Pinpointing the hottest Go code paths with high CPU usage (using OpenResty XRay)
Today I will show you another step-by-step guide for analyzing Go applications with OpenResty XRay. We’ll quickly pinpoint the hottest Go code paths in an already-running golang process. These code paths might take most of the CPU time of your applications.
Problem: high CPU usage
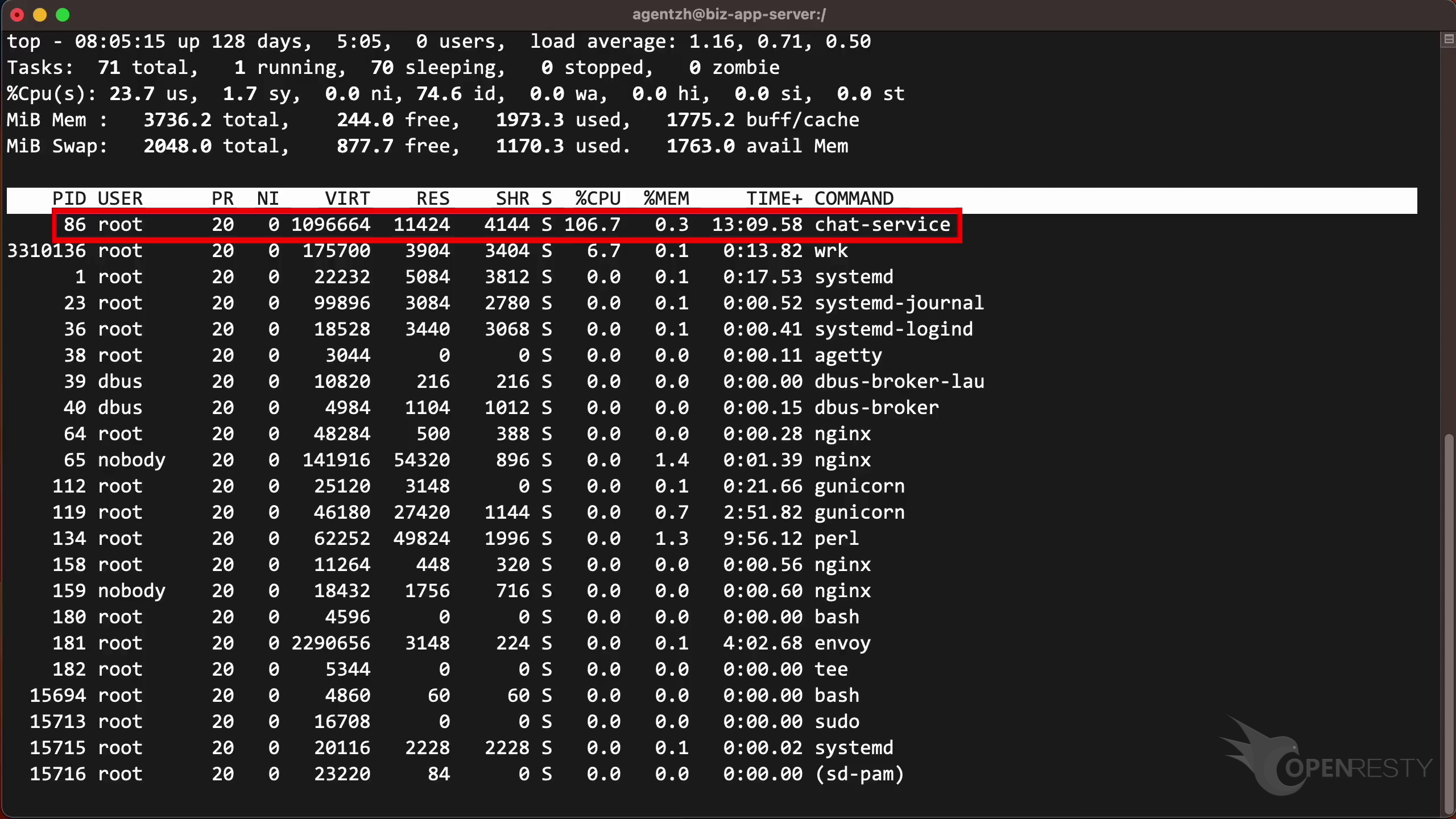
Let’s start by running the top command to check the CPU usage. As shown, the CPU core is being consumed more than 100% by the process named chat-service. We already know it is written in Go.
Use the guidede analysis feature of OpenResty XRay to spot the hottest Go code paths
Let’s use OpenResty XRay to check out this unmodified process. We don’t need to add any special modules or code to the target Go application.
Open the OpenResty XRay web console in the web browser. Here we can analyze the machine in real time and figure out what’s going on.
Make sure it is the right machine you are watching.
Go to the “Guided Analysis” page.
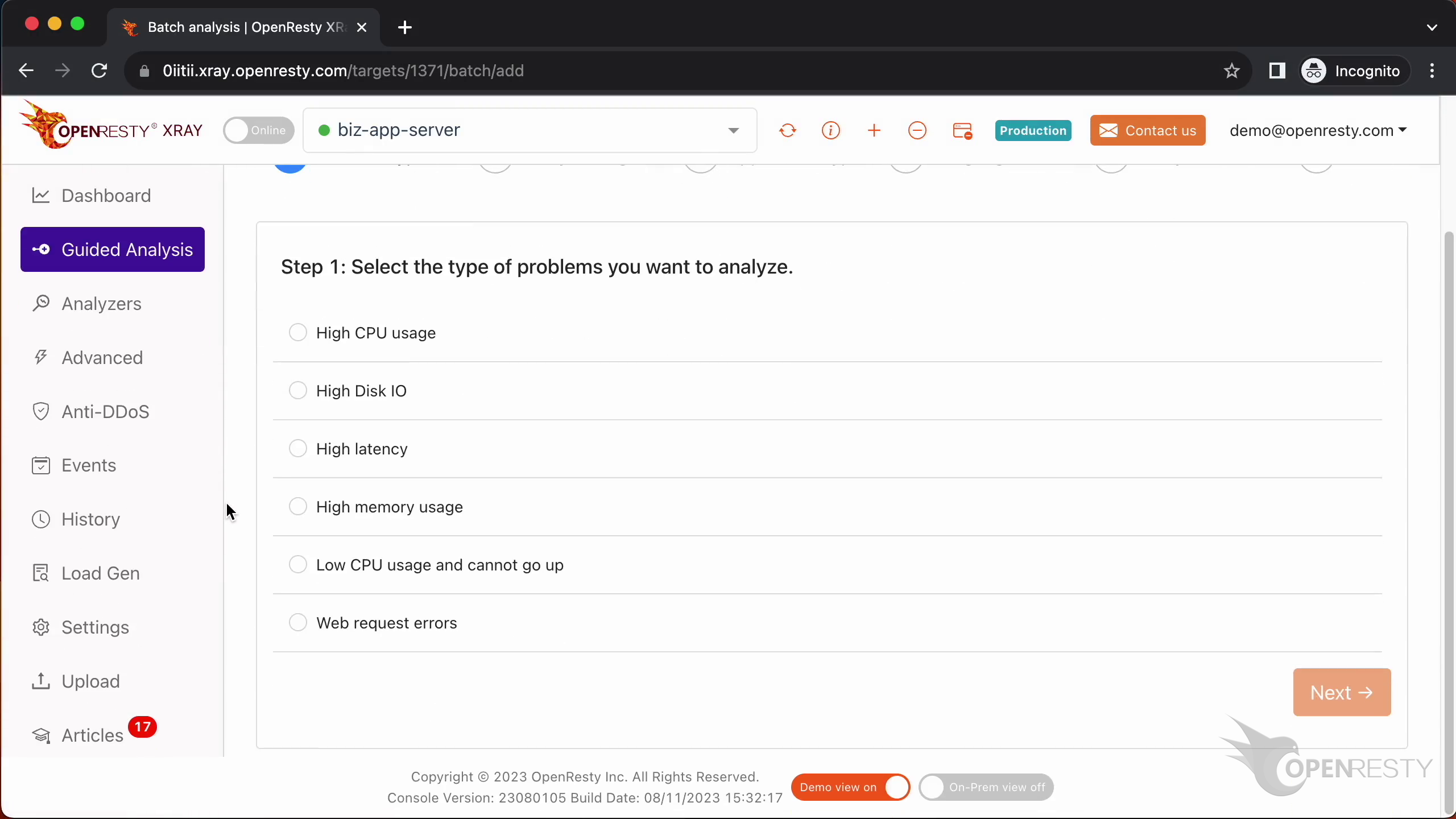
Here you can see different types of problems that you can diagnose.
Let’s select “High CPU Usage”.
Click on “Next”.
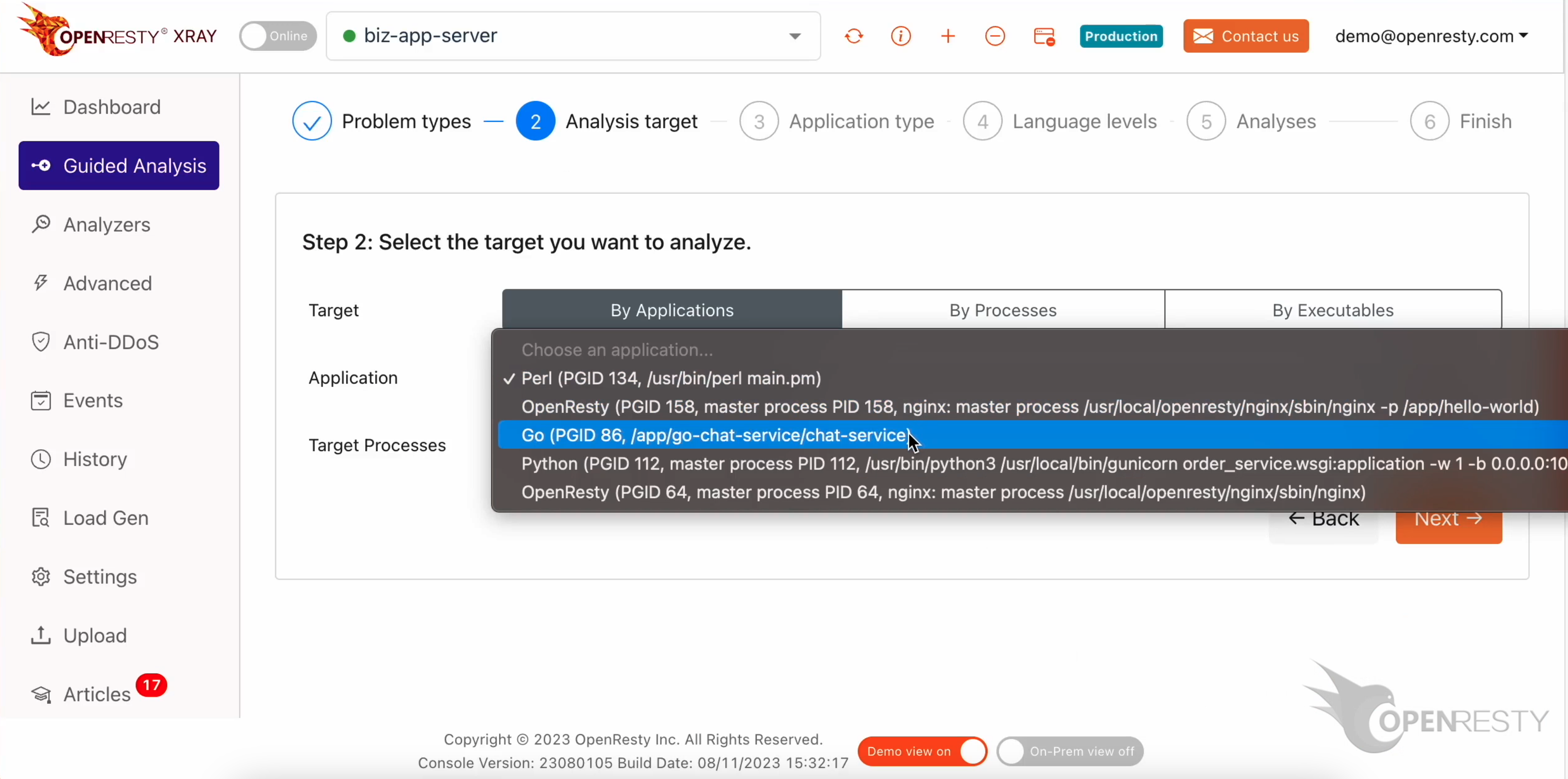
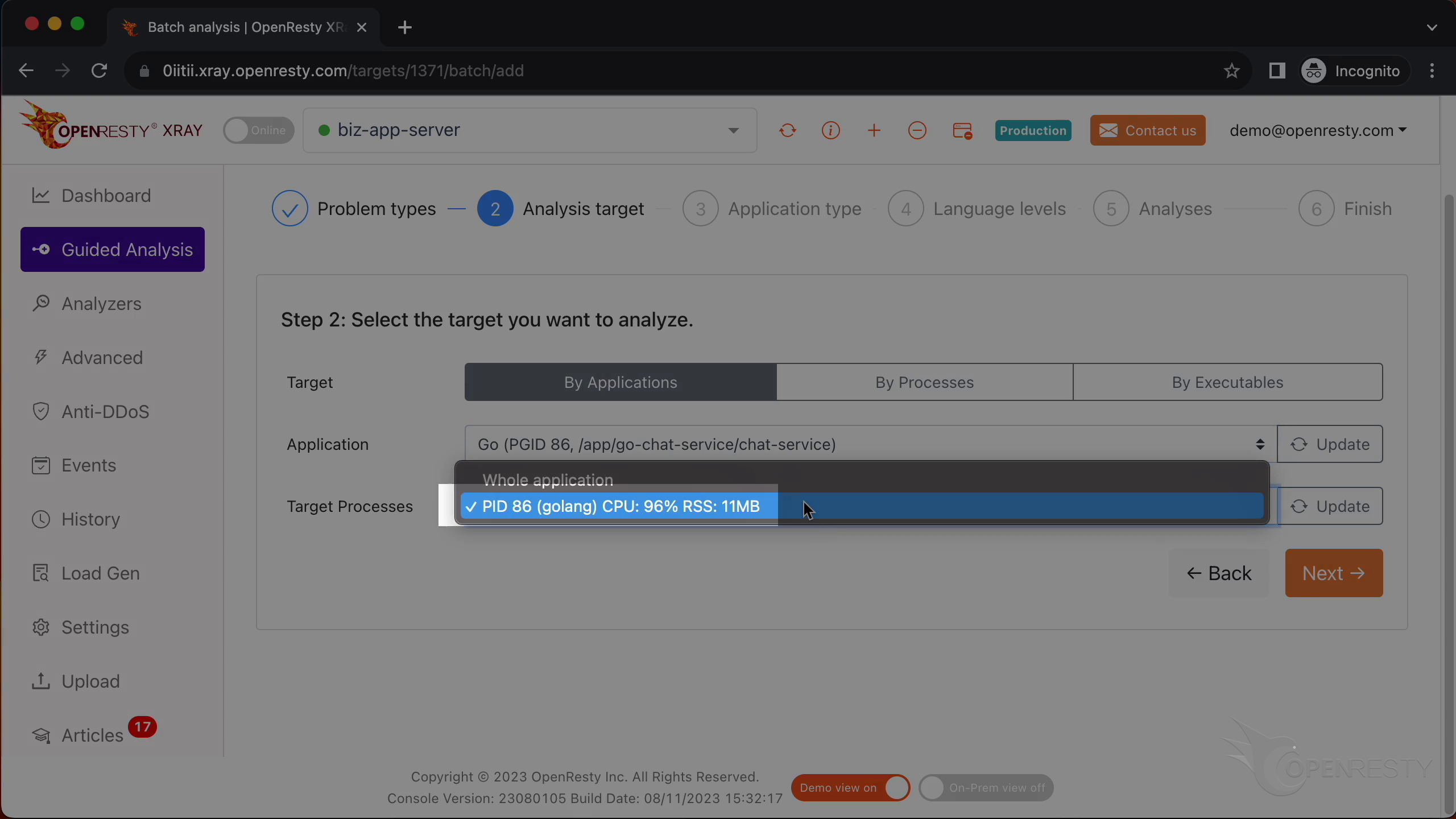
Select the Go application.
