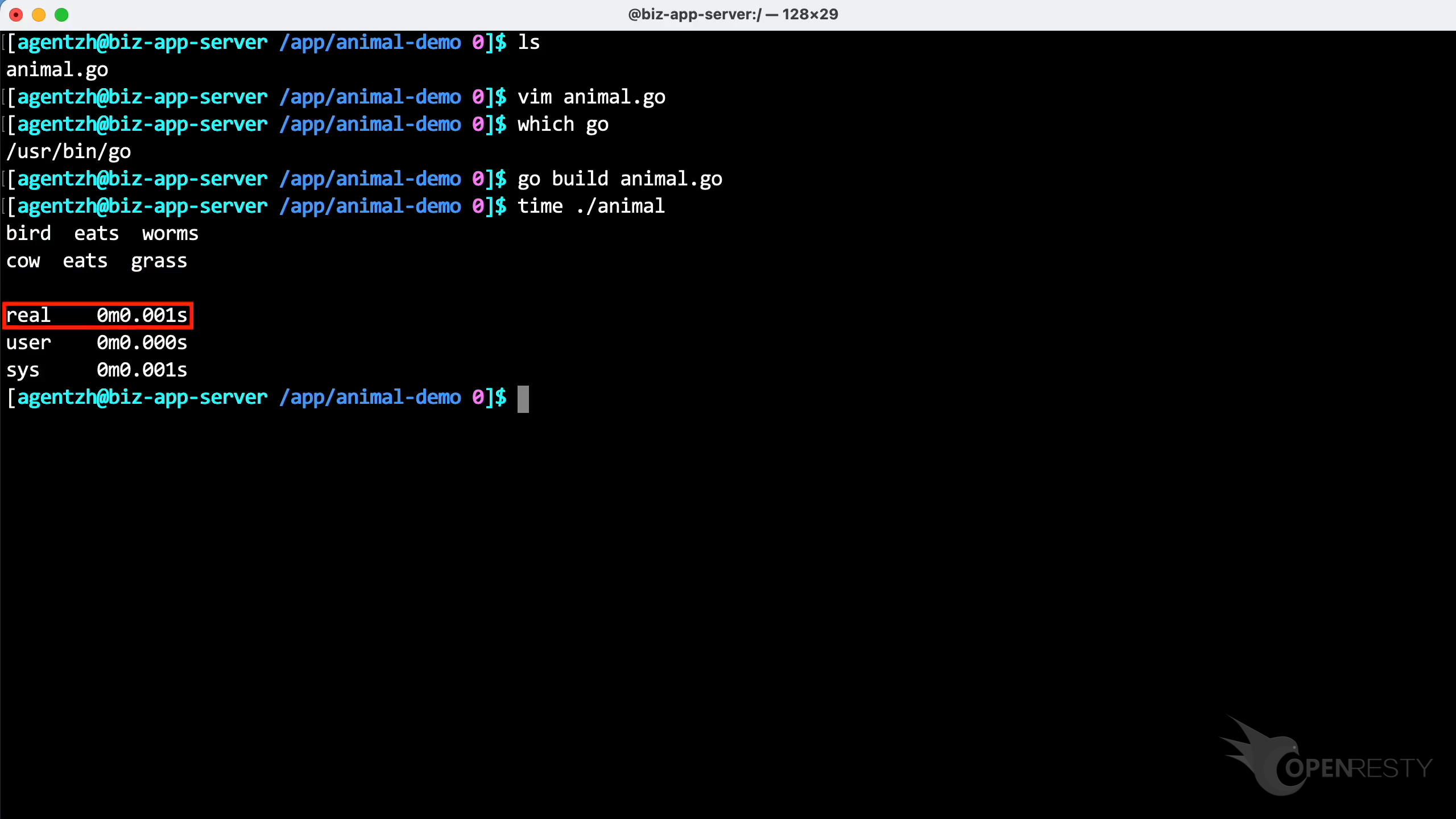
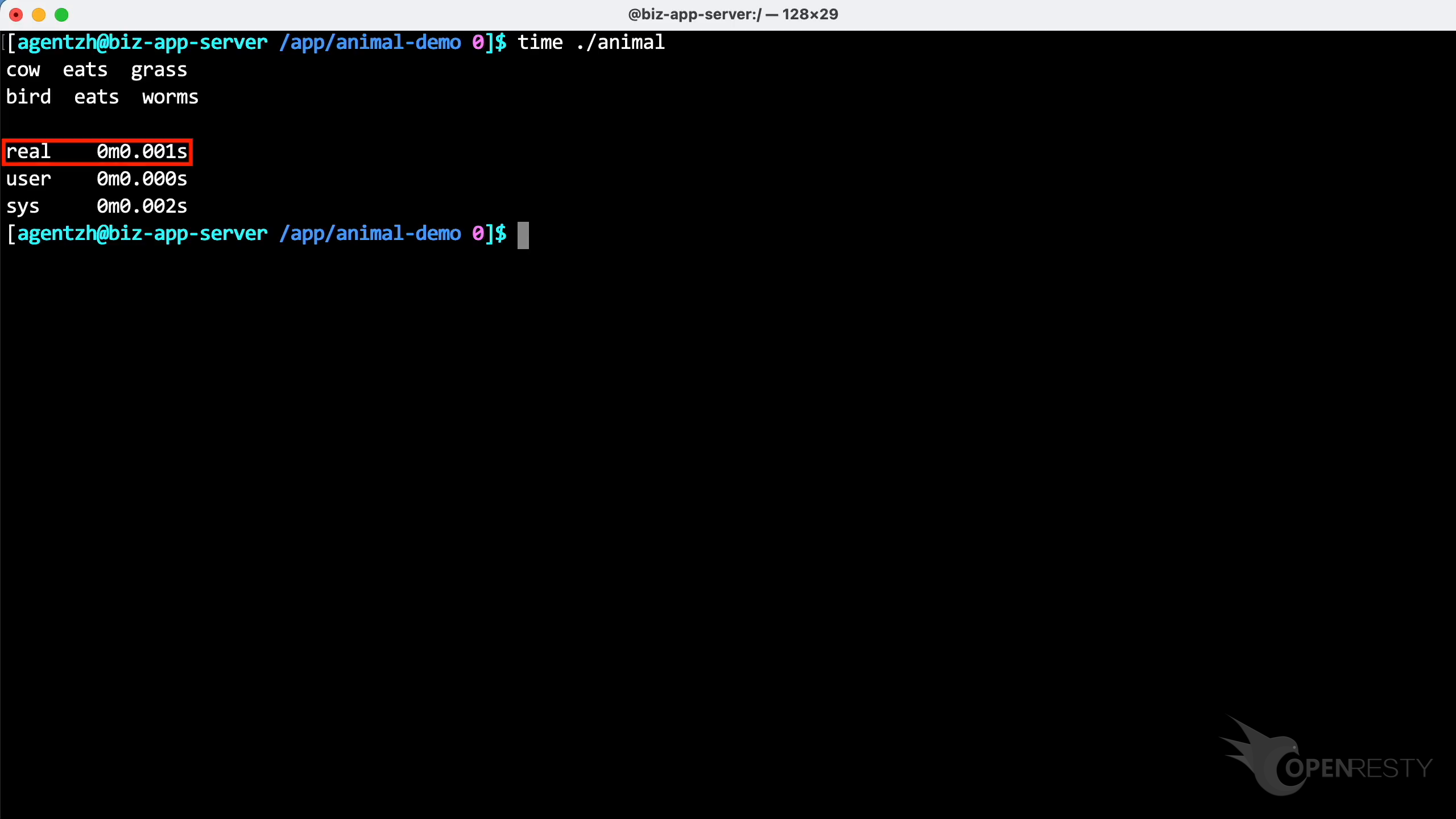
This program had a very fast execution time, lasting only 1 millisecond.
Let’s write a custom Ylang analyzer to dynamically trace the execution of this Go program.
Write a Customize Ylang Analyzer to Dynamically Trace the Go program
Switch to the OpenResty XRay Web console.