Select the process that consumes 96% of the CPU resources. This is what we saw previously in top.
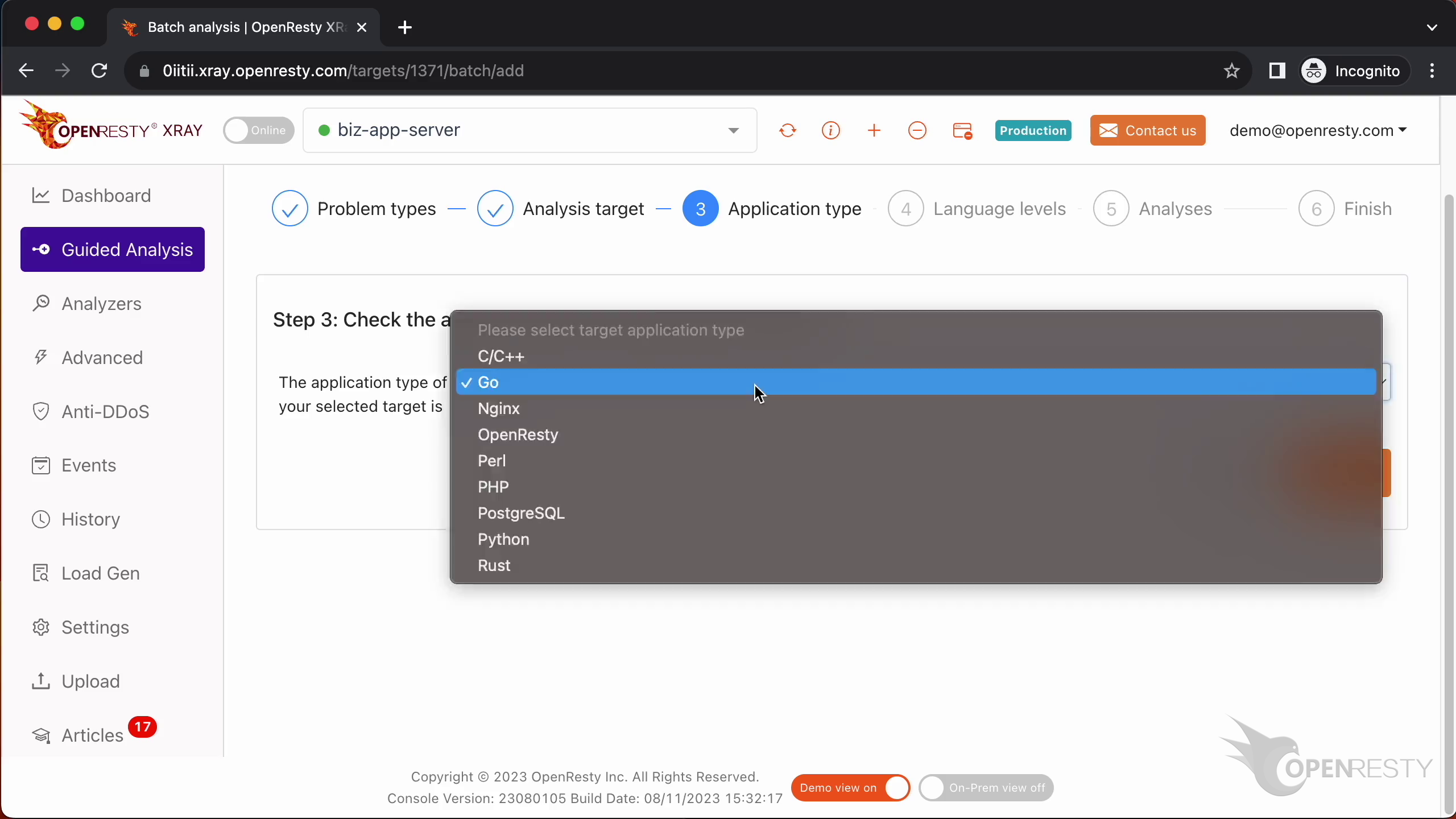
Make sure that the application type is right. Usually the default should be correct.
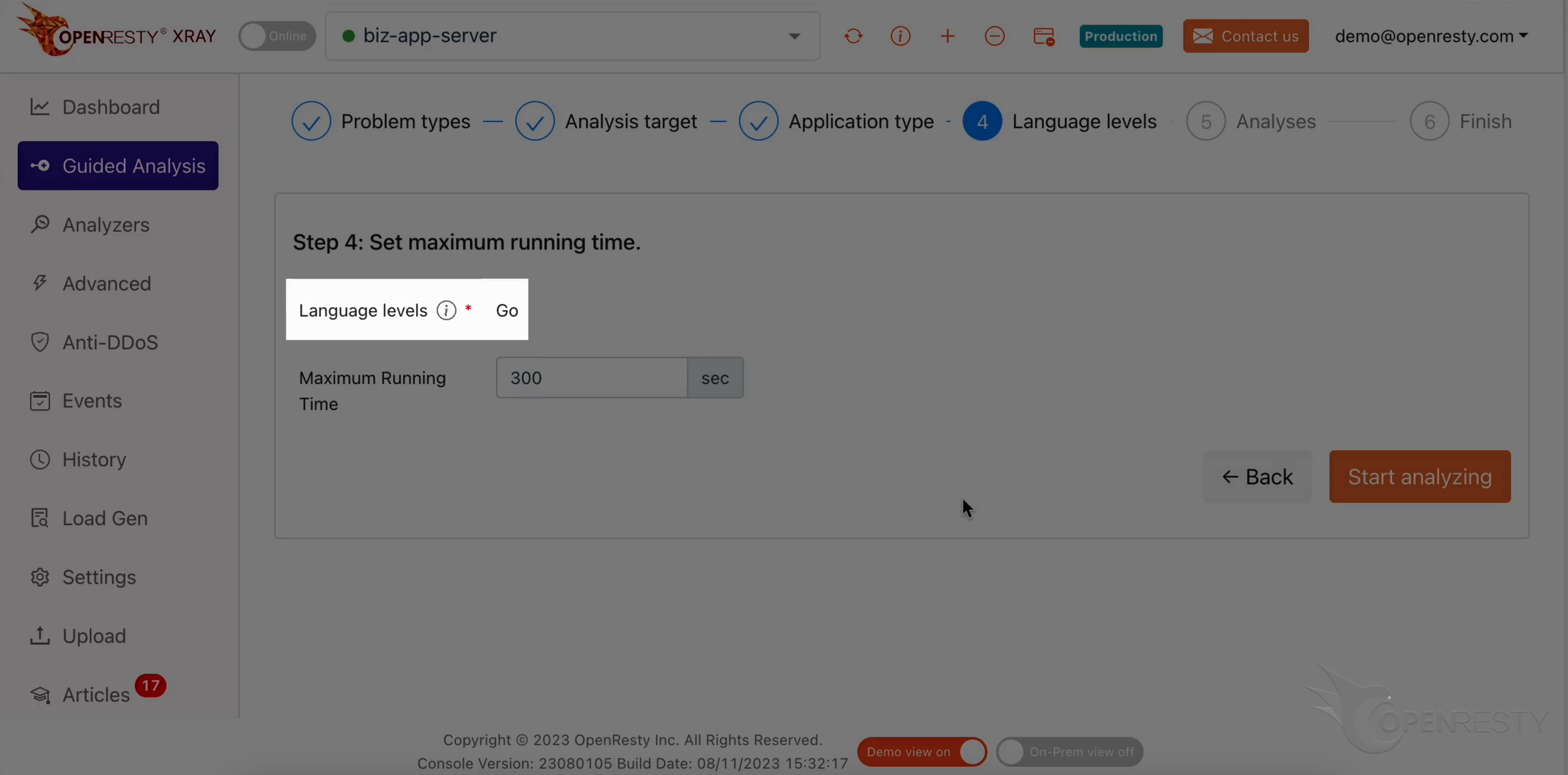
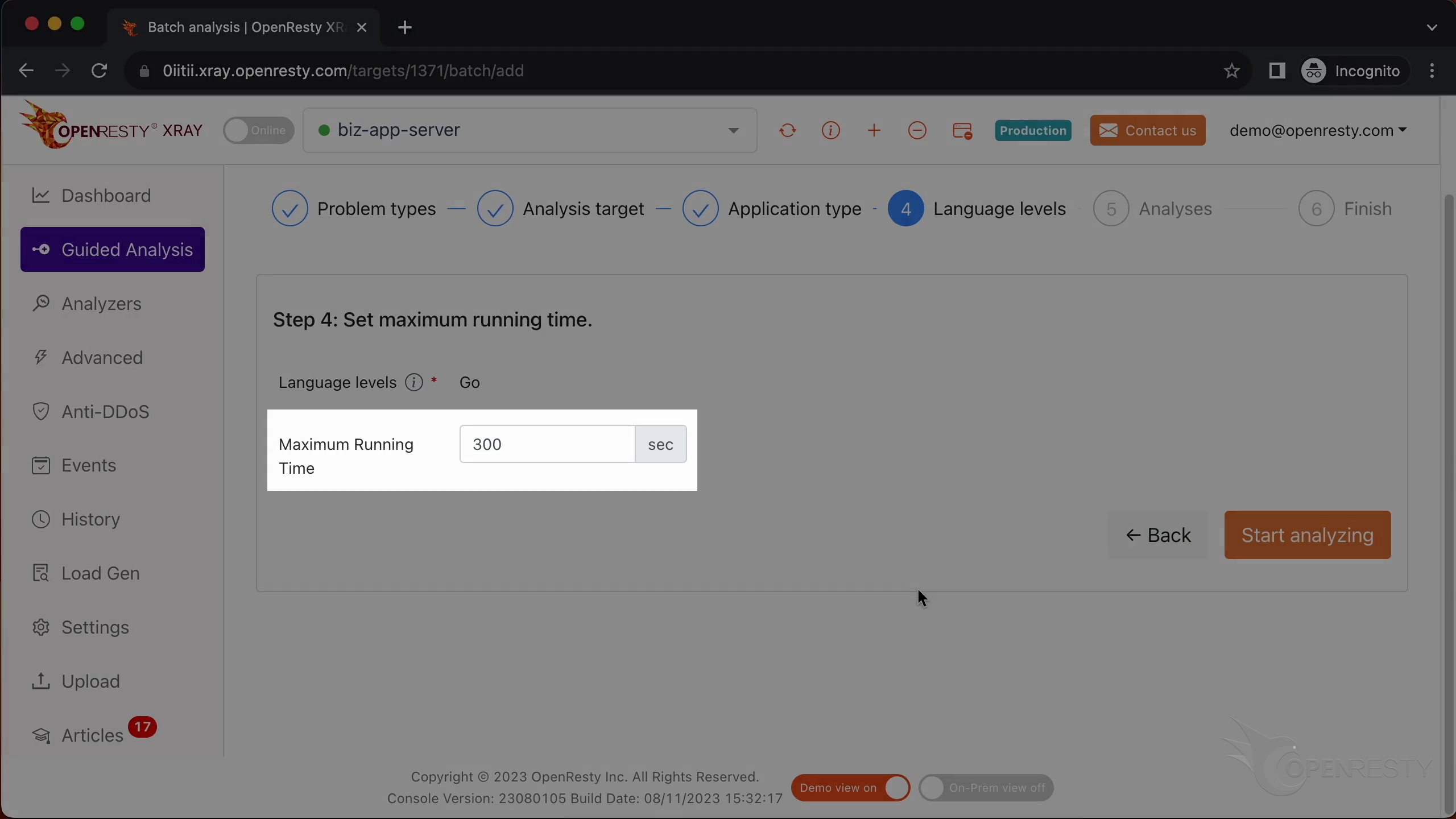
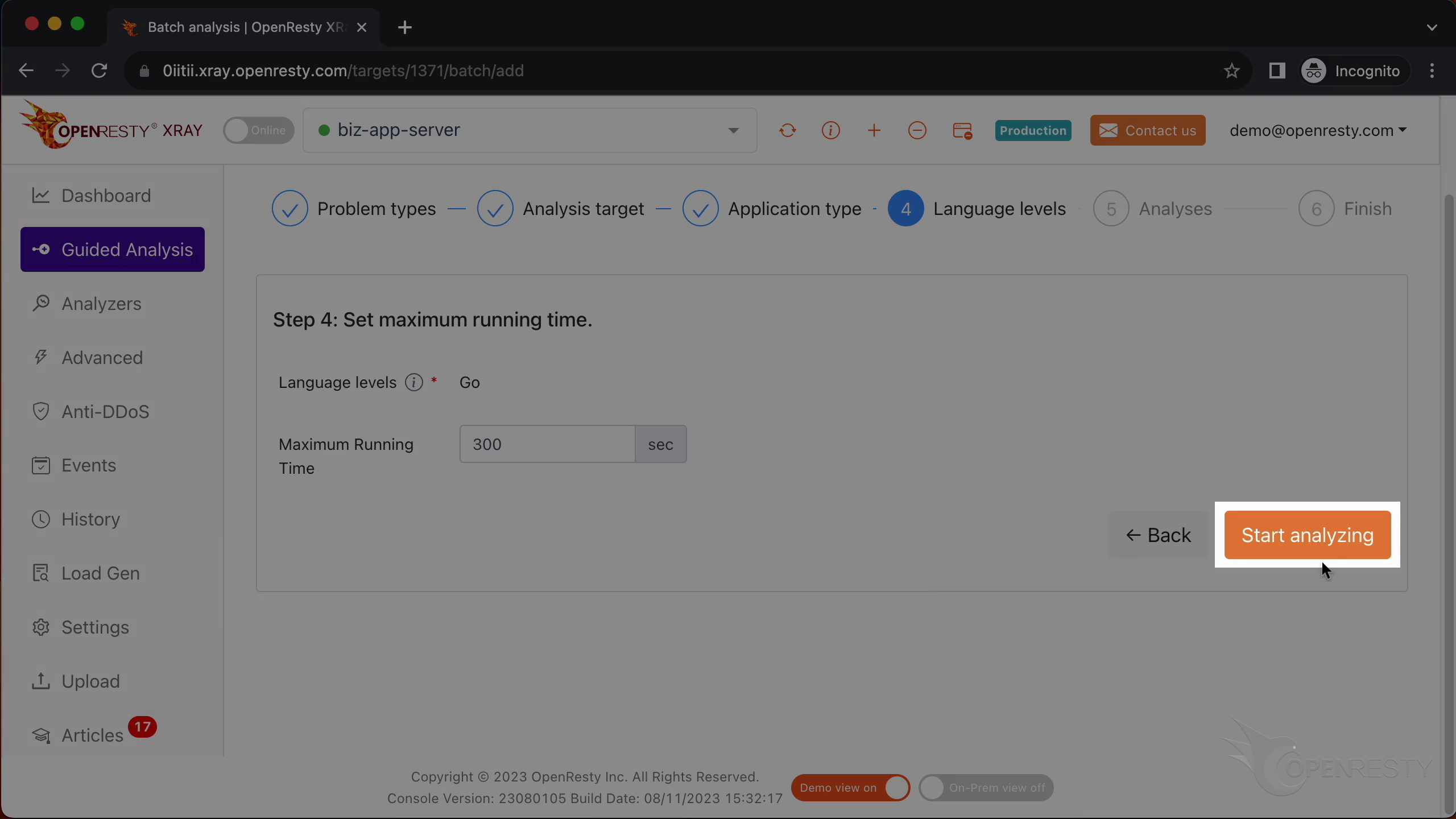
The language level is just “Go”.