Go to the “Analyzers” page.
Click on the “Add new analyzer”.
Enter the name in the “Analyzer name” textbox.
Select the “YLang” language type.
Delete the sample Ylang program provided by default.
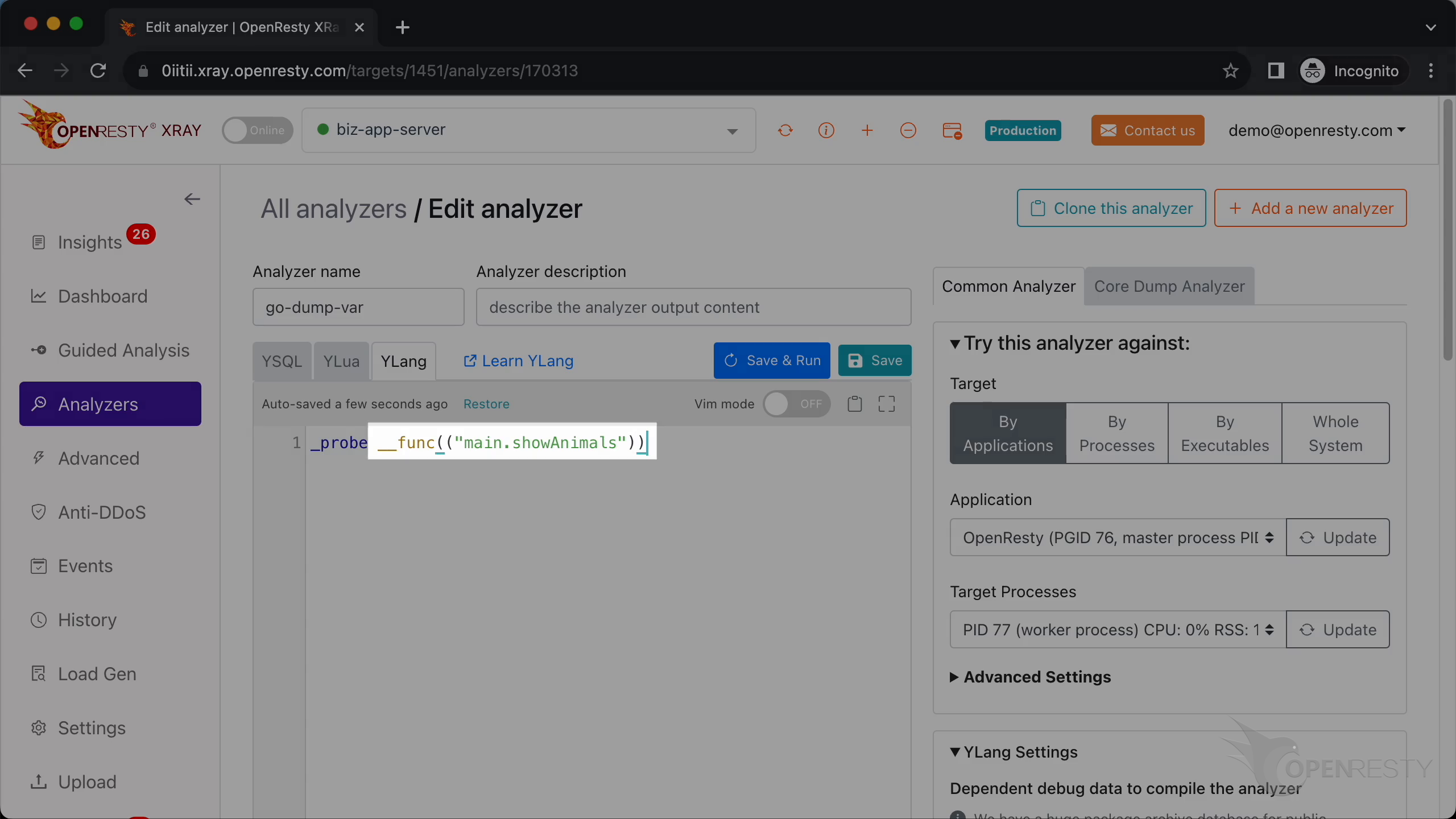
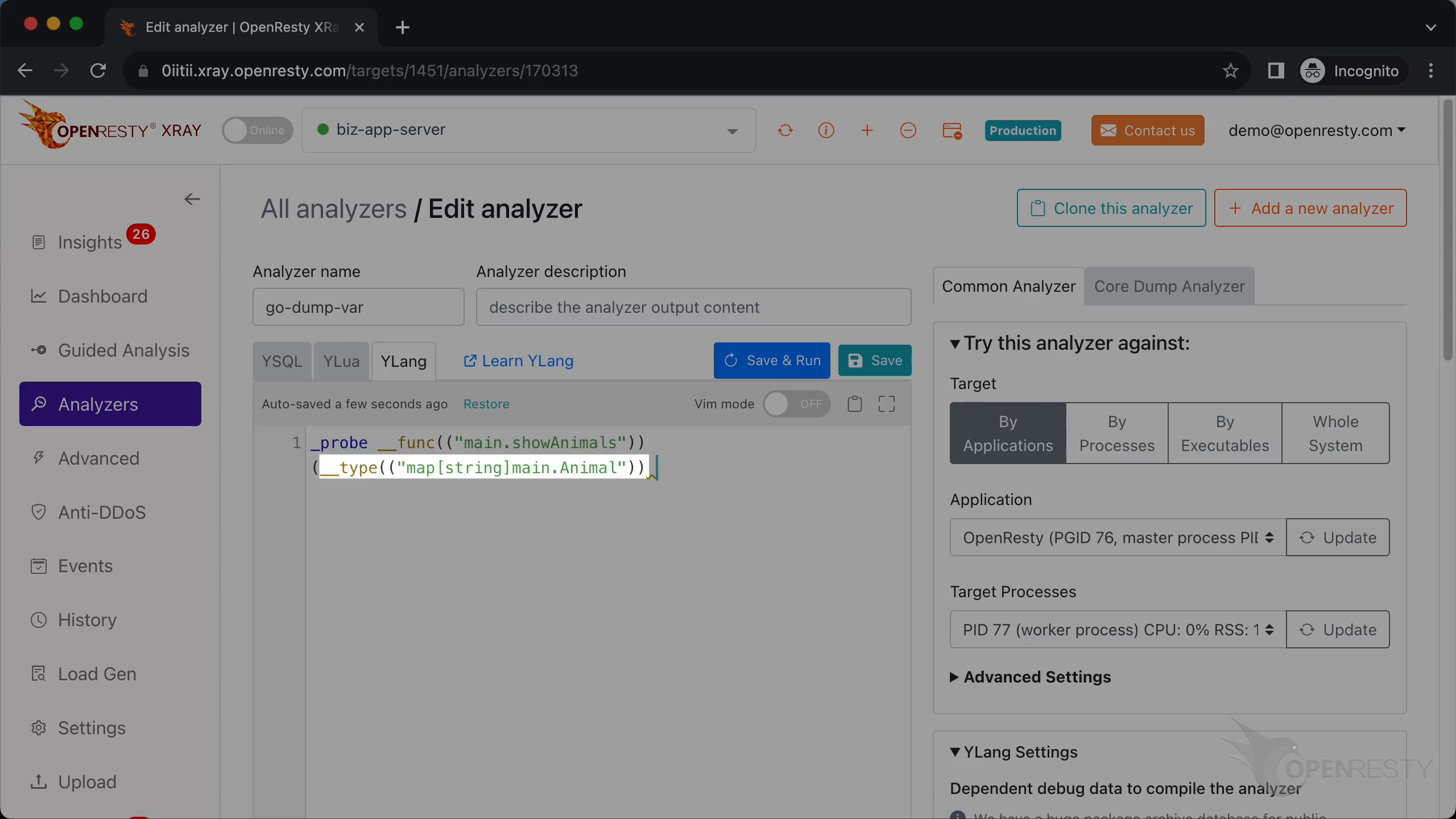
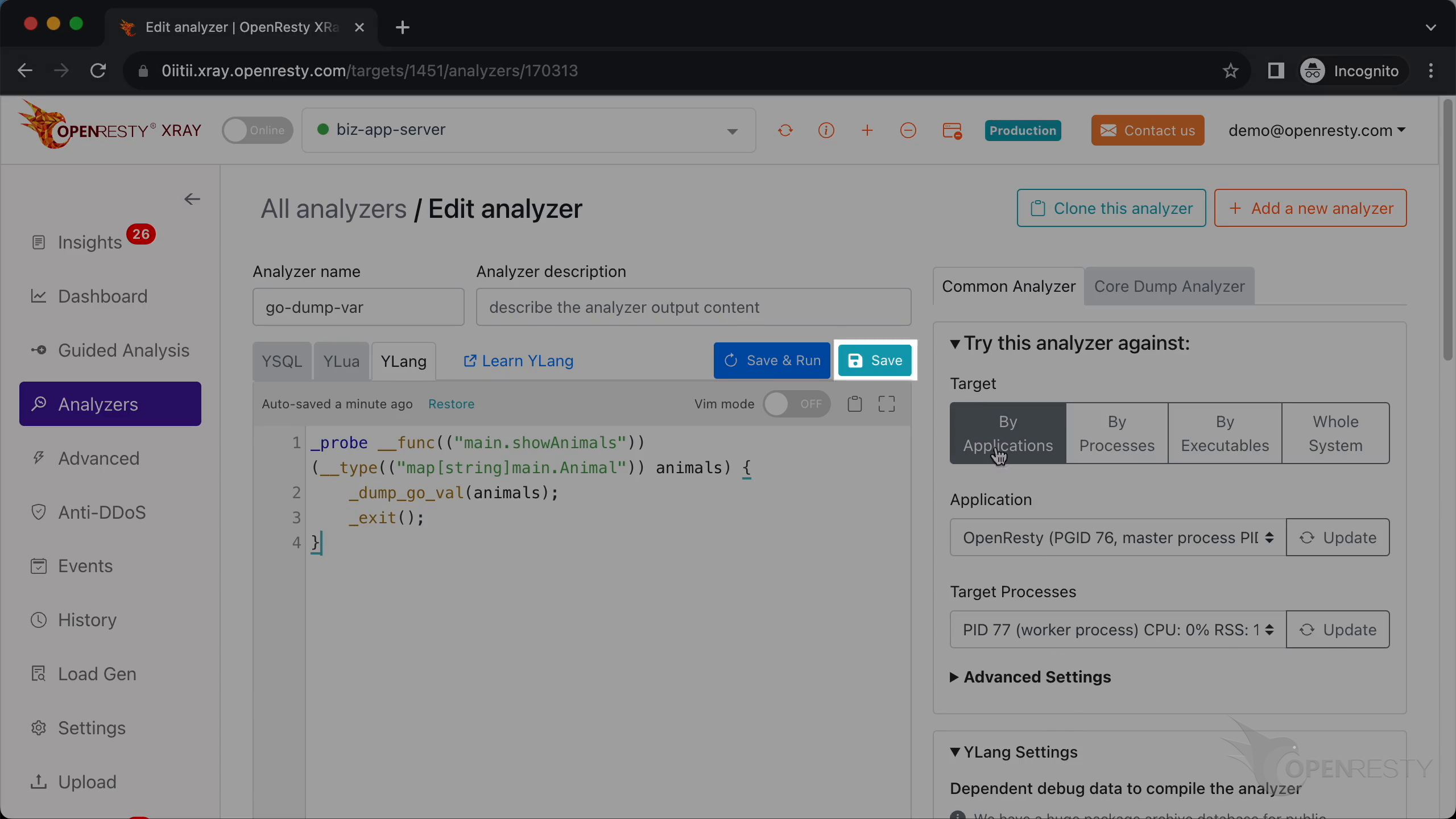
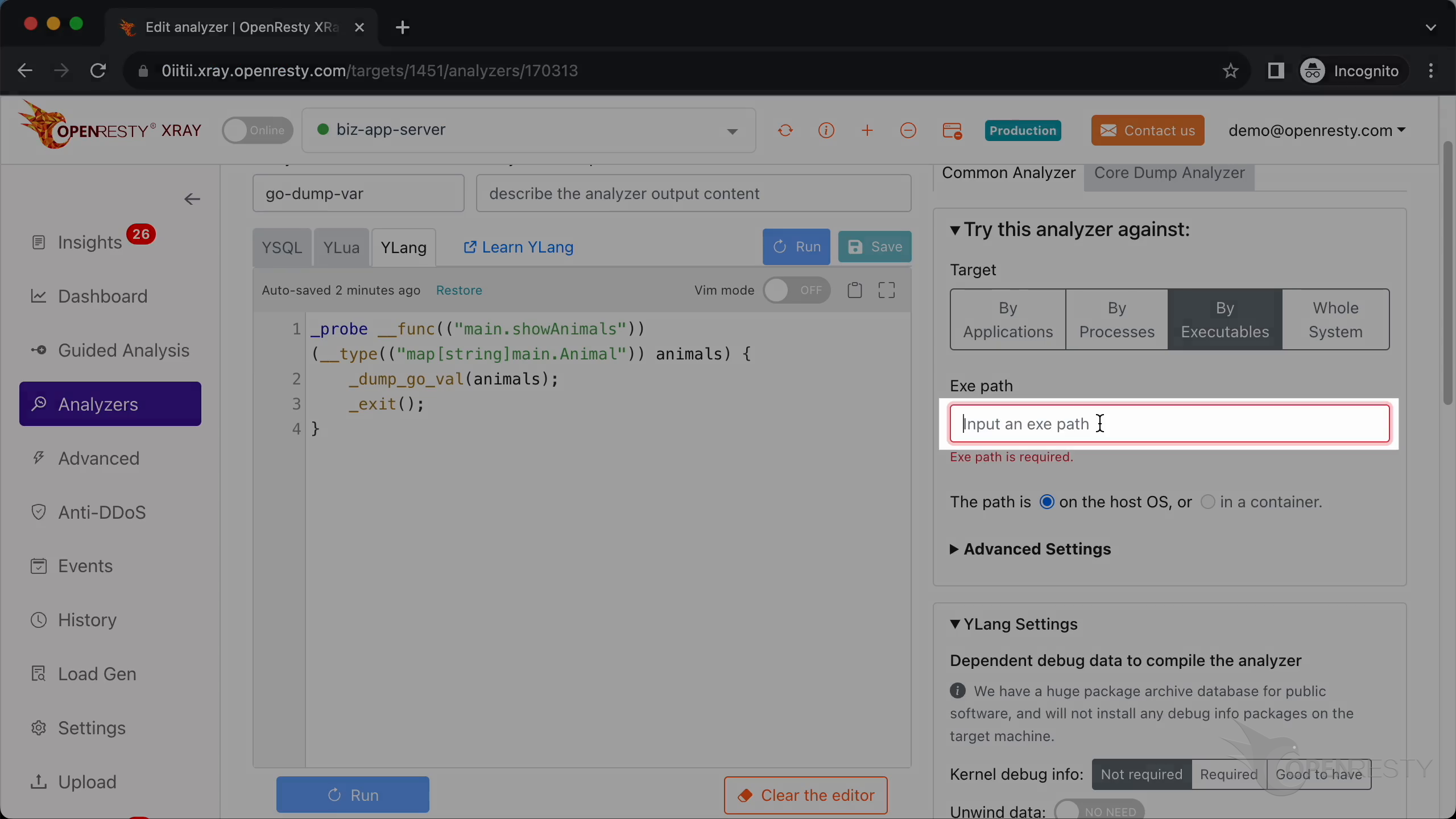