We can set the maximum analyzing time. We’ll leave it as 300 seconds, which is the default value.
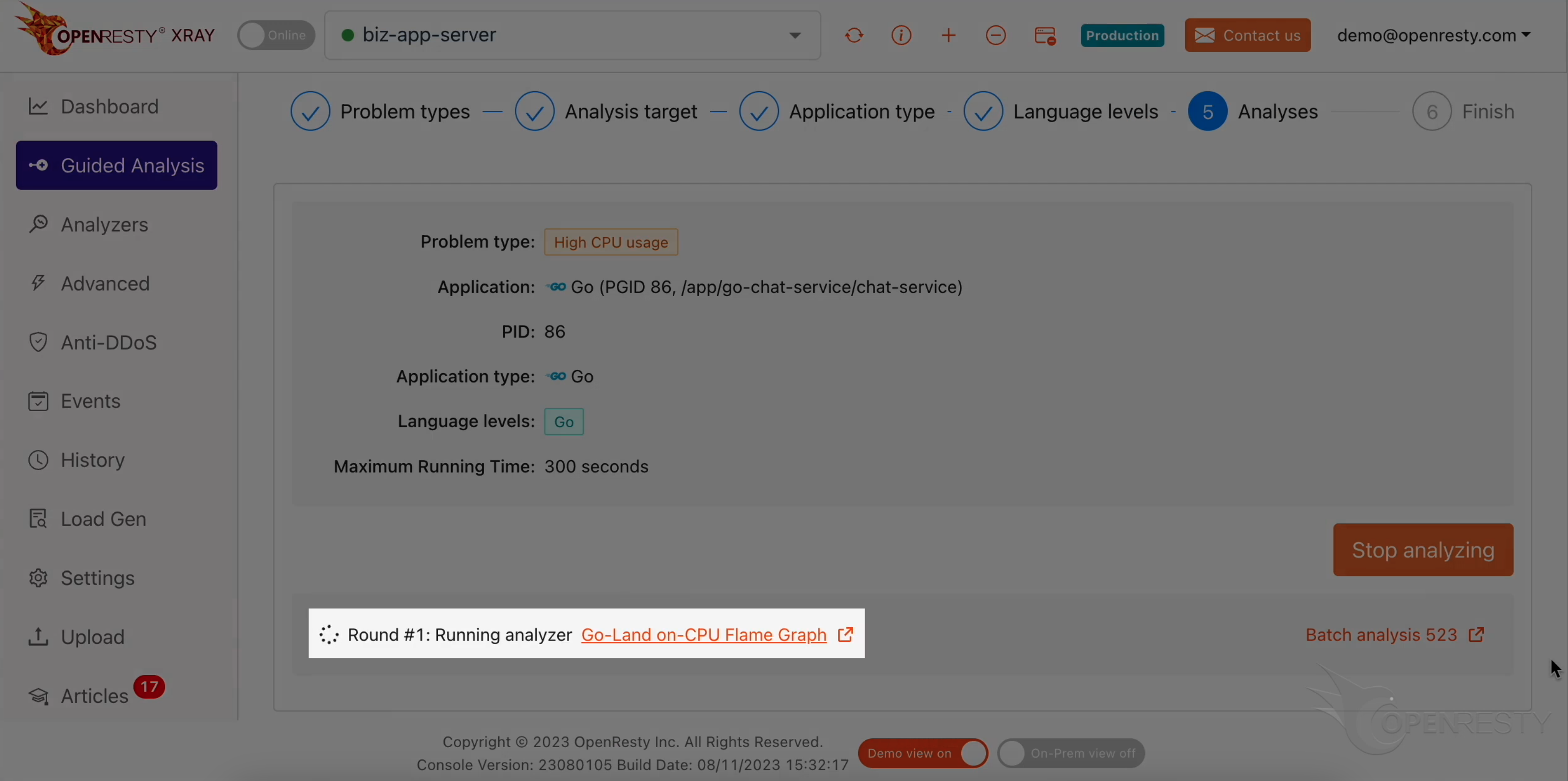
Let’s start analyzing.
The system will keep performing different rounds of analysis. Now it’s executing the first round.
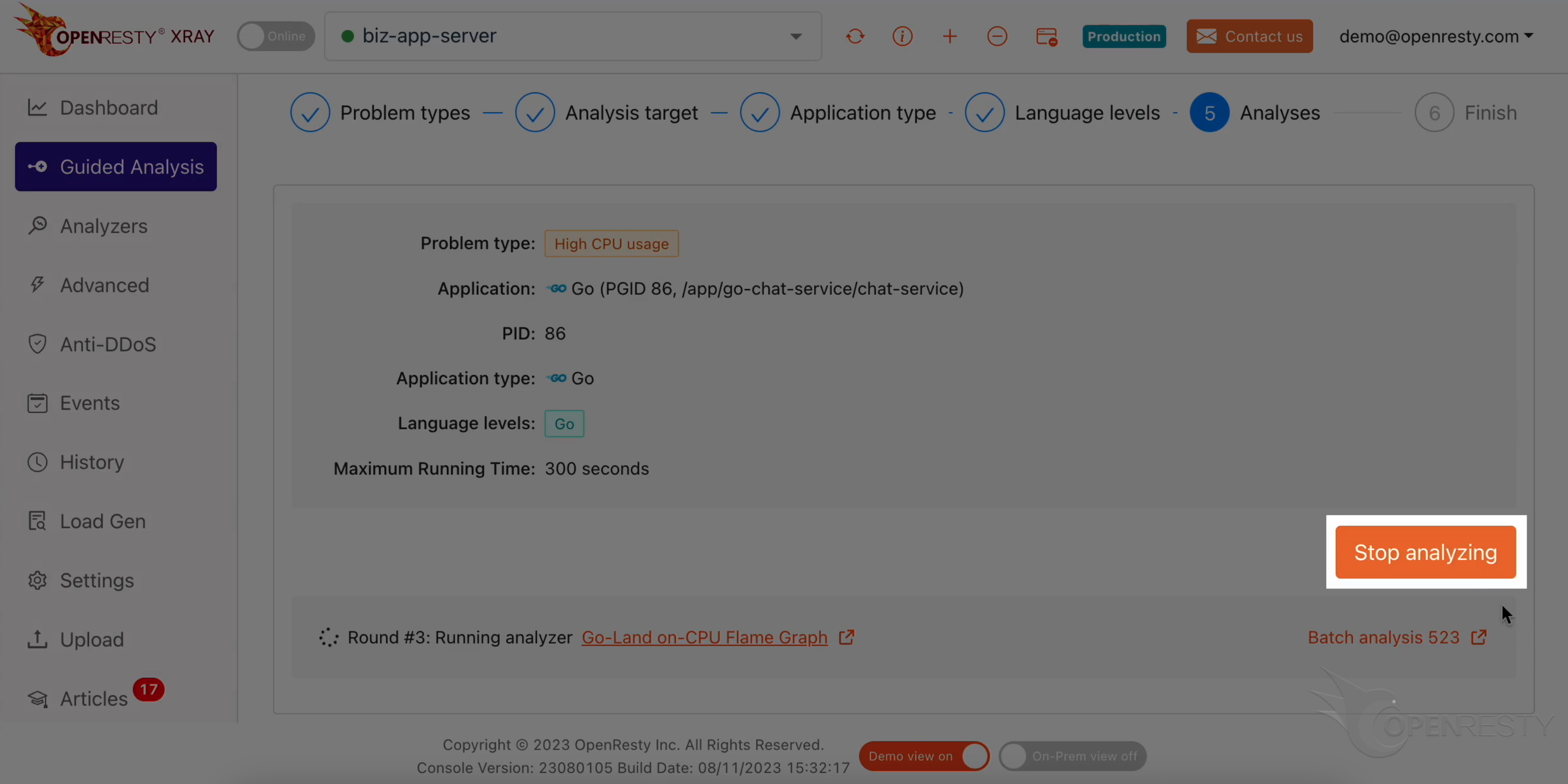
The first round is done and it’s on to the second one already. That’s enough for this case.