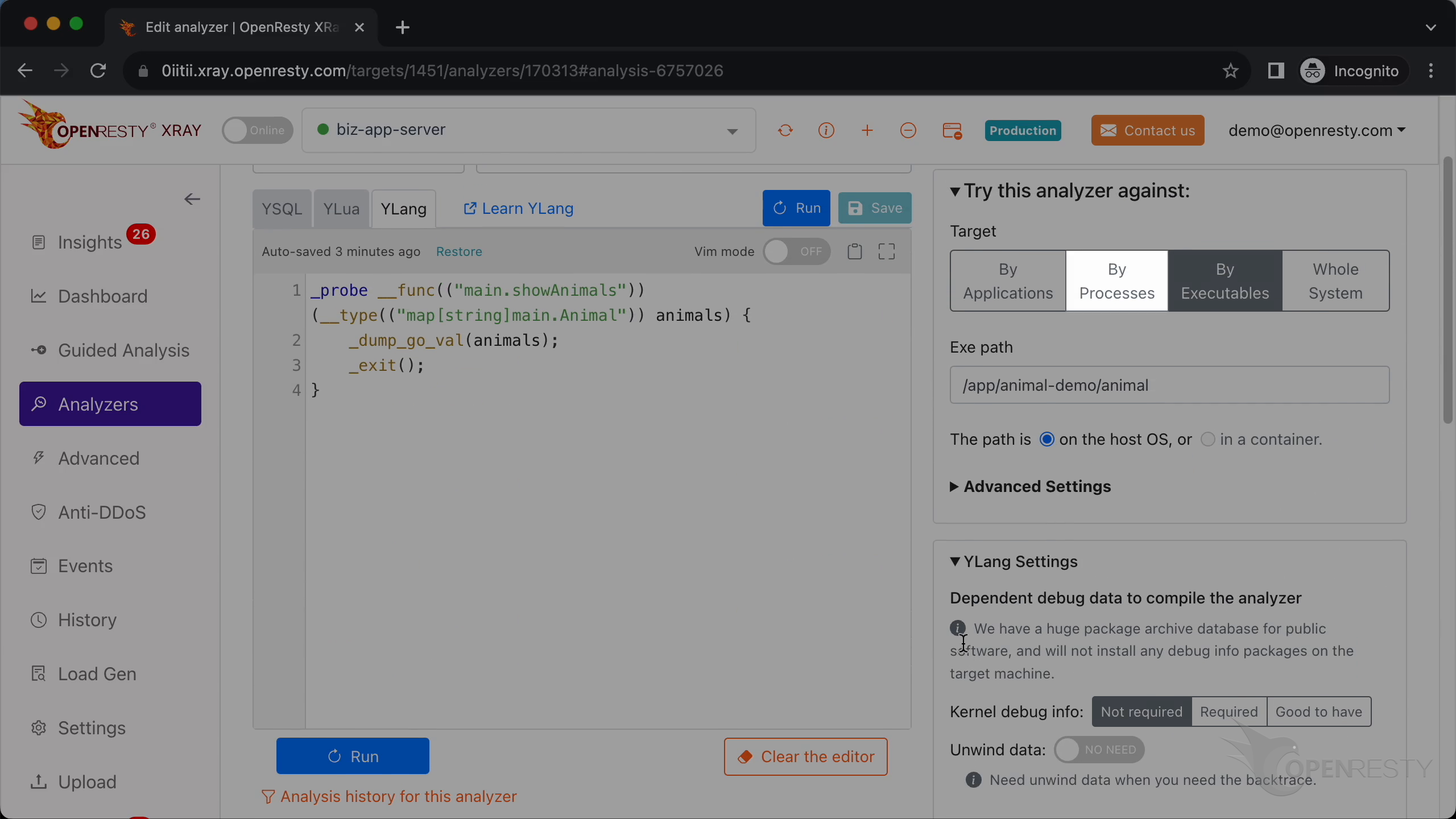
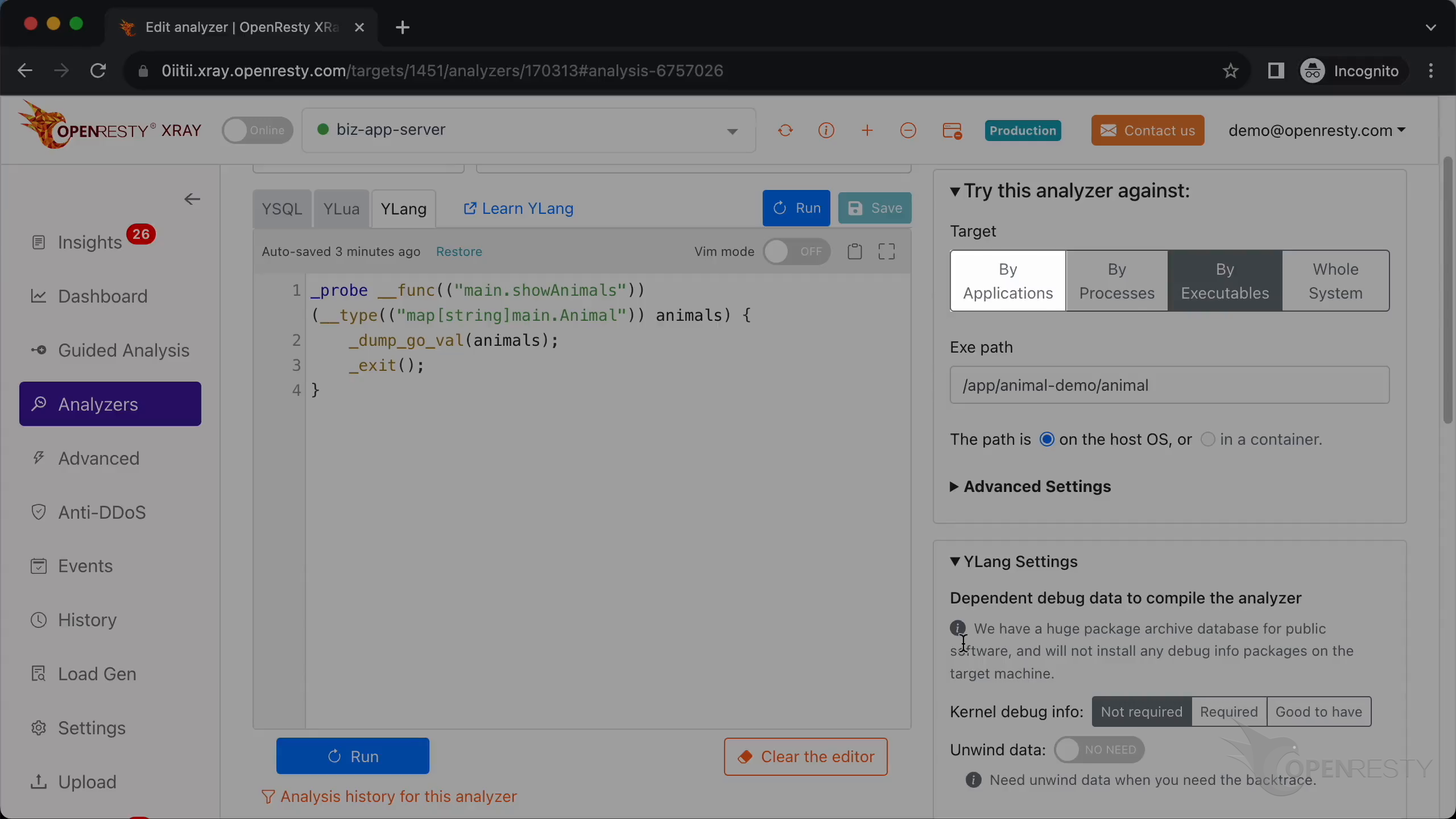
Here we add a dynamic probe onto the entry point of our Go function showAnimals in the main package.
This parameter type is a map with string keys and values of type main.Animal.
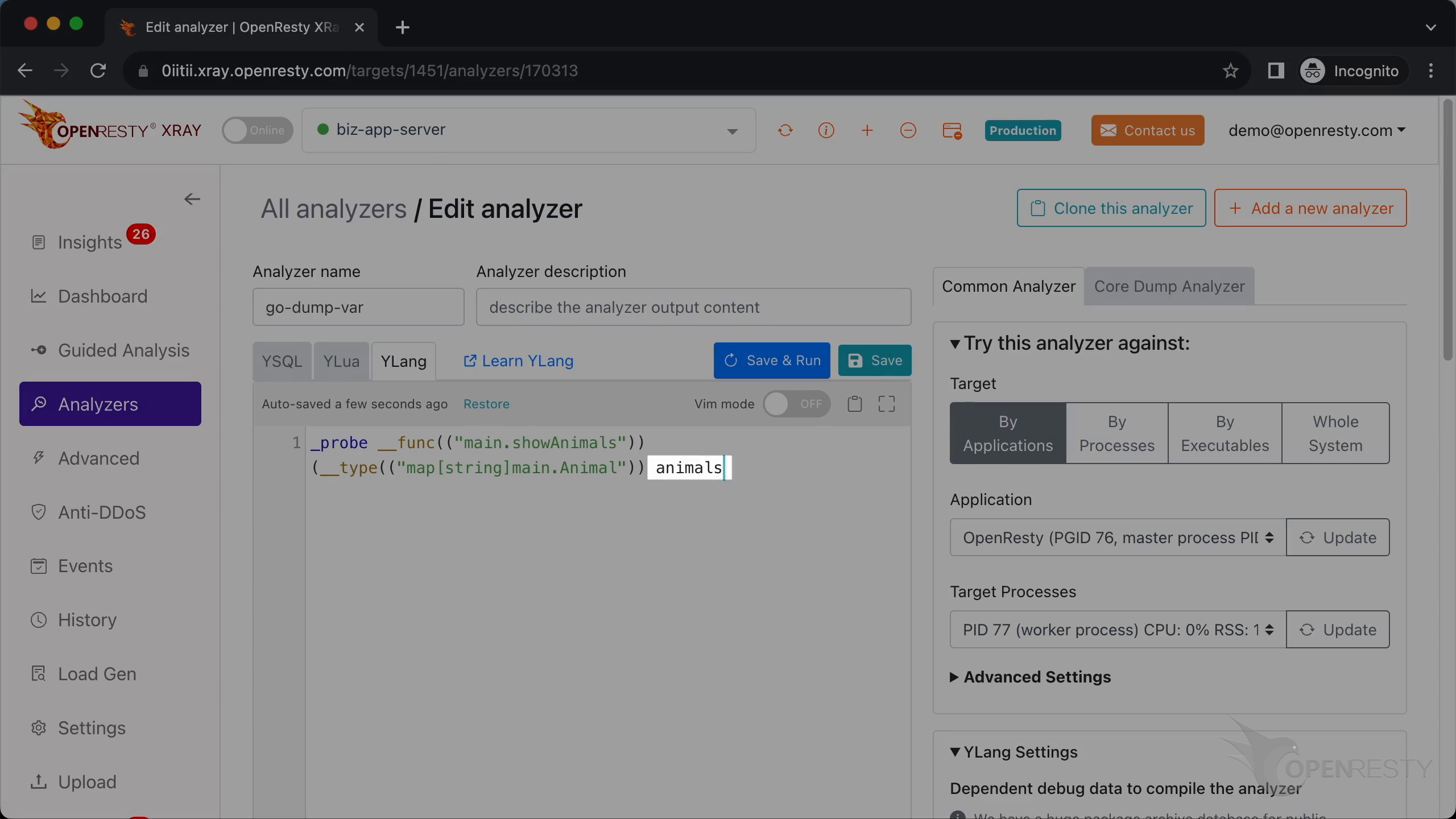
The parameter name is animals.