Let’s stop analyzing now.
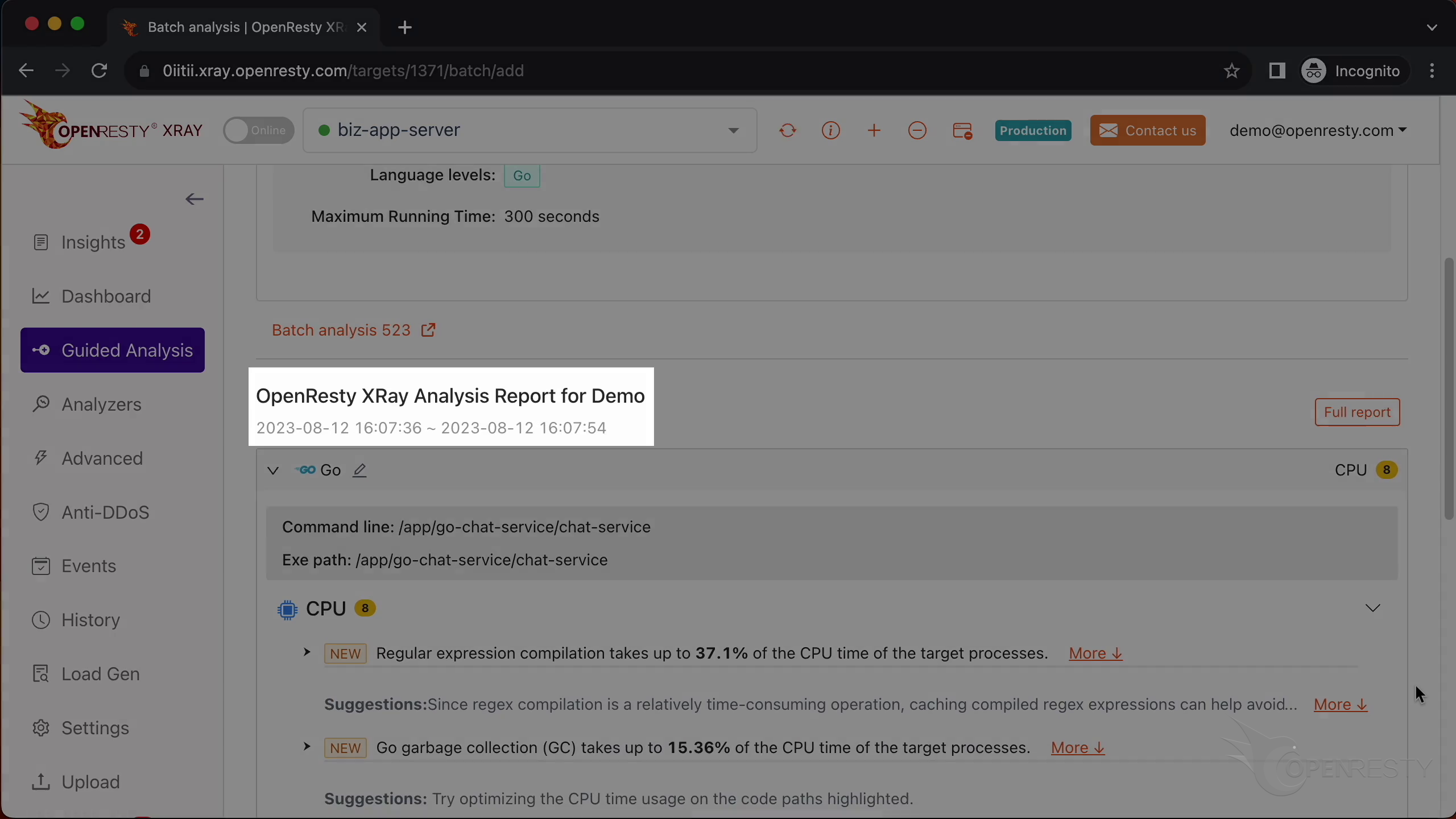
We can see it automatically creates a report.
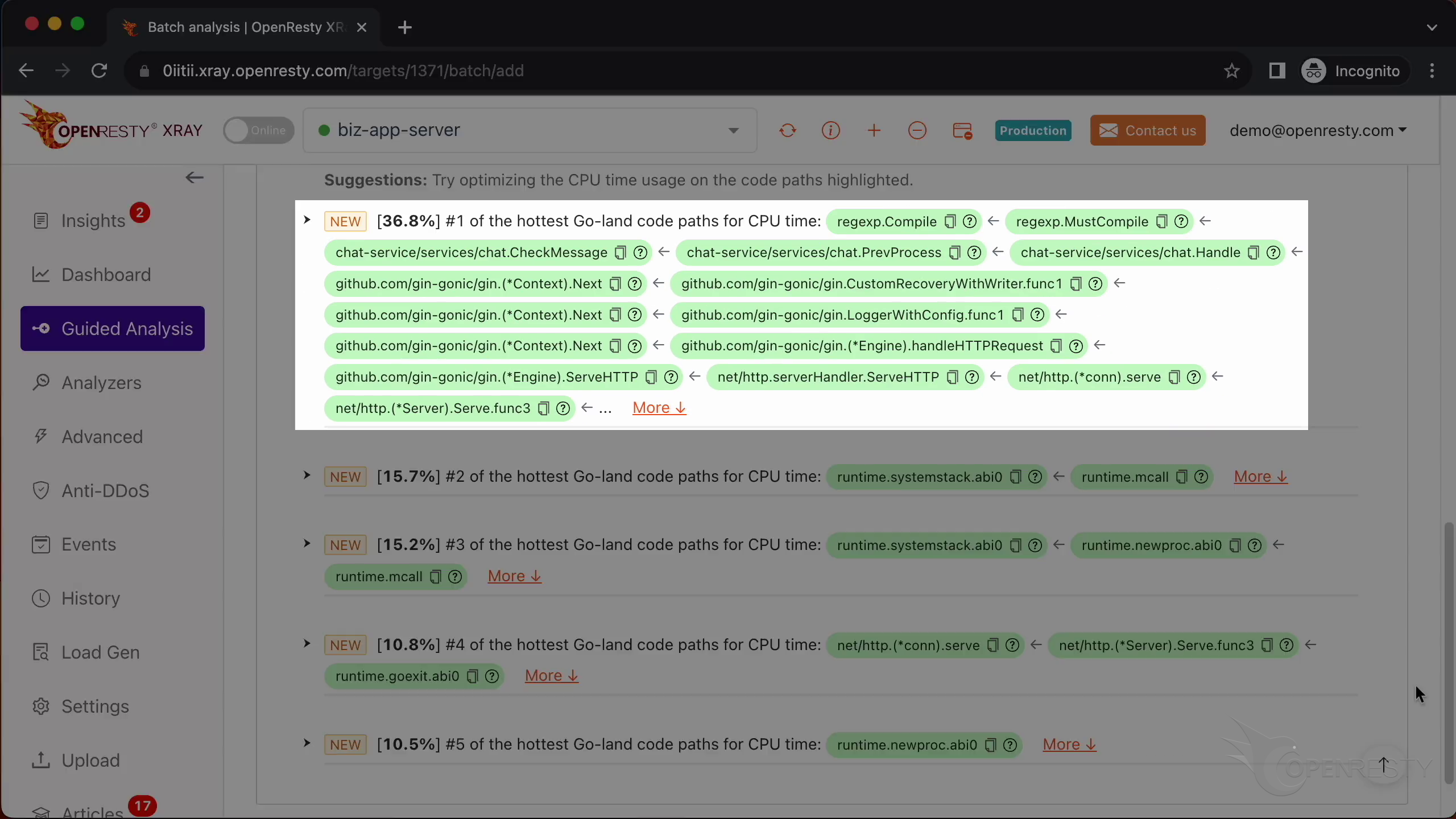
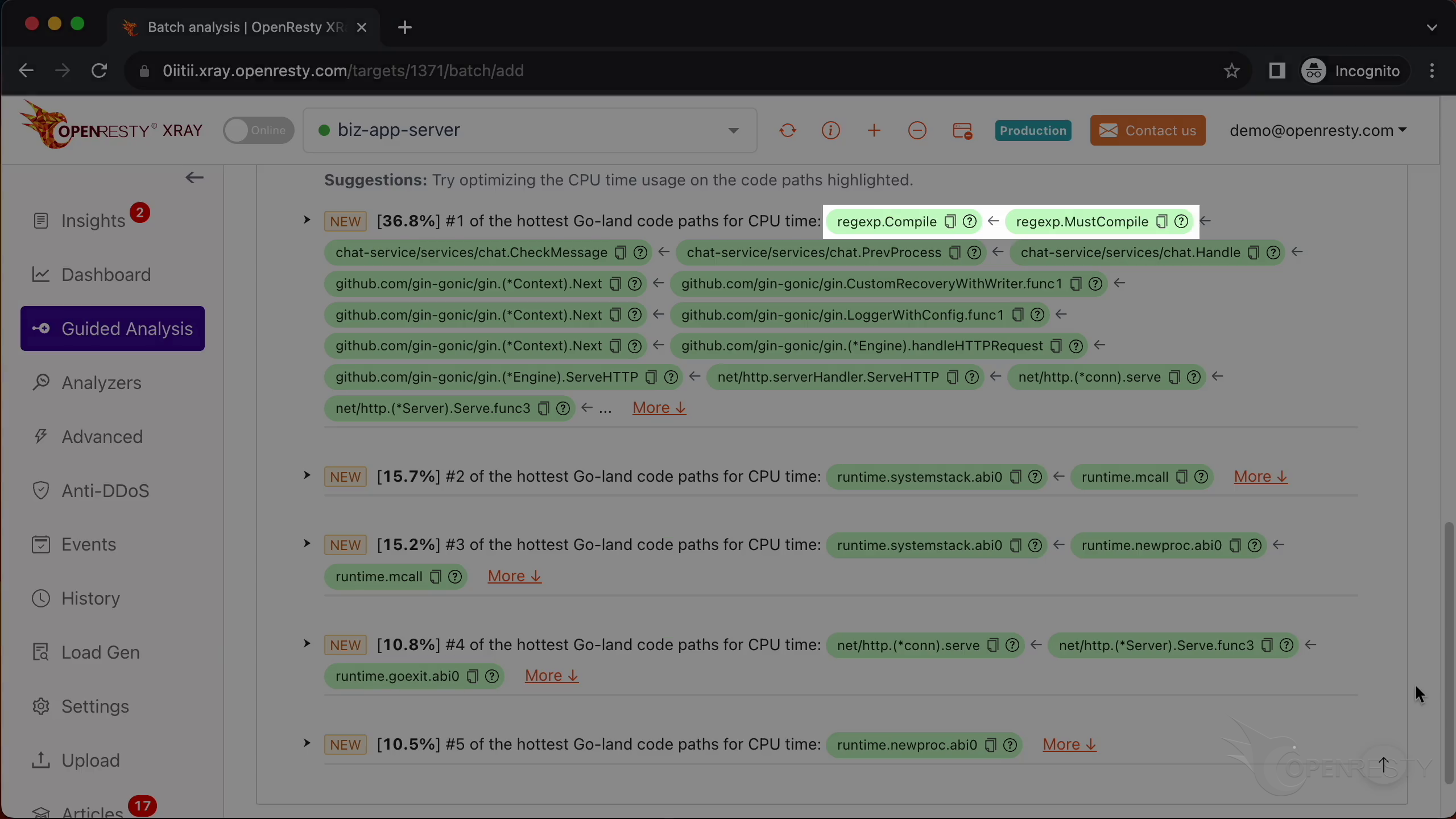
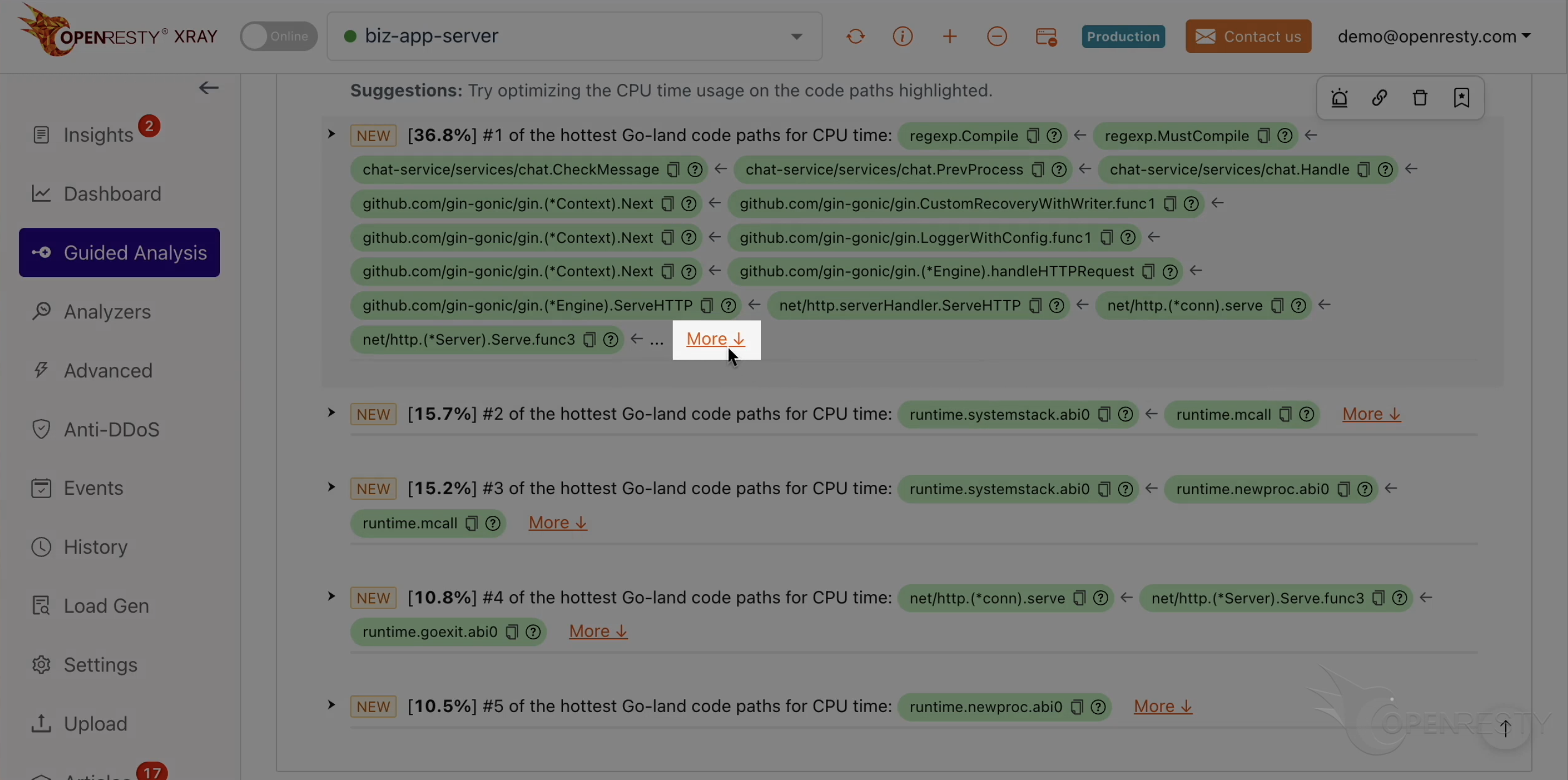
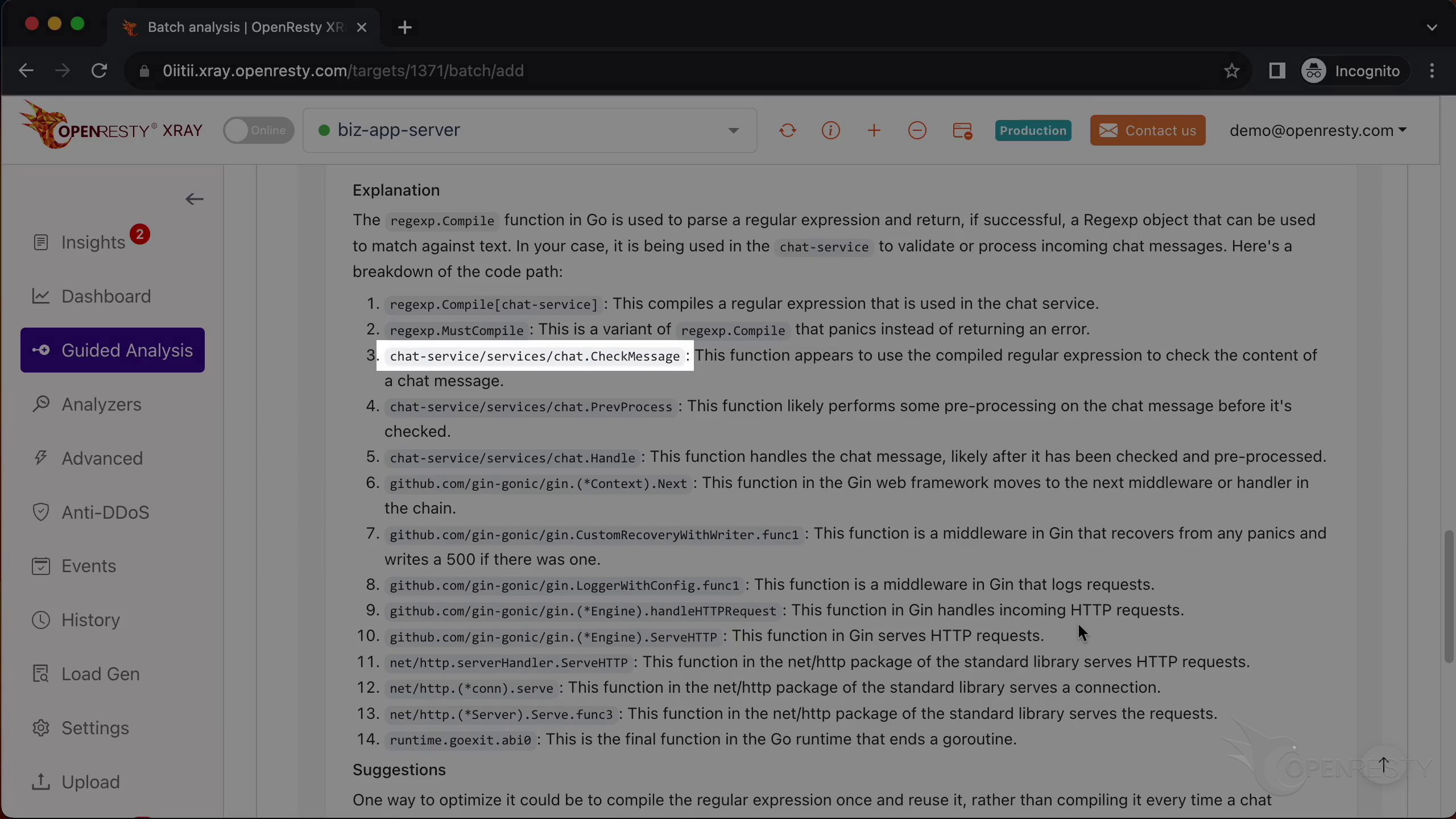
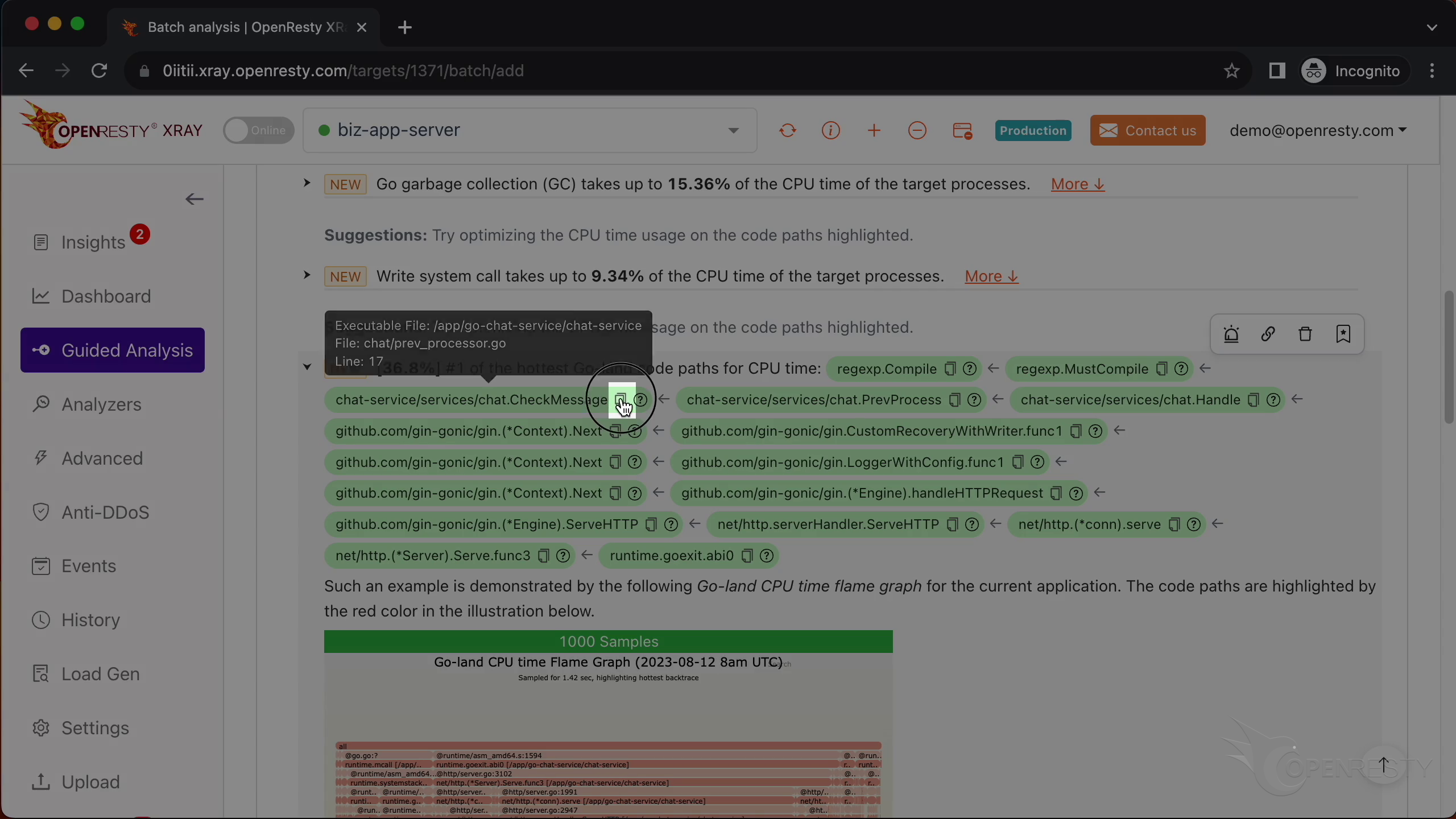