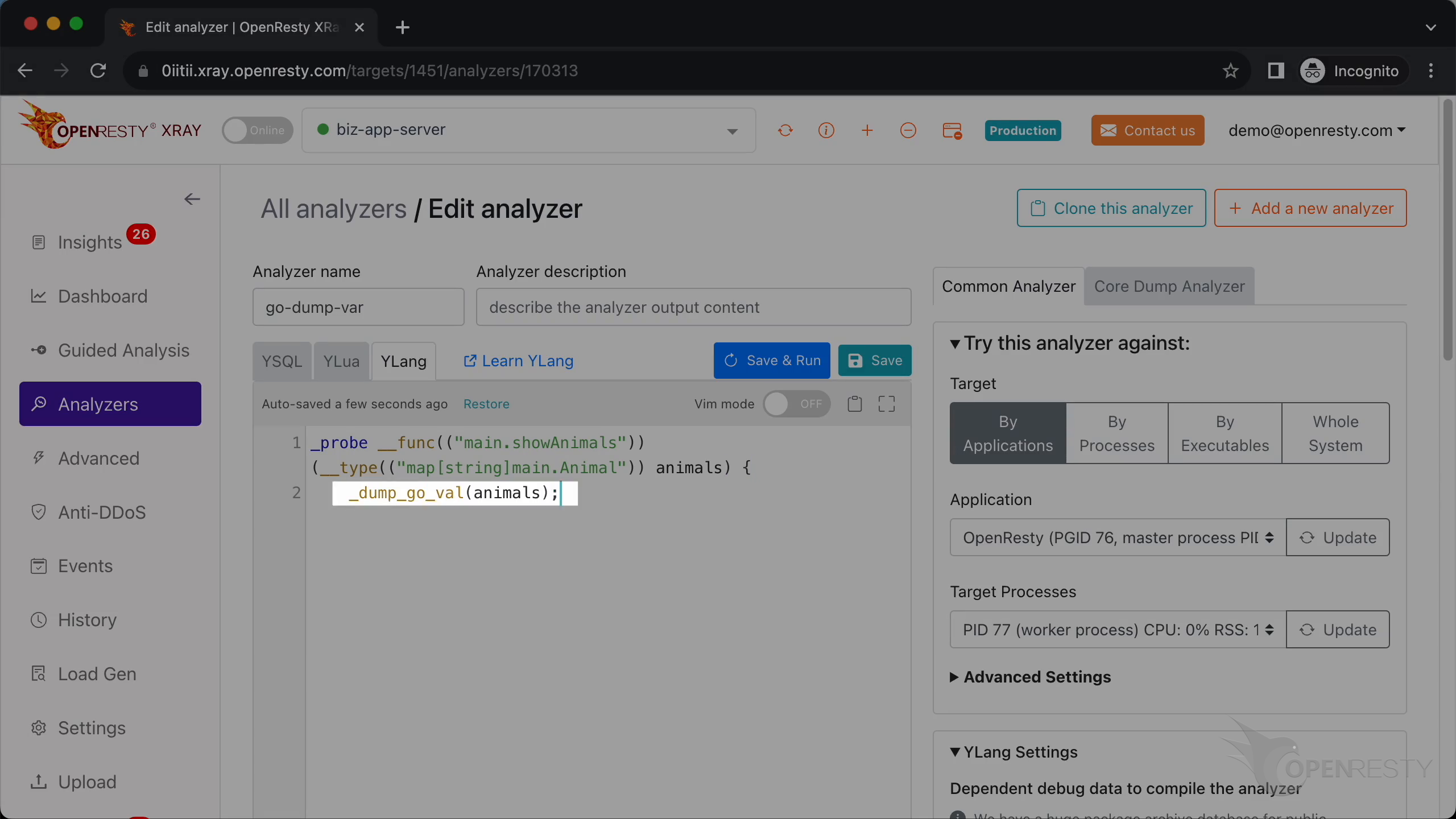
Call _dump_go_val to print the value of the animals variable.
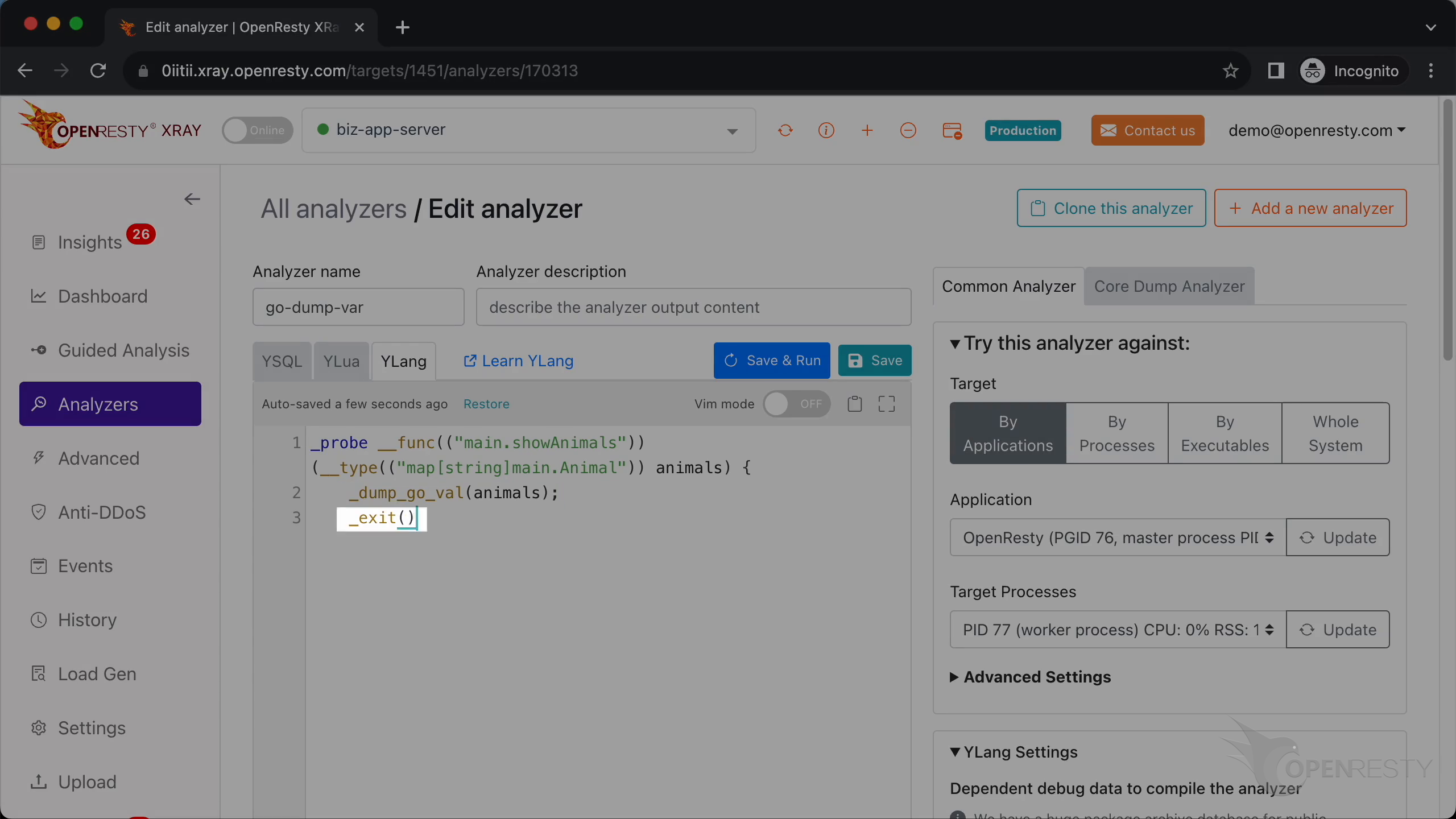
Call _exit() to make the analyzer exit after running this probe handler.
Save the code.
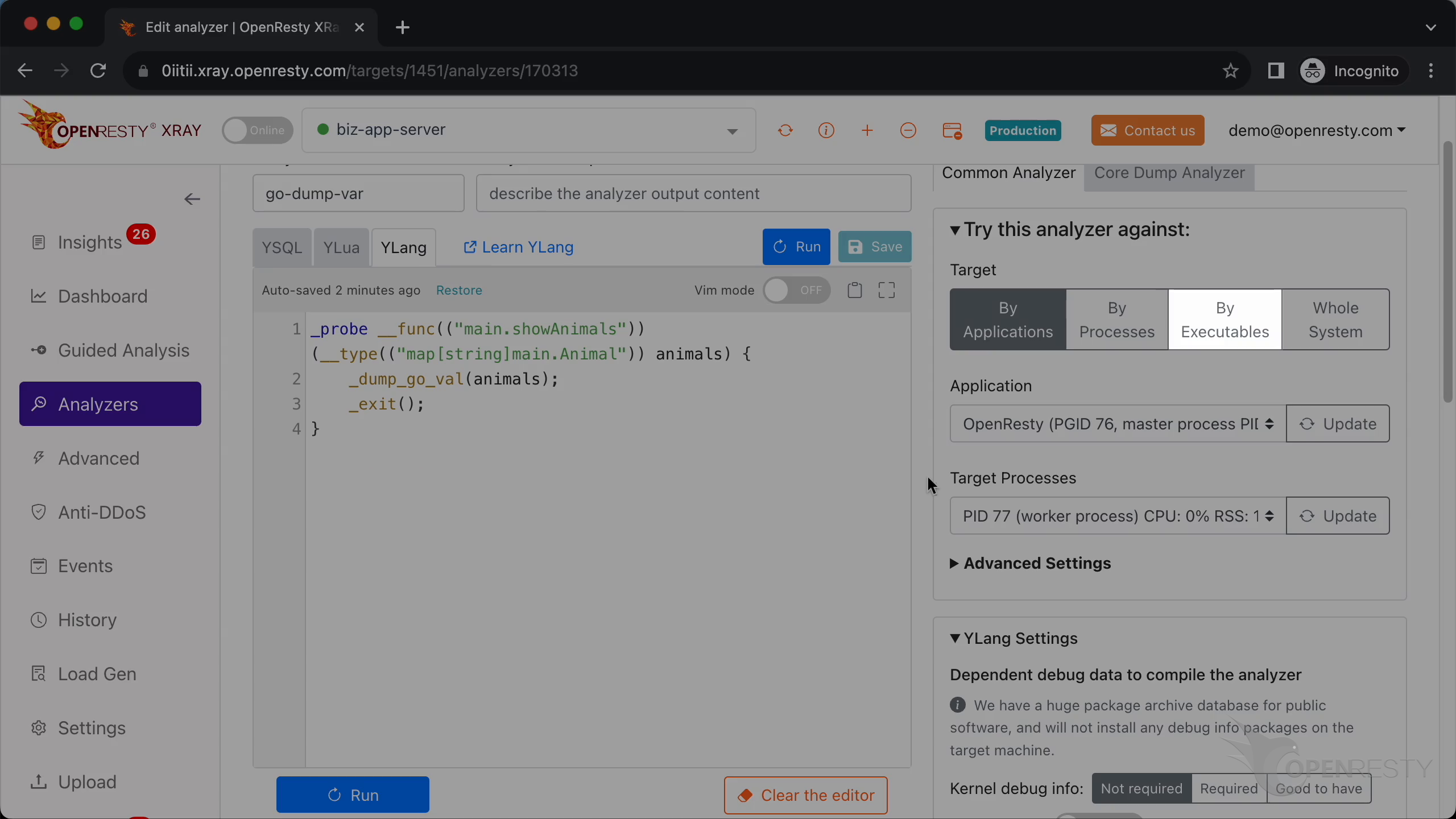
This is a short-lived program, so we choose the “By Executables” mode.
Let’s go back to the terminal window.
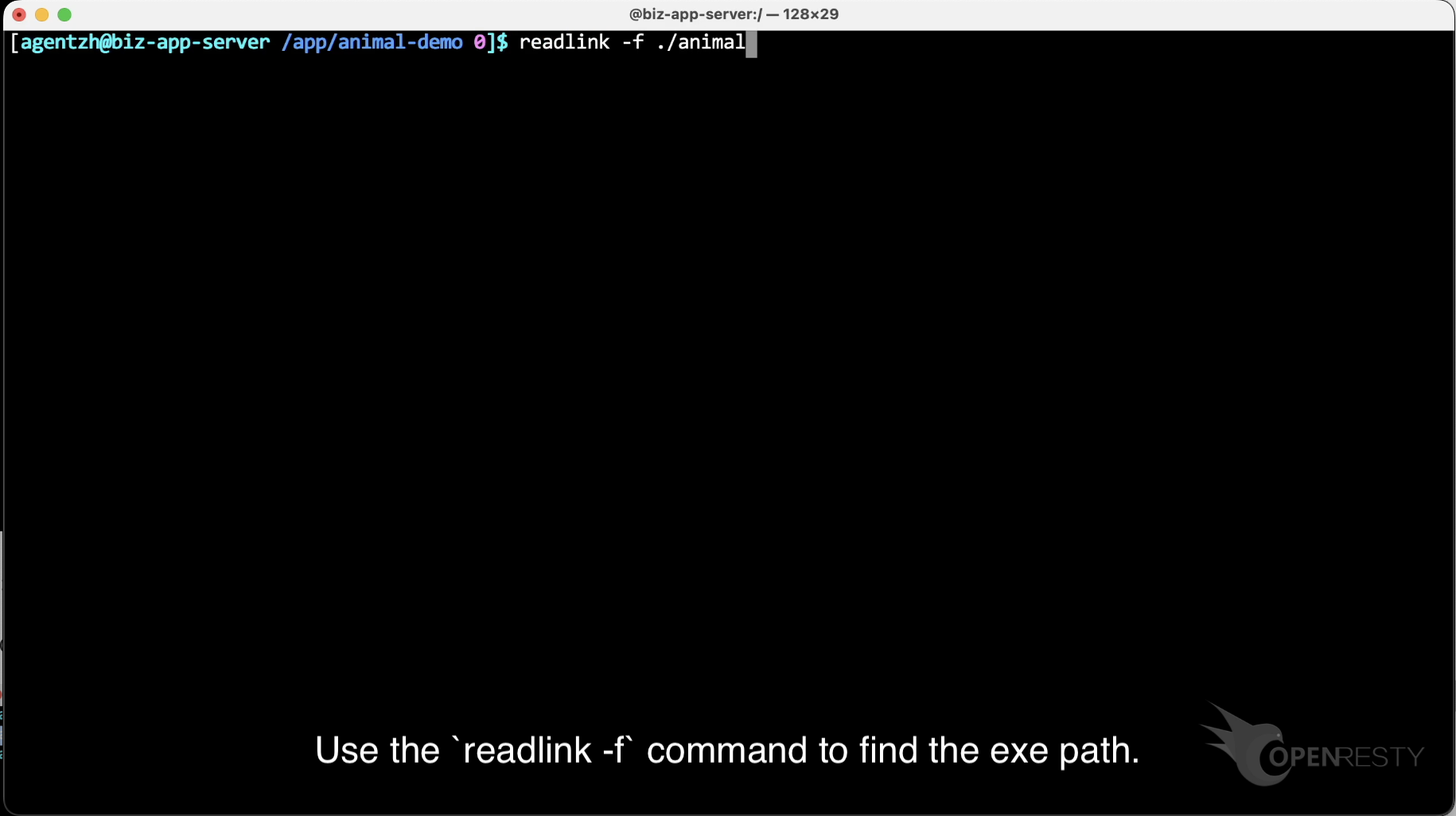
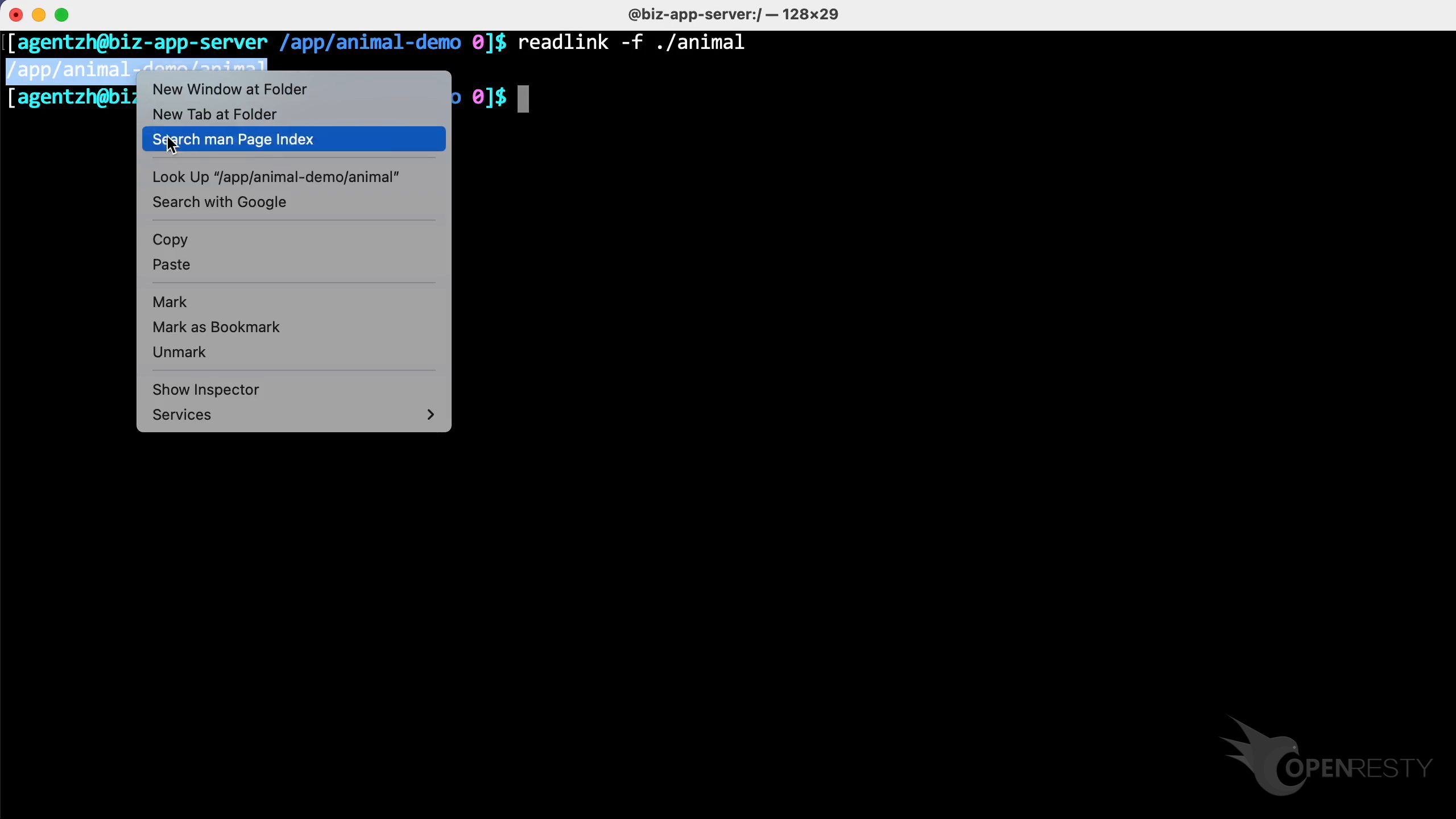
Use the readlink -f command to find the exe path.
Copy it.
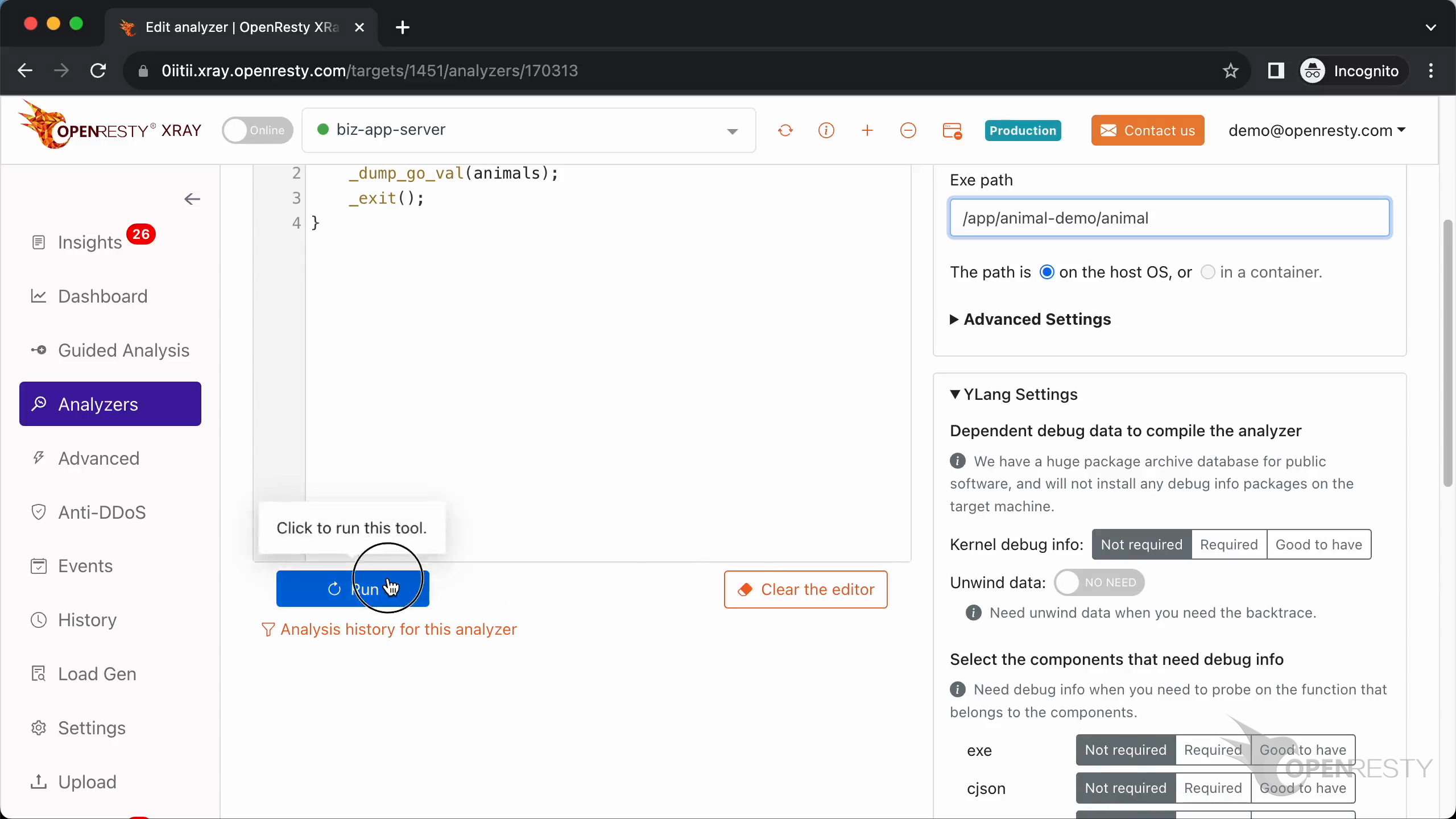
Paste the executable file path.