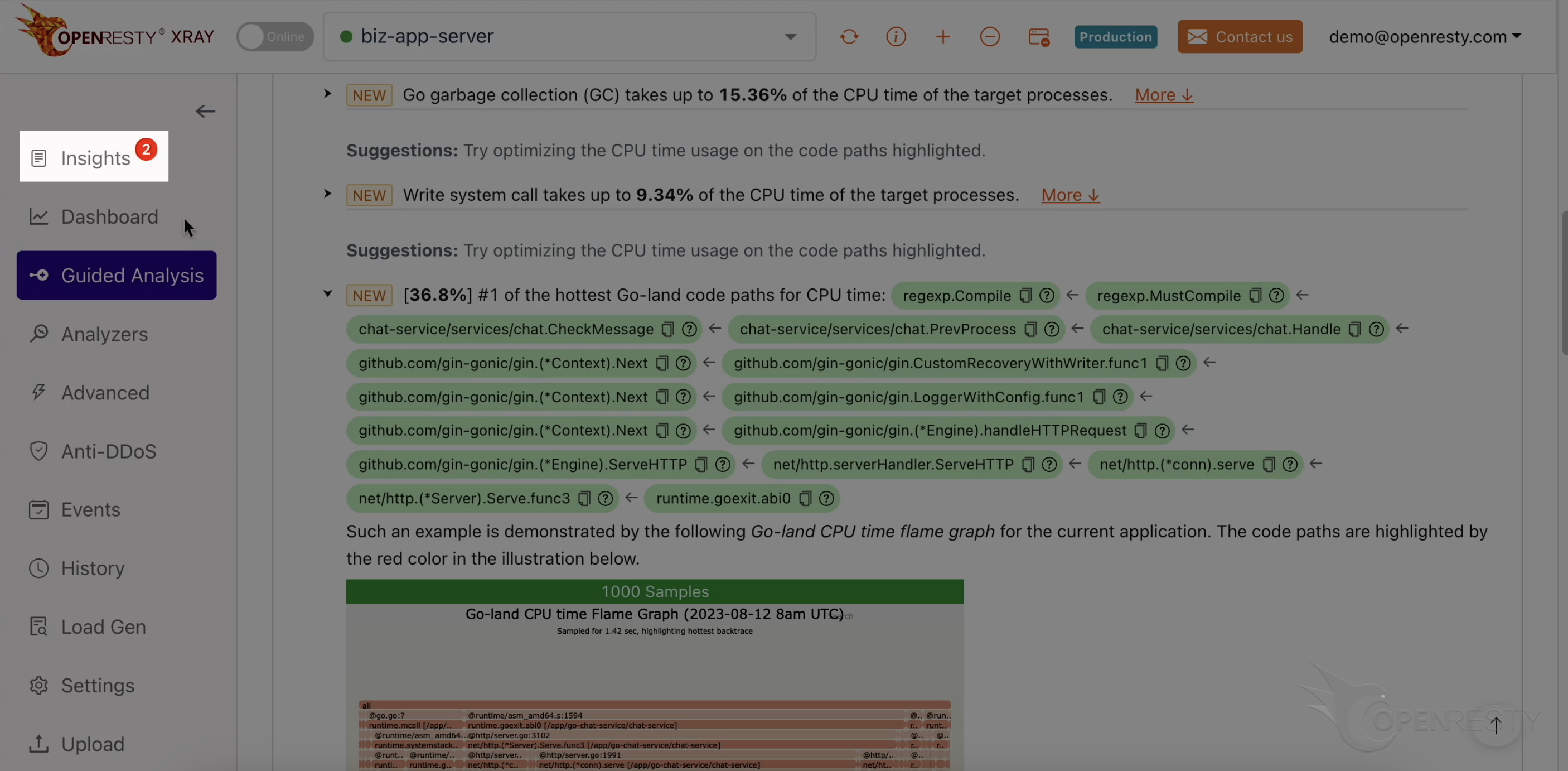
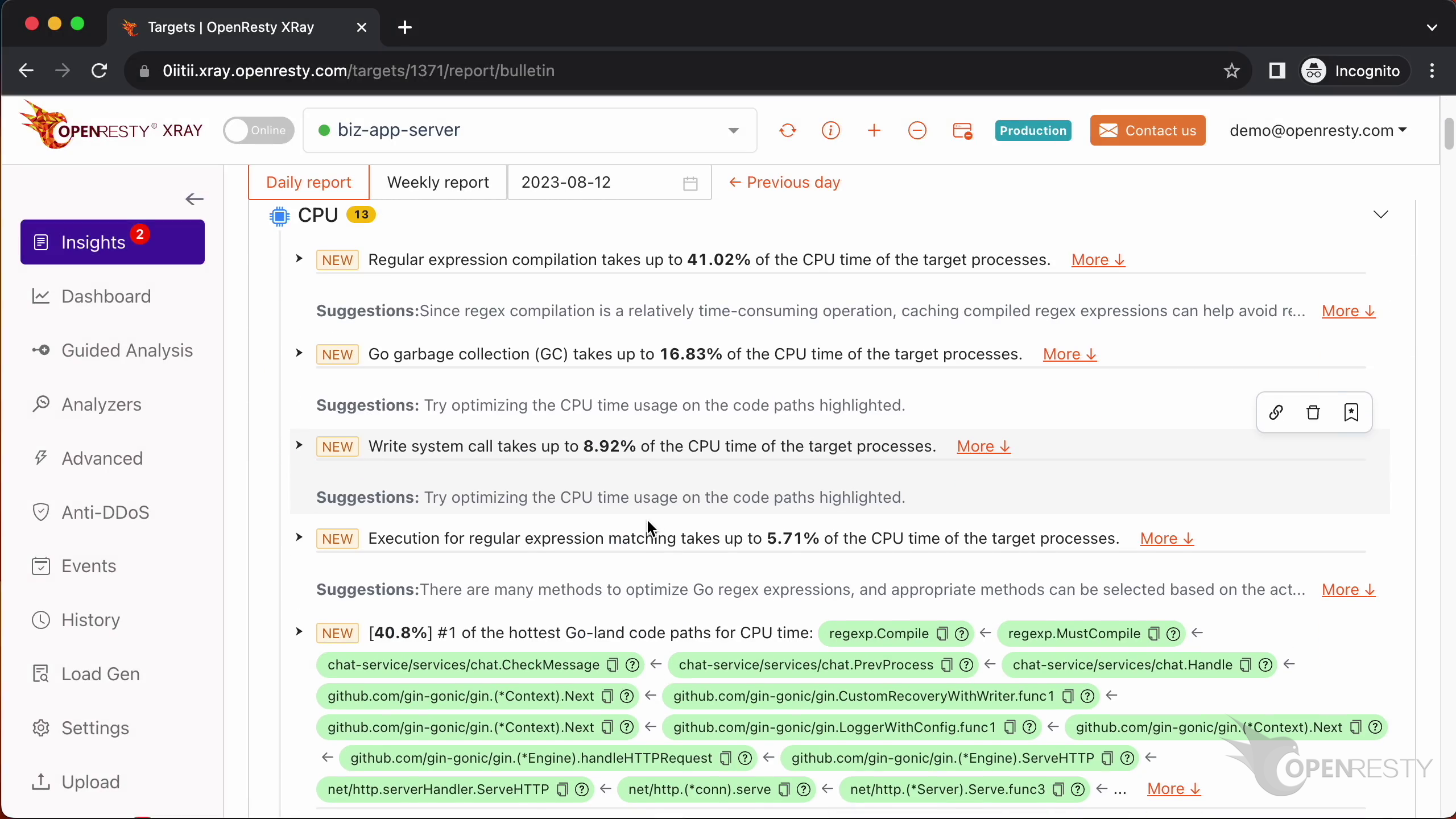
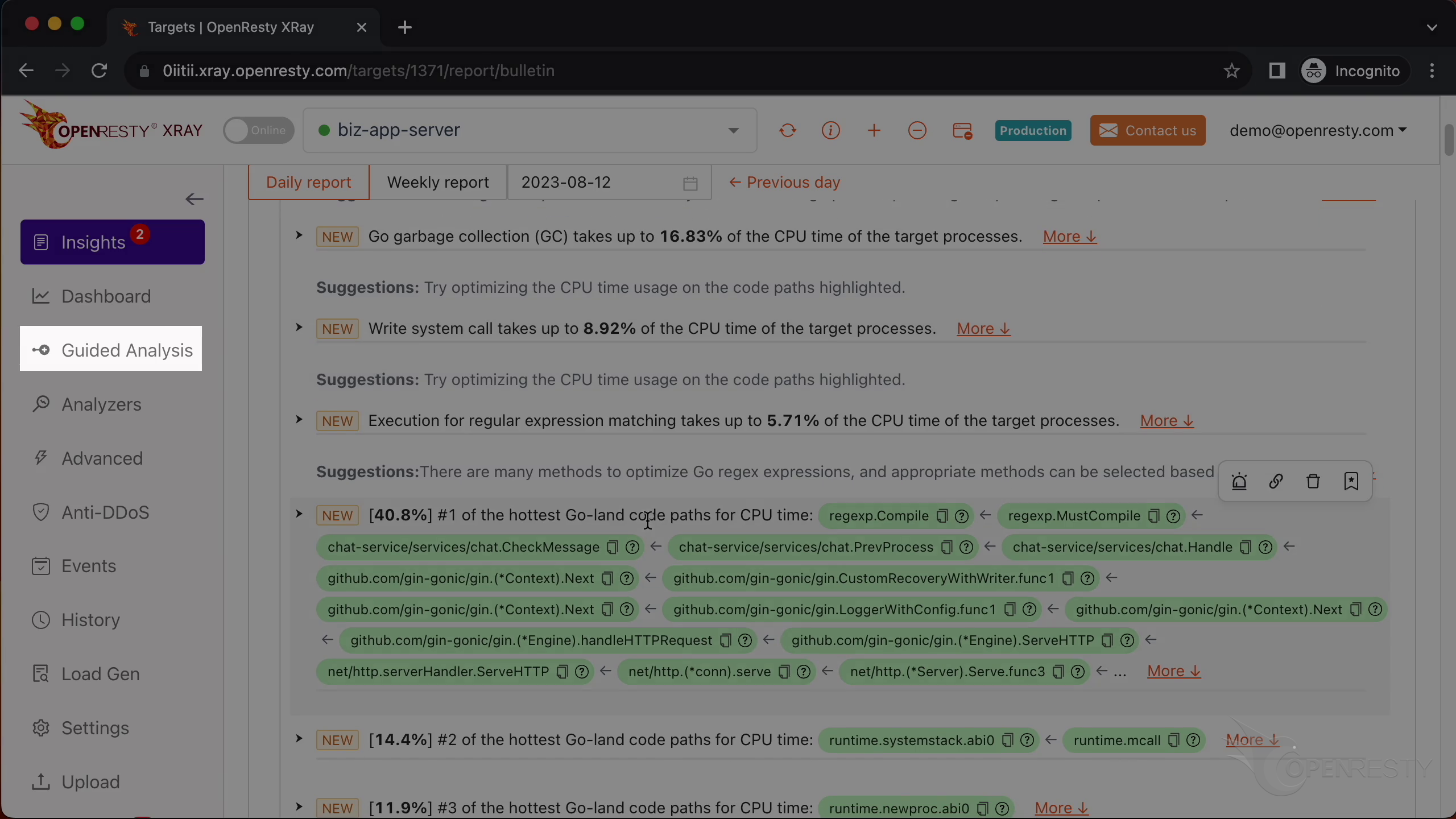
This report shows us the most critical Go-land code paths that consume the most CPU time. The top one is the regular expression compilation, which takes up 36.8% of the CPU time.