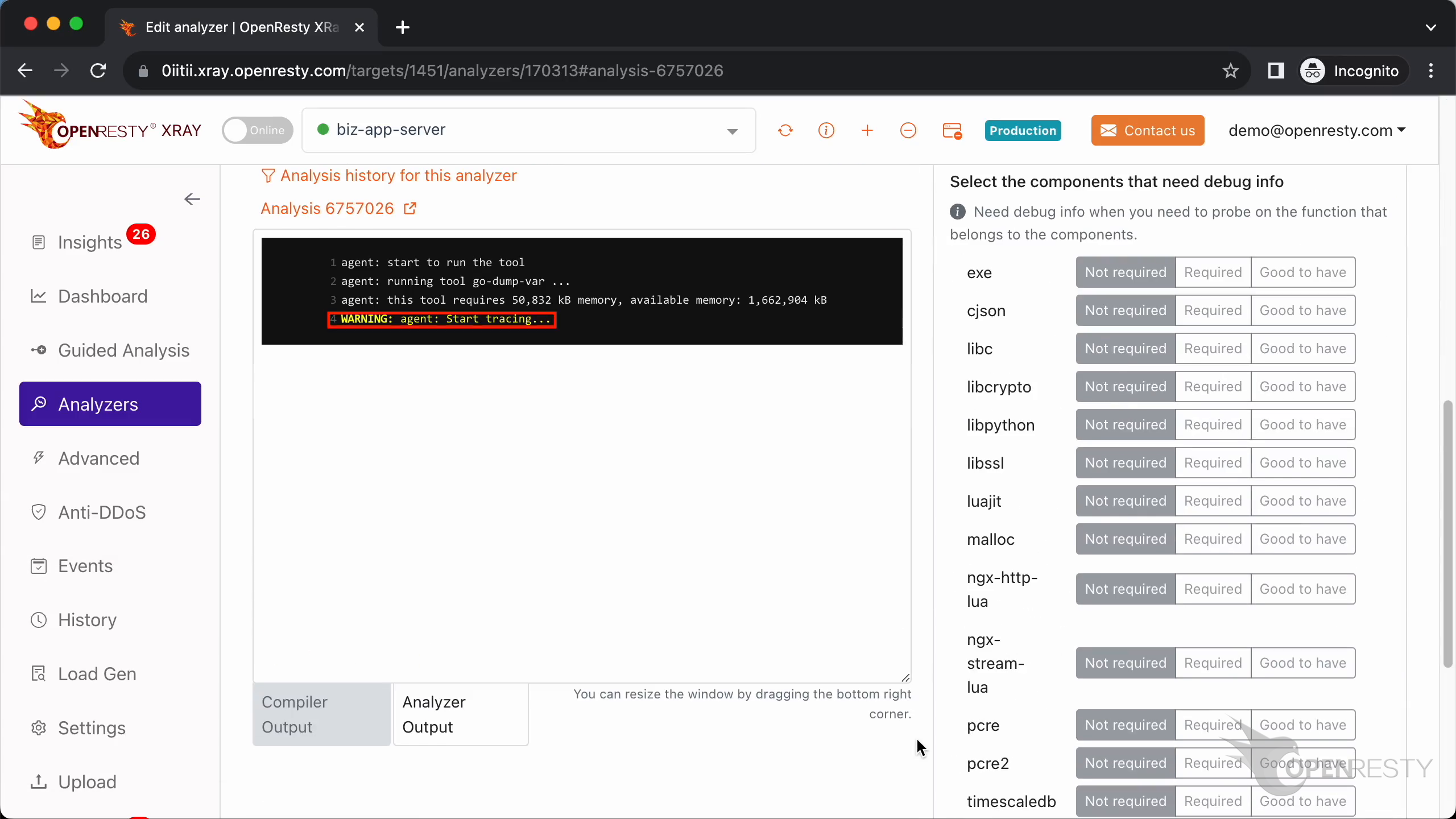
Click “Run” to start execution.
Tracing has started.
Test the Results
Switch to the terminal.
Execute the Go program. As shown, the program is operating normally.
The execution time of this program remained swift, still only 1 millisecond.
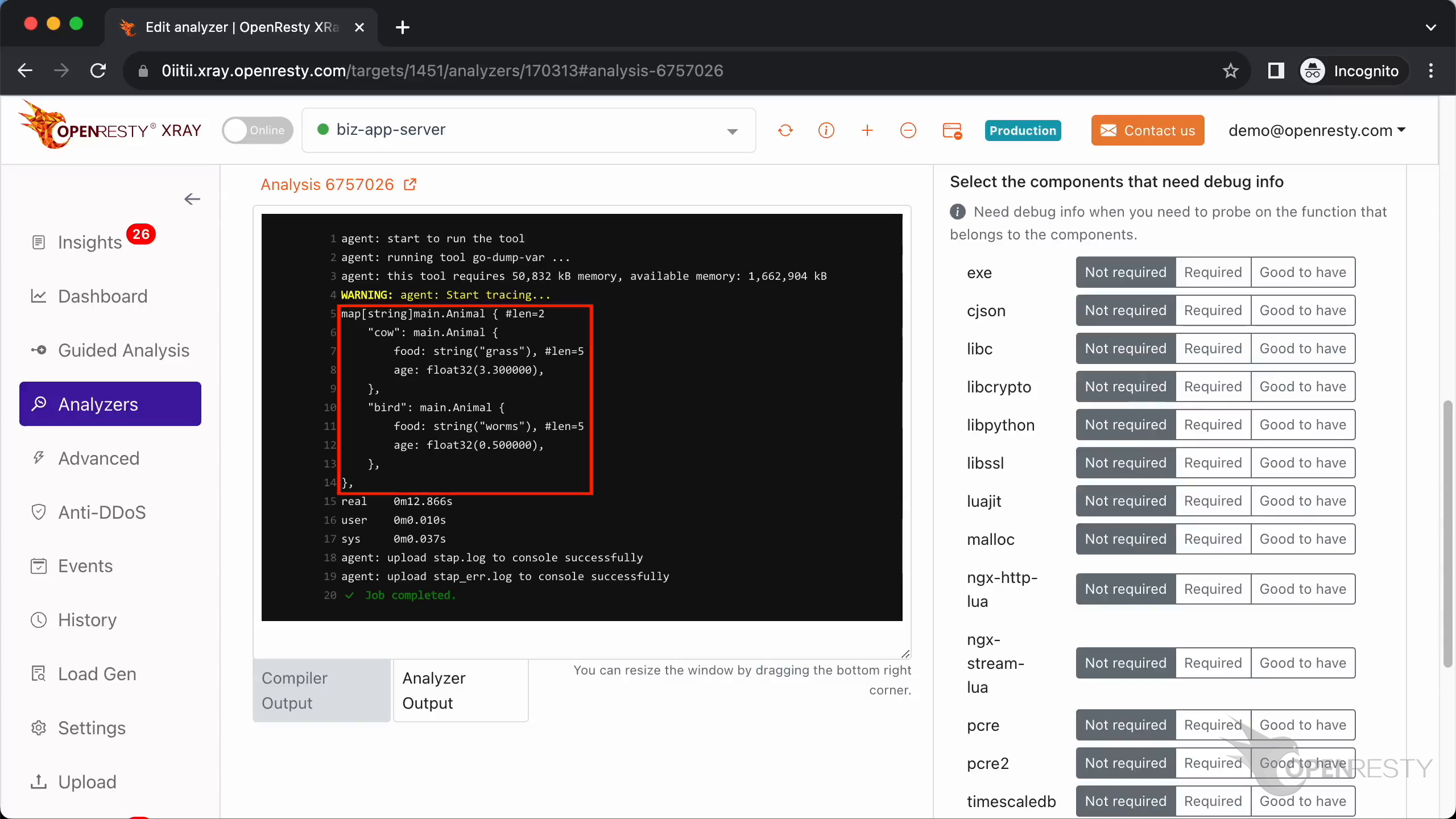
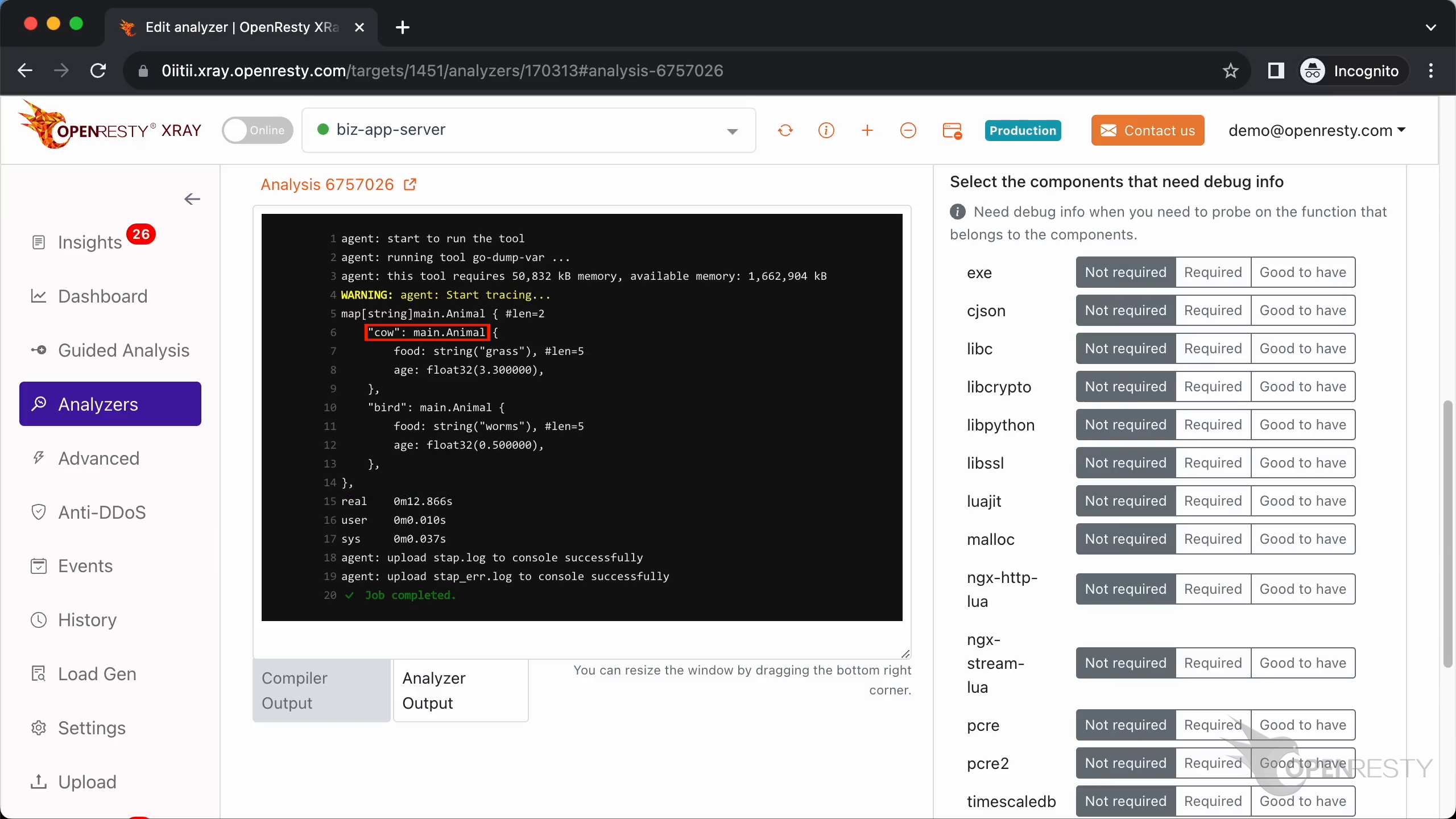
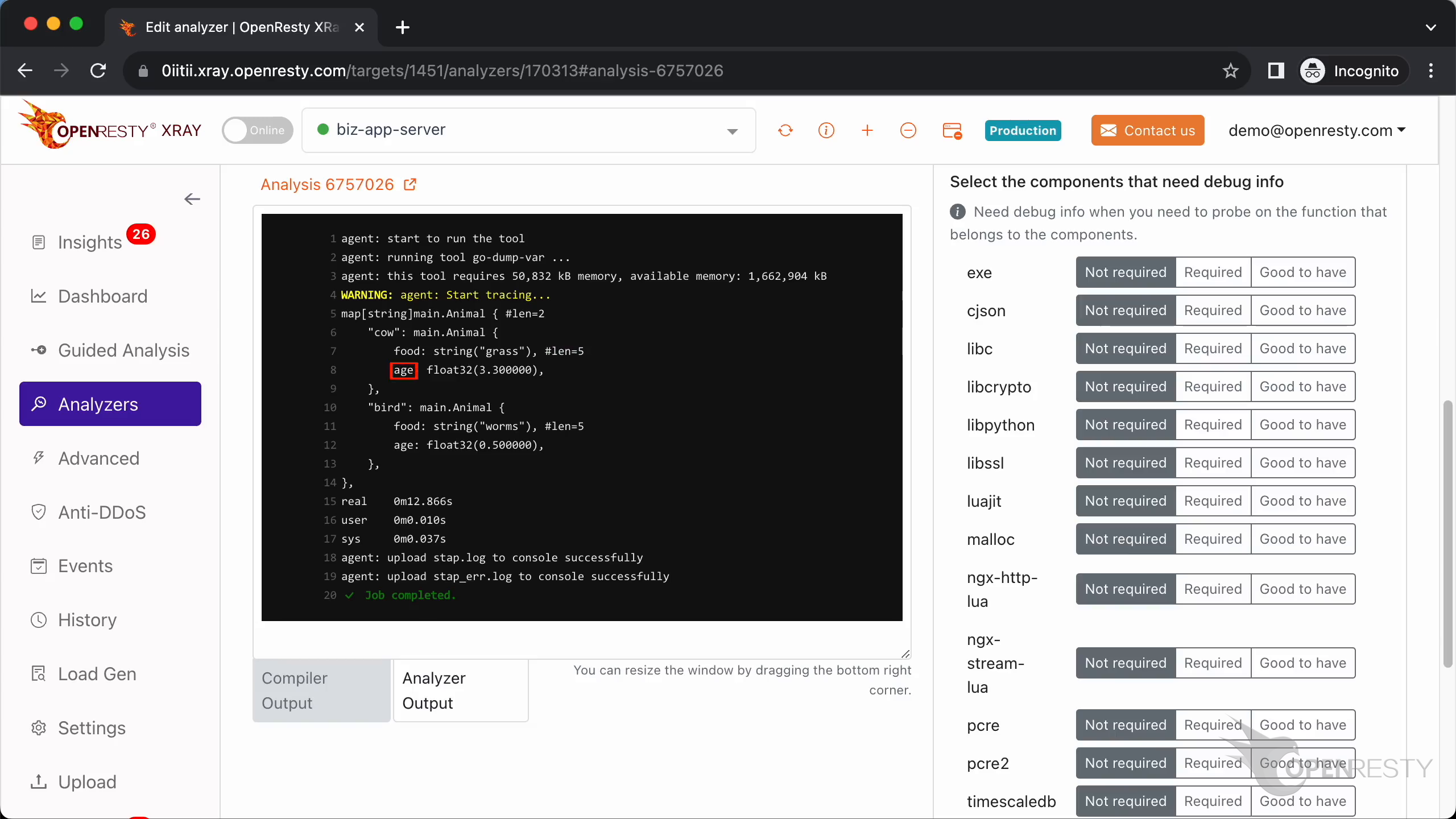
Go back to the Web console. We can see the XRay analyzer printed the value of the animals variable correctly. The map contains two key-value pairs.