These two functions are responsible for compiling regular expressions. They are part of the standard regexp library in Go’s runtime.
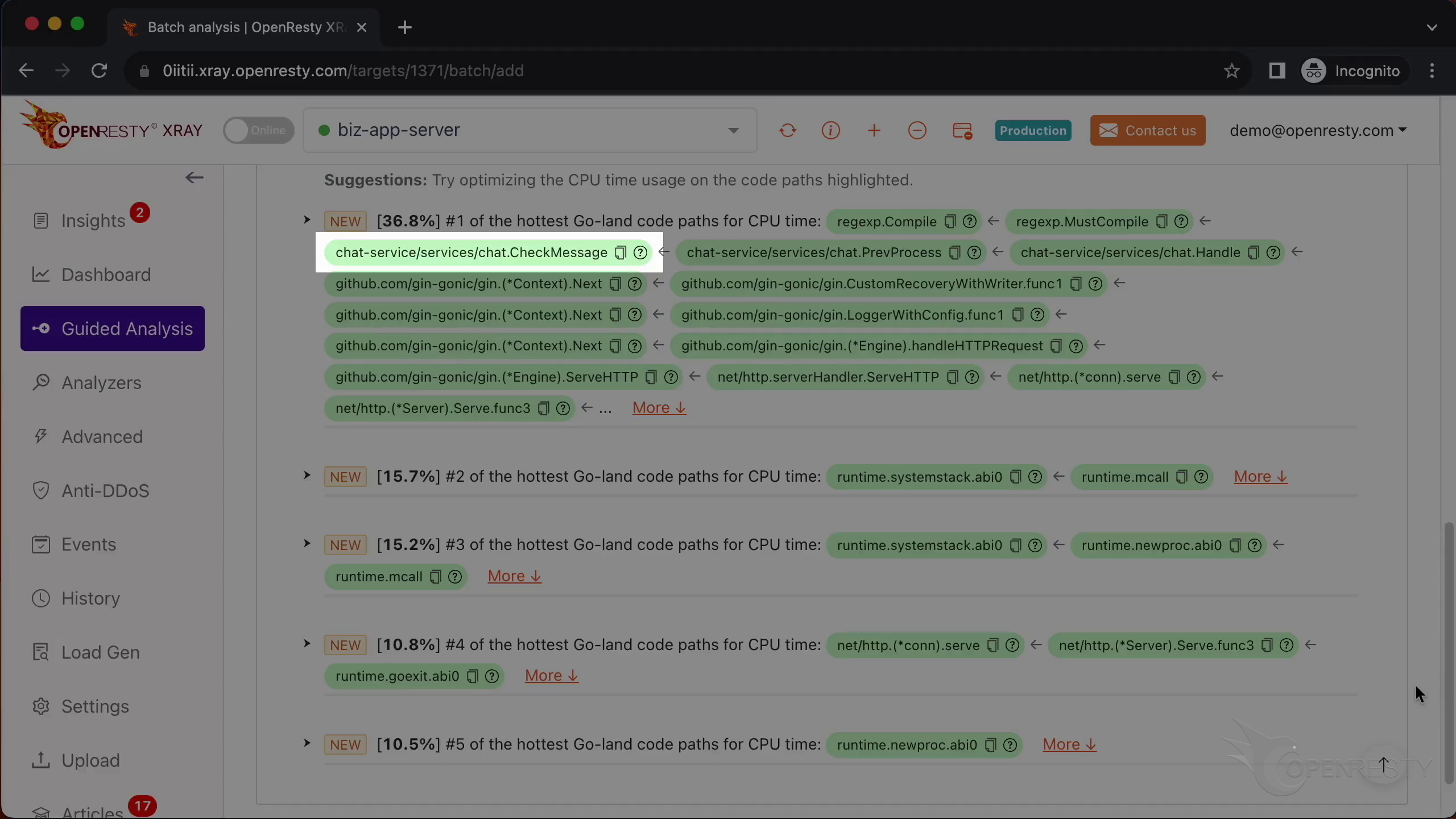
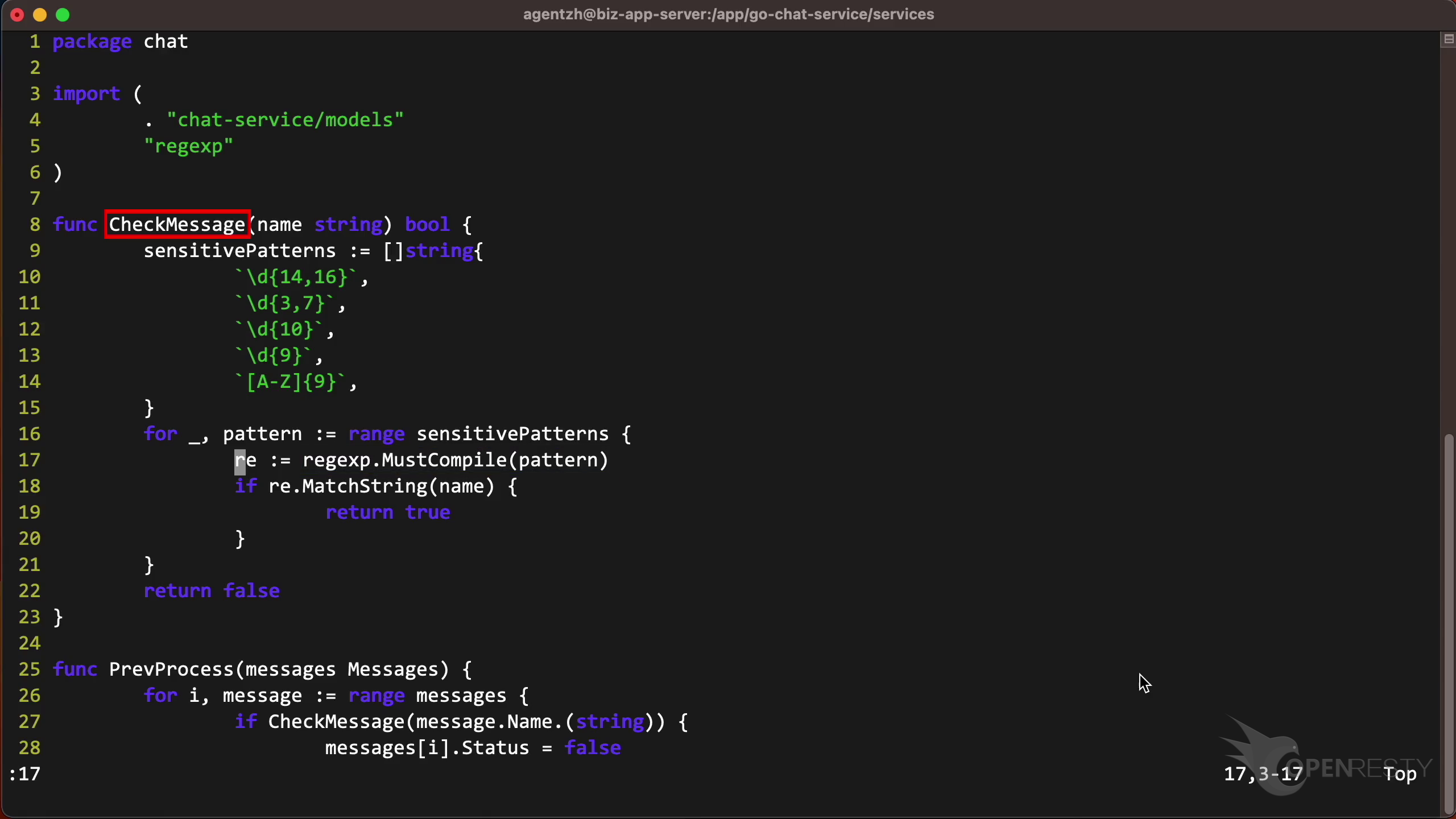
This checkMessage function is where our business logic happens. It calls the regex compilation functions that we just saw.