The value that the key cow points to is of type main.Animal.
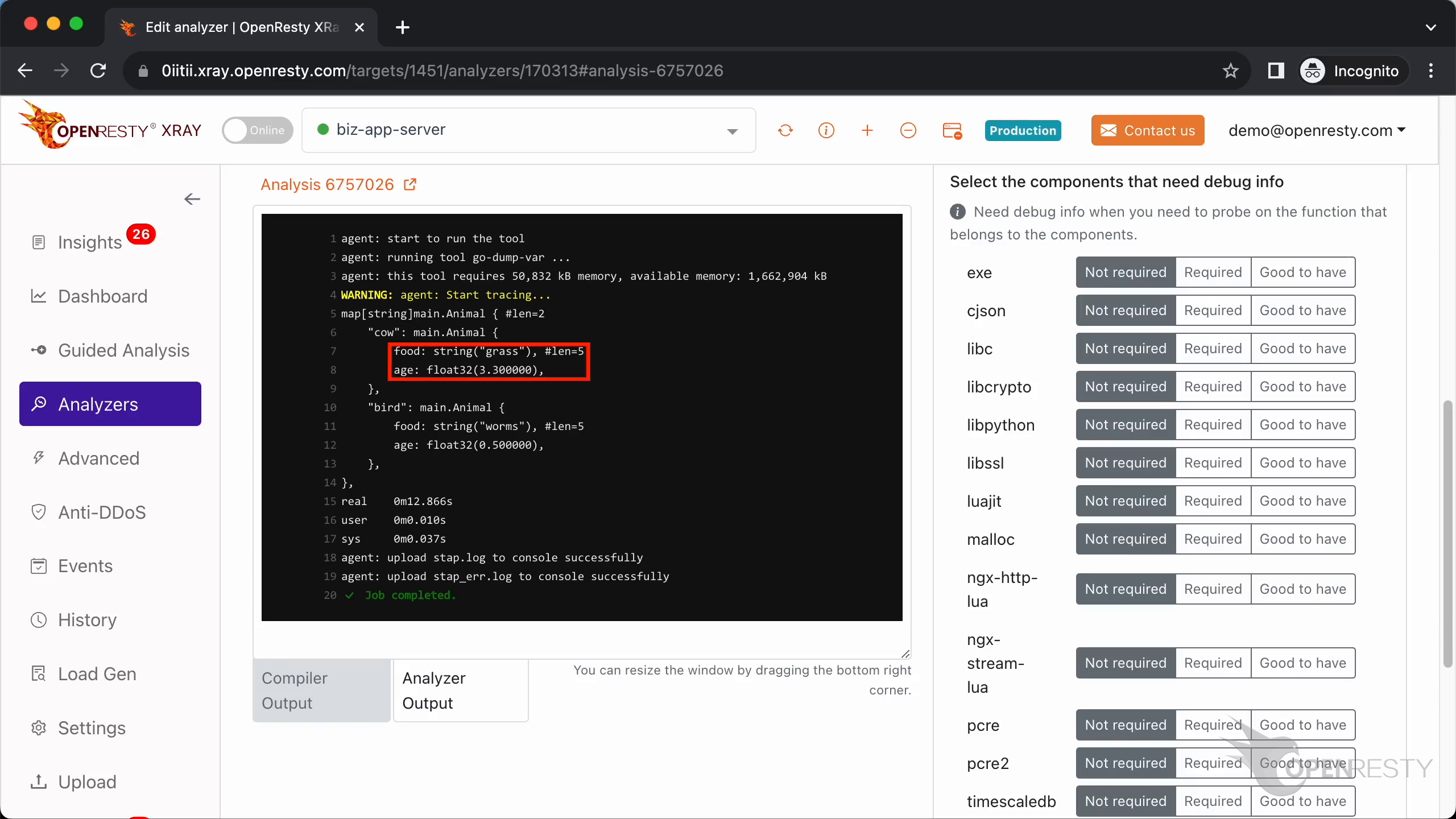
main.Animal has two members, which are food and age.
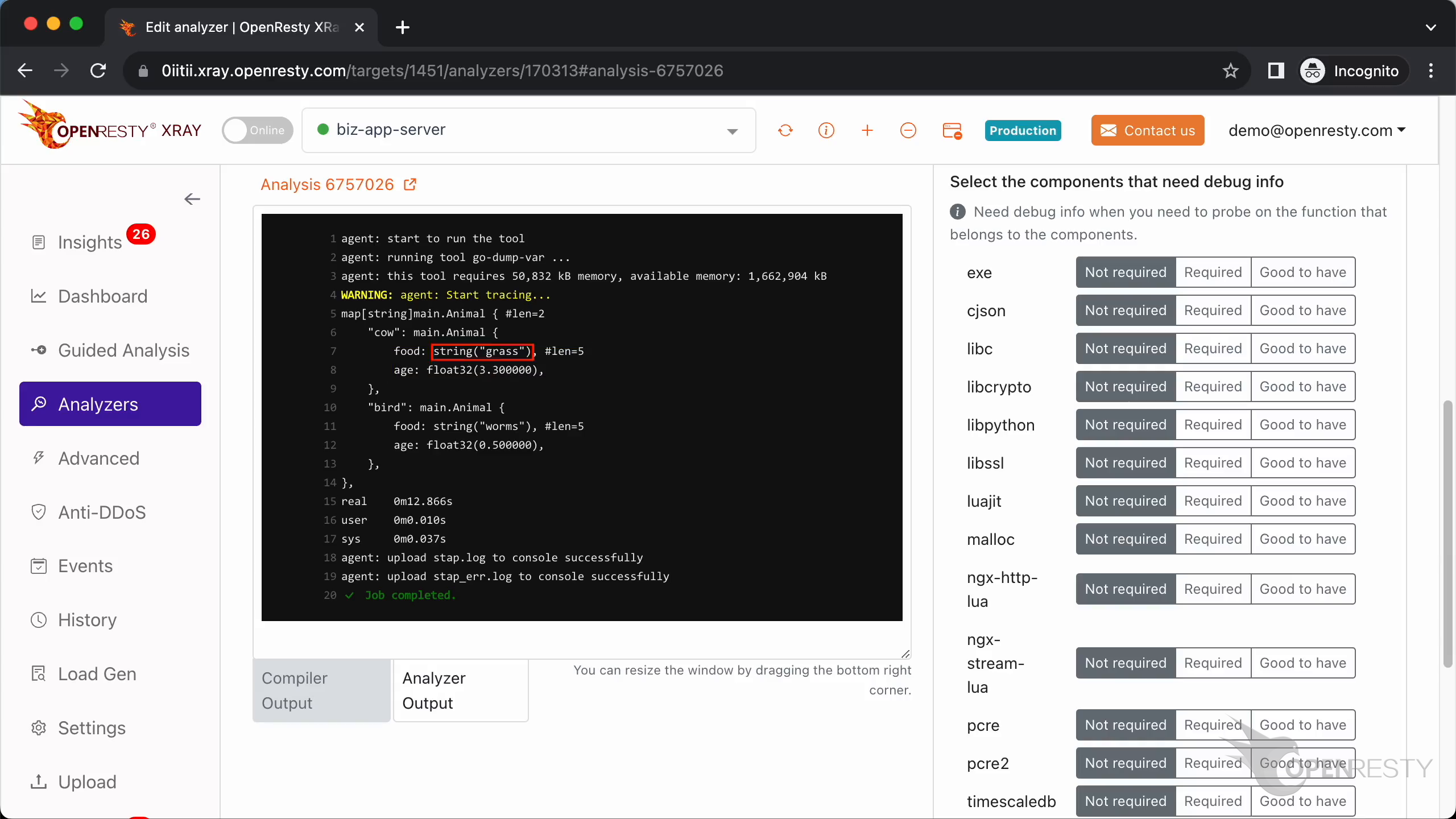
The type of member food is a string and its value is “grass”.