If we want to learn more about this code path, we can click on the “More” link.
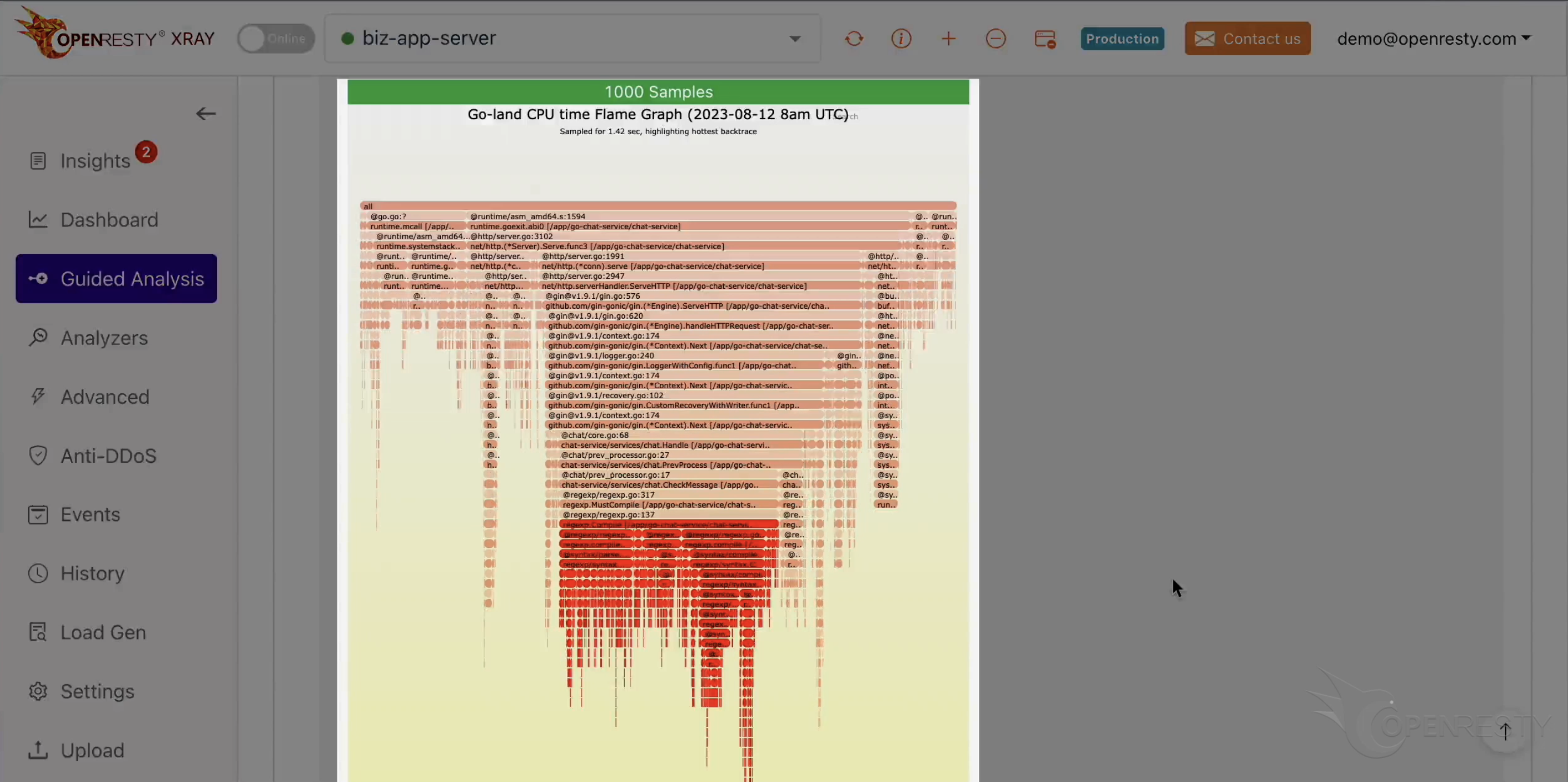
This will take us to a detailed view of the code path, which is derived from this Go-land CPU flame graph.
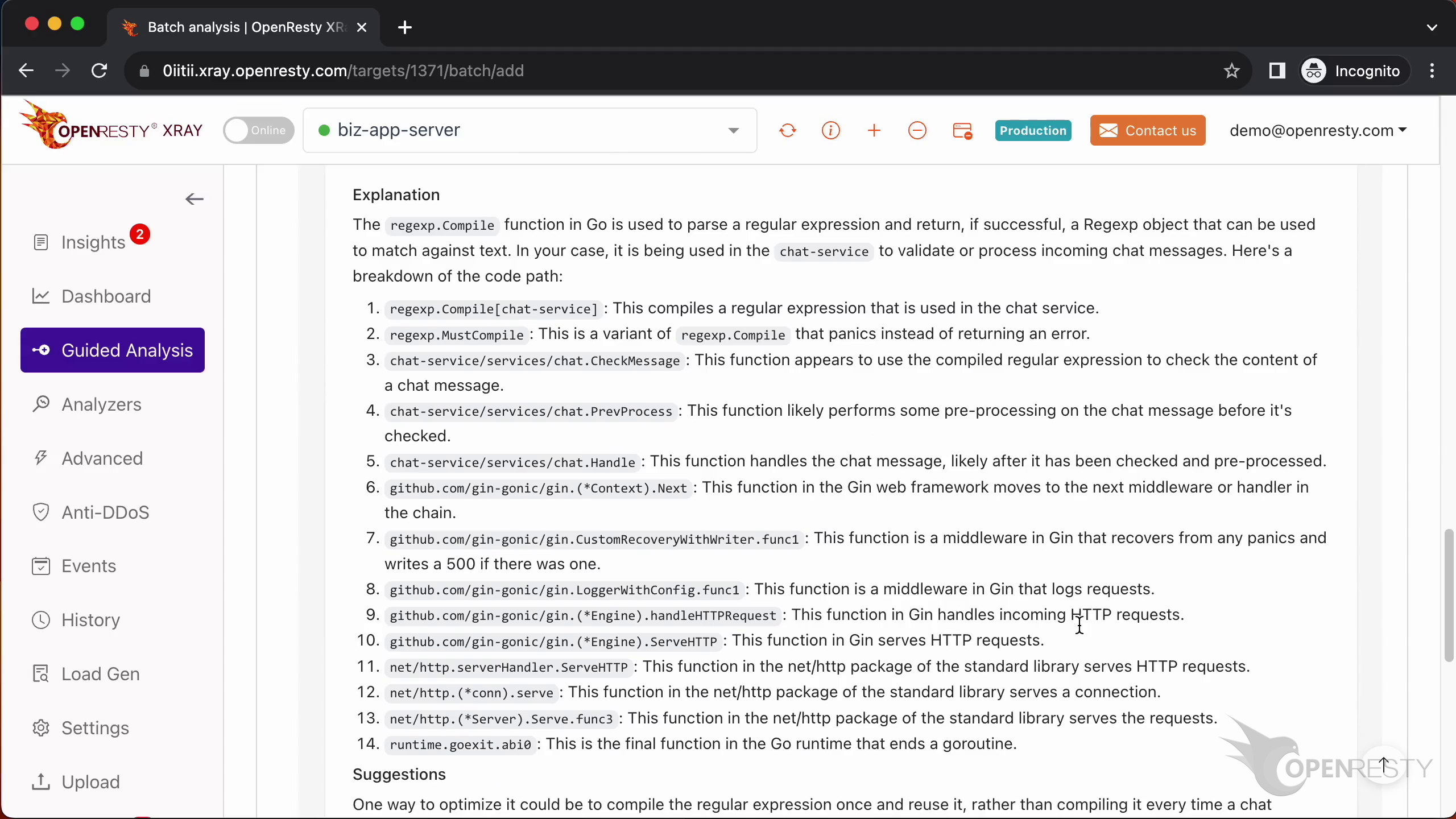
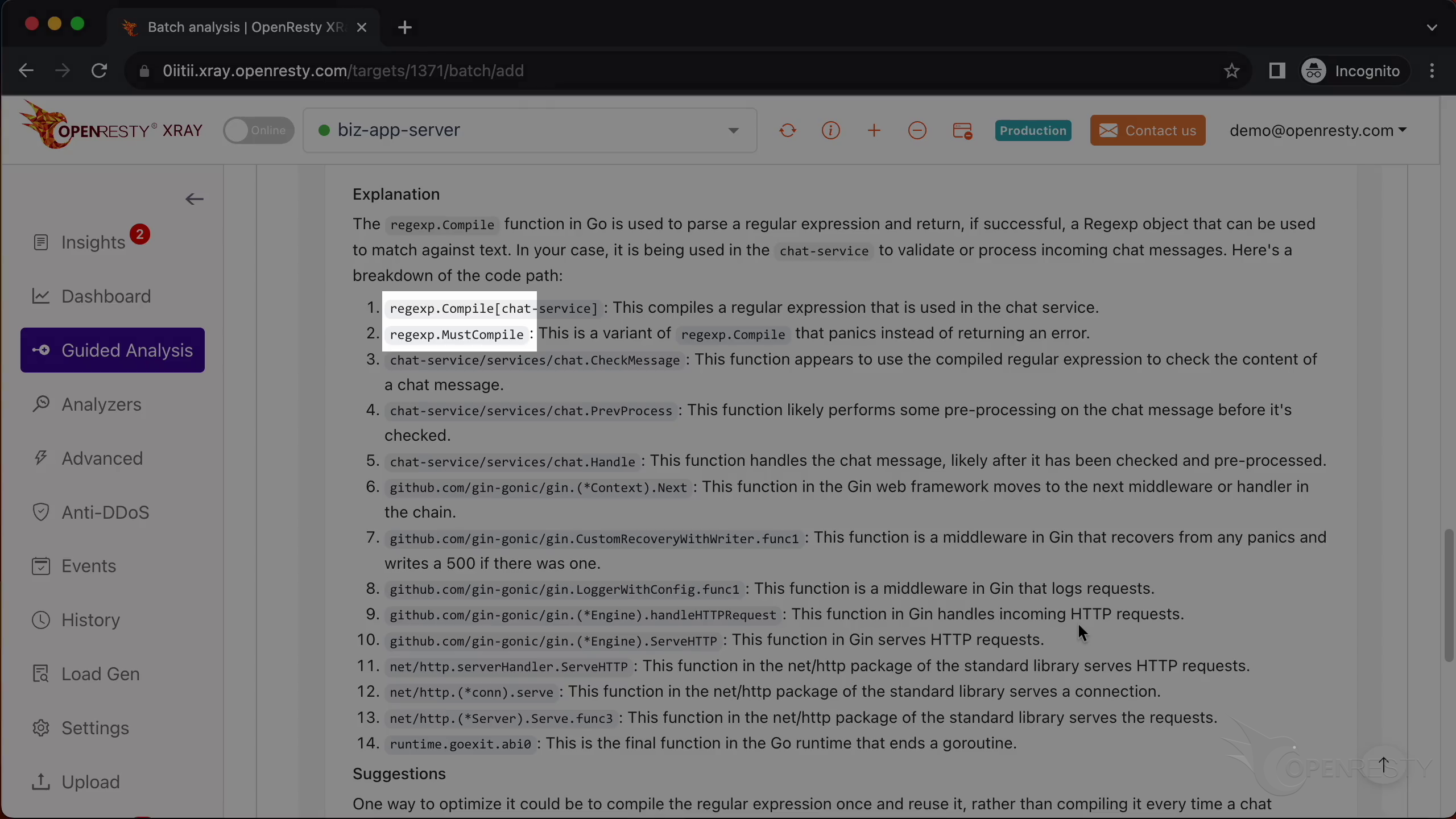
Here we can see some explanations and suggestions on how to improve the performance of this code path.