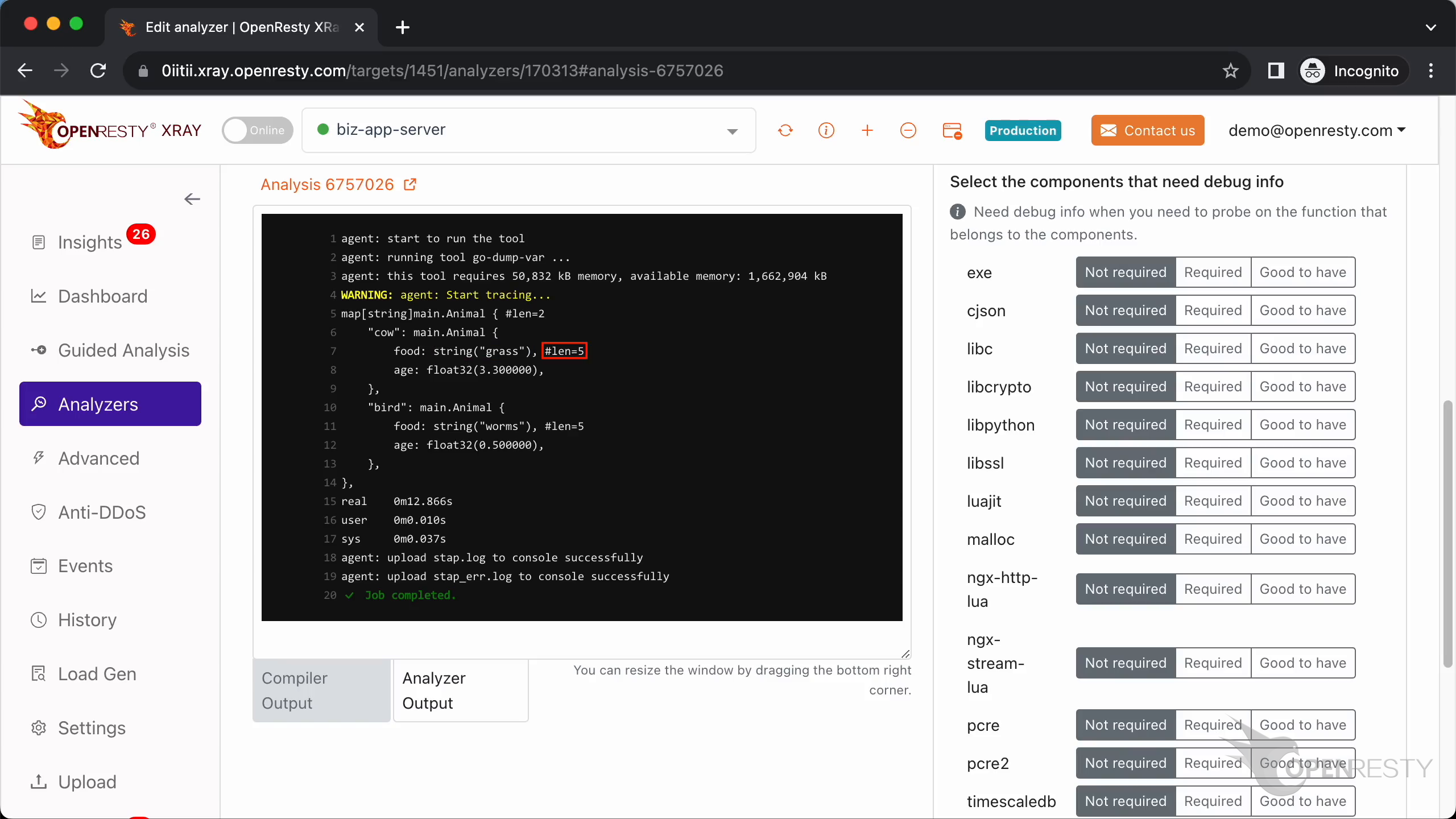
The length of this string is 5.
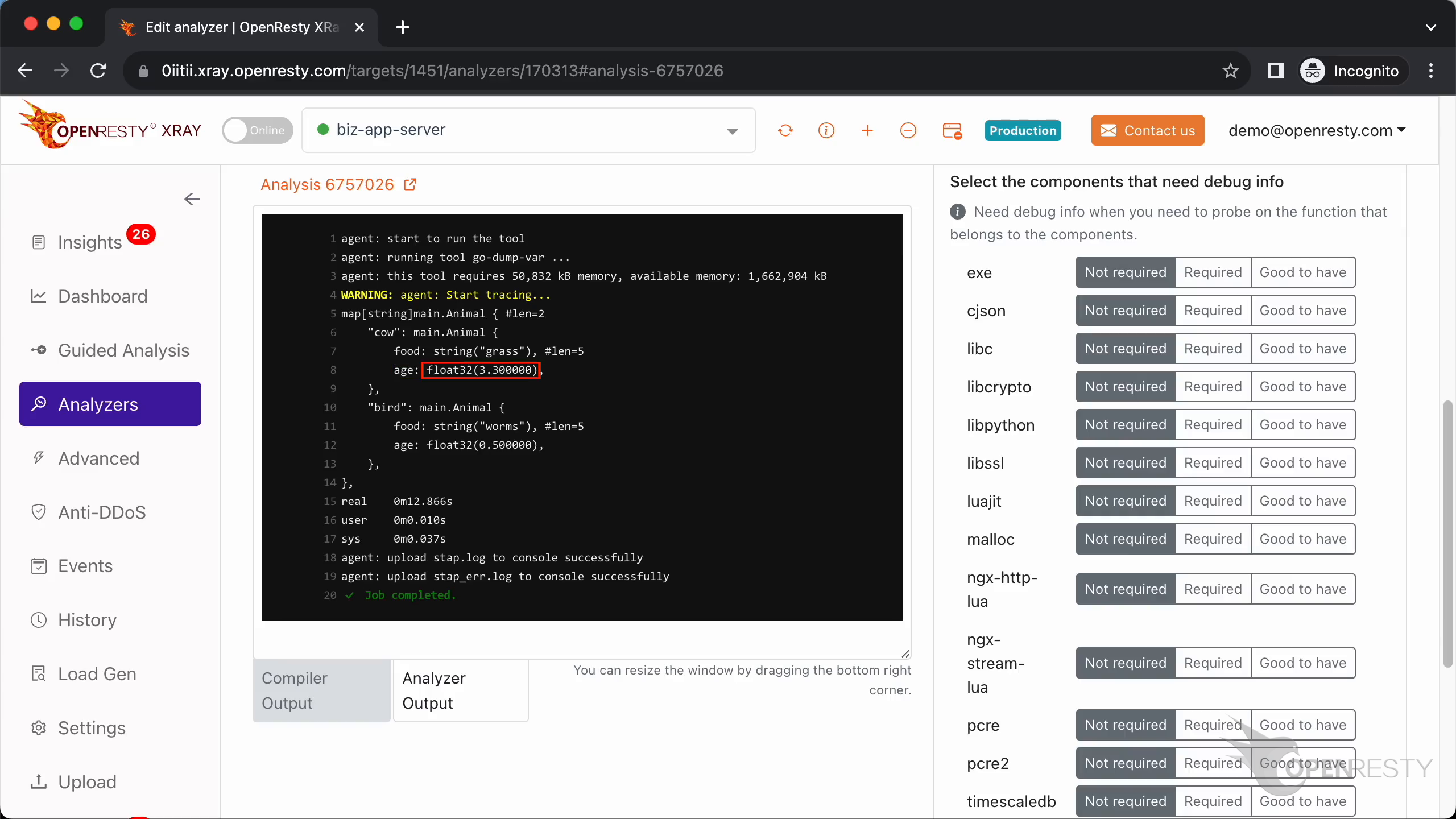
The second field of main.Animal is age.
The type of age is float32.
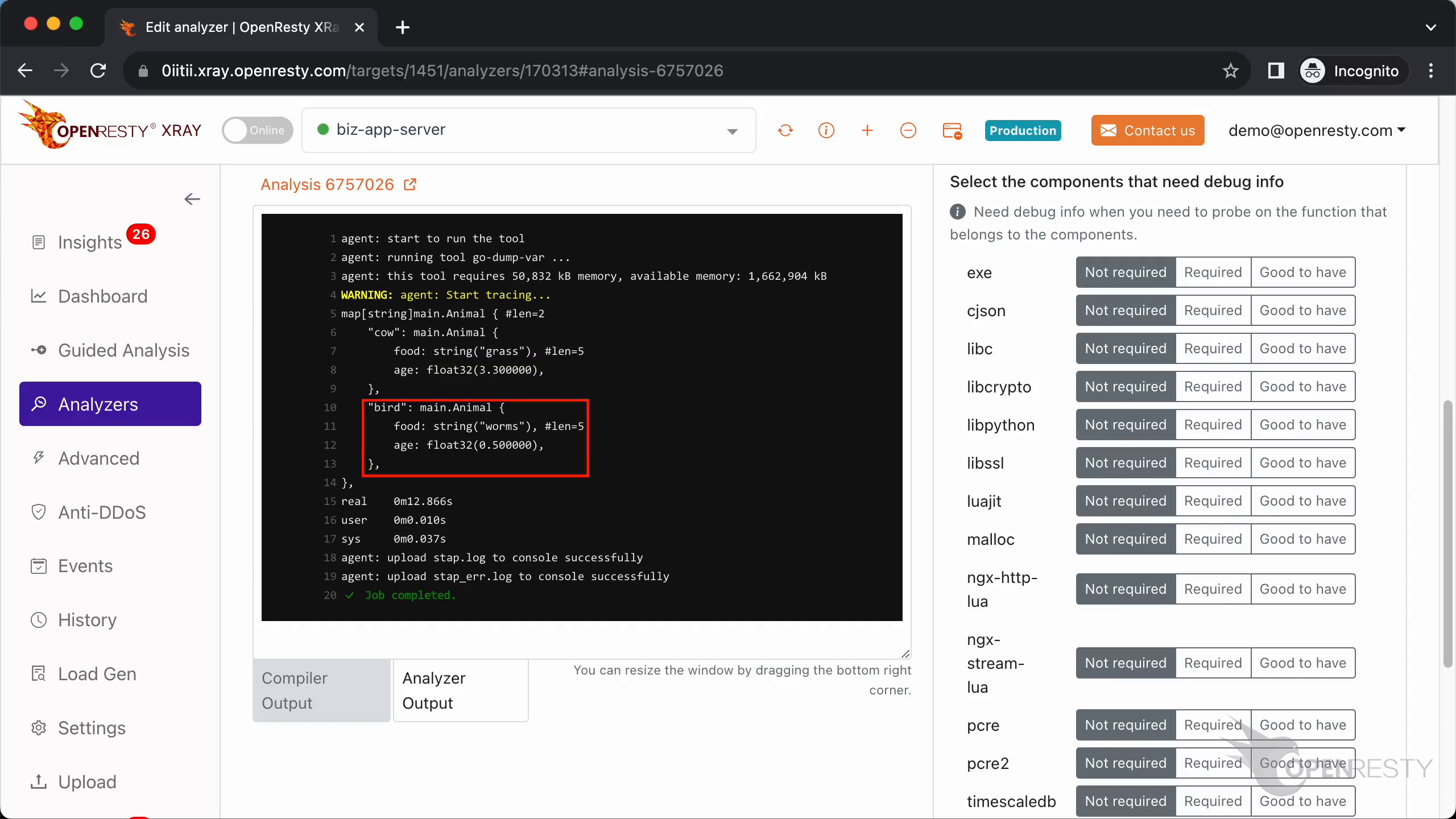
It is similar to the previous key.
According to actual needs, we can also choose the “By Processes” mode.
Or choose the “By Applications” mode.
What is OpenResty XRay
OpenResty XRay is a dynamic-tracing product that automatically analyzes your running applications to troubleshoot performance problems, behavioral issues, and security vulnerabilities with actionable suggestions. Under the hood, OpenResty XRay is powered by our Y language targeting various runtimes like Stap+, eBPF+, GDB, and ODB, depending on the contexts.
If you like this tutorial, please subscribe to this blog site and/or our YouTube channel. Thank you!
About The Author
Yichun Zhang (Github handle: agentzh), is the original creator of the OpenResty® open-source project and the CEO of OpenResty Inc..
Yichun is one of the earliest advocates and leaders of “open-source technology”. He worked at many internationally renowned tech companies, such as Cloudflare, Yahoo!. He is a pioneer of “edge computing”, “dynamic tracing” and “machine coding”, with over 22 years of programming and 16 years of open source experience. Yichun is well-known in the open-source space as the project leader of OpenResty®, adopted by more than 40 million global website domains.
OpenResty Inc., the enterprise software start-up founded by Yichun in 2017, has customers from some of the biggest companies in the world. Its flagship product, OpenResty XRay, is a non-invasive profiling and troubleshooting tool that significantly enhances and utilizes dynamic tracing technology. And its OpenResty Edge product is a powerful distributed traffic management and private CDN software product.
As an avid open-source contributor, Yichun has contributed more than a million lines of code to numerous open-source projects, including Linux kernel, Nginx, LuaJIT, GDB, SystemTap, LLVM, Perl, etc. He has also authored more than 60 open-source software libraries.