For example, it tells us that the regular expression compilation functions are very expensive and should be avoided if possible.
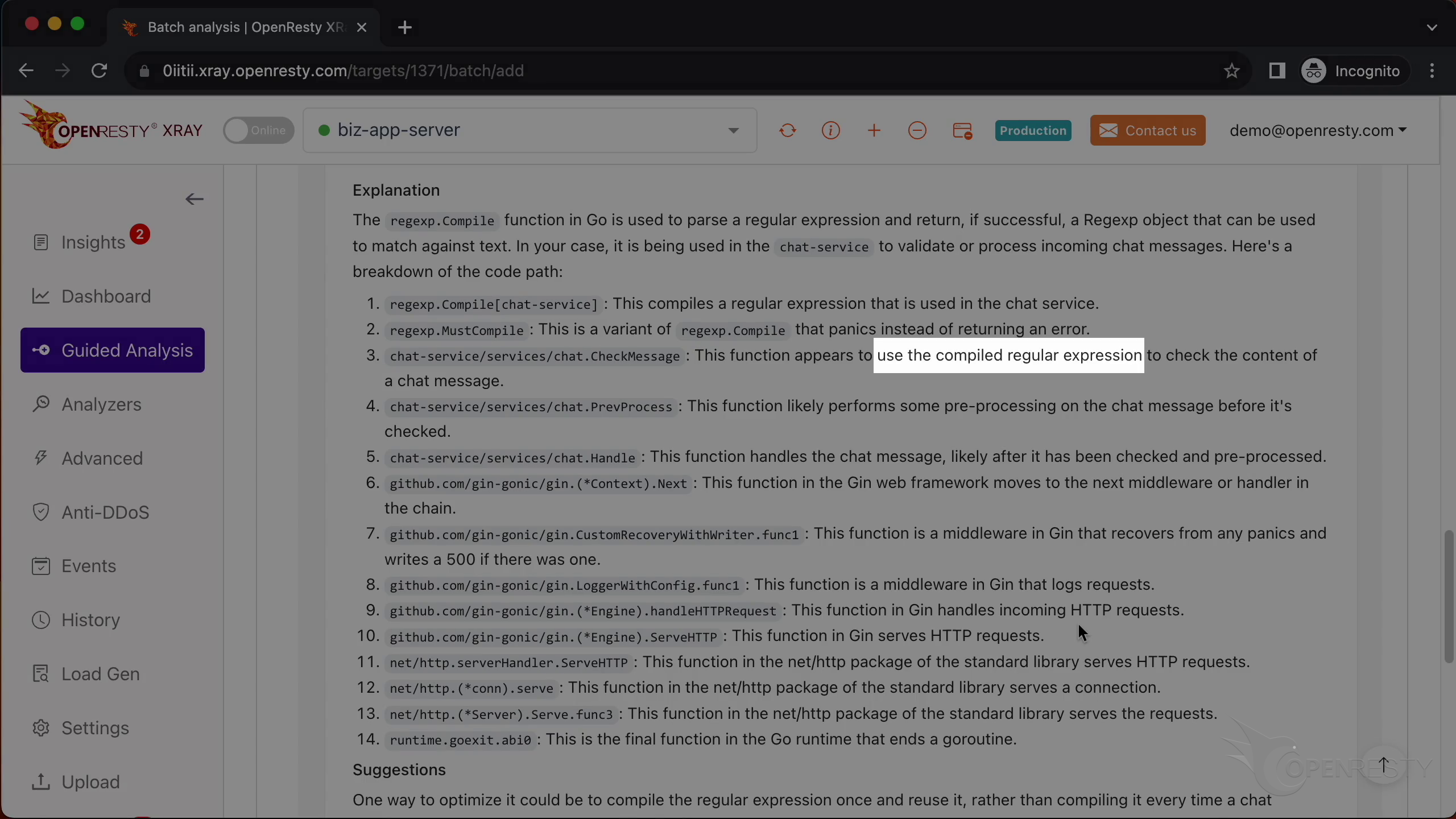
Next, it explains the business-level function CheckMessage and that it uses and compiles regular expressions.
It also covers the compiled regular expressions.
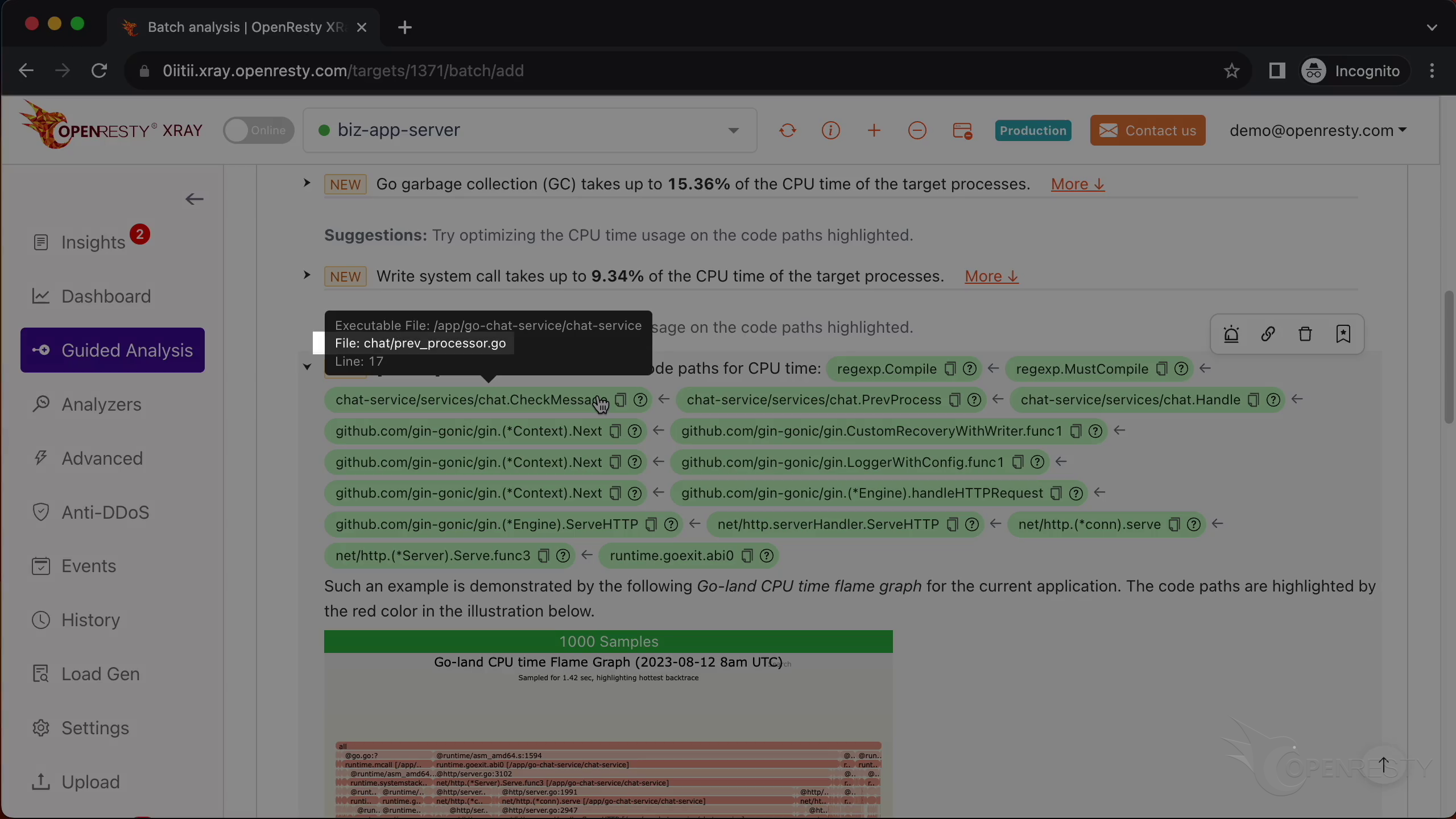
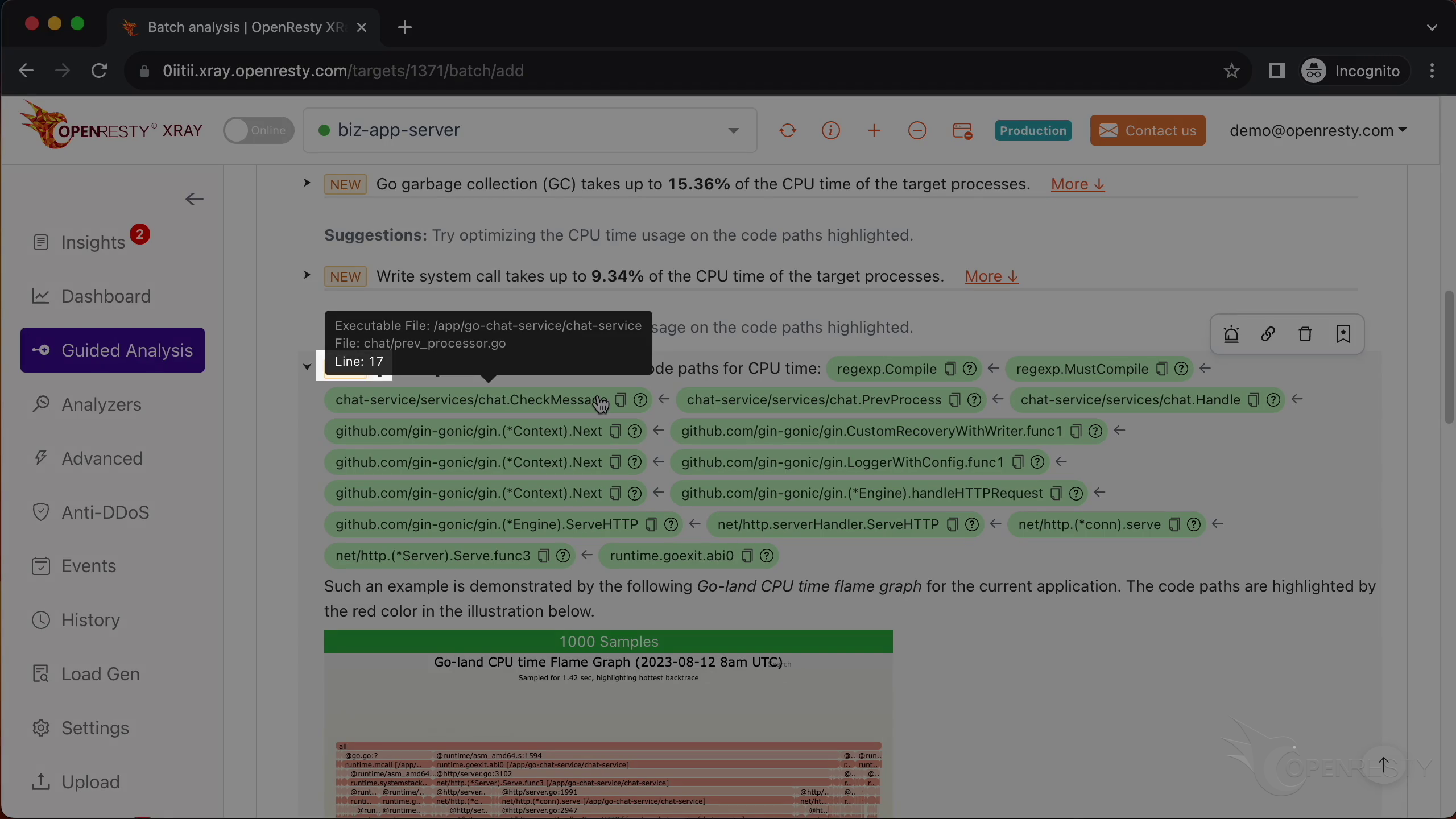
Let’s go back to the code path. And hover the mouse over the green box for the Go function named CheckMessage.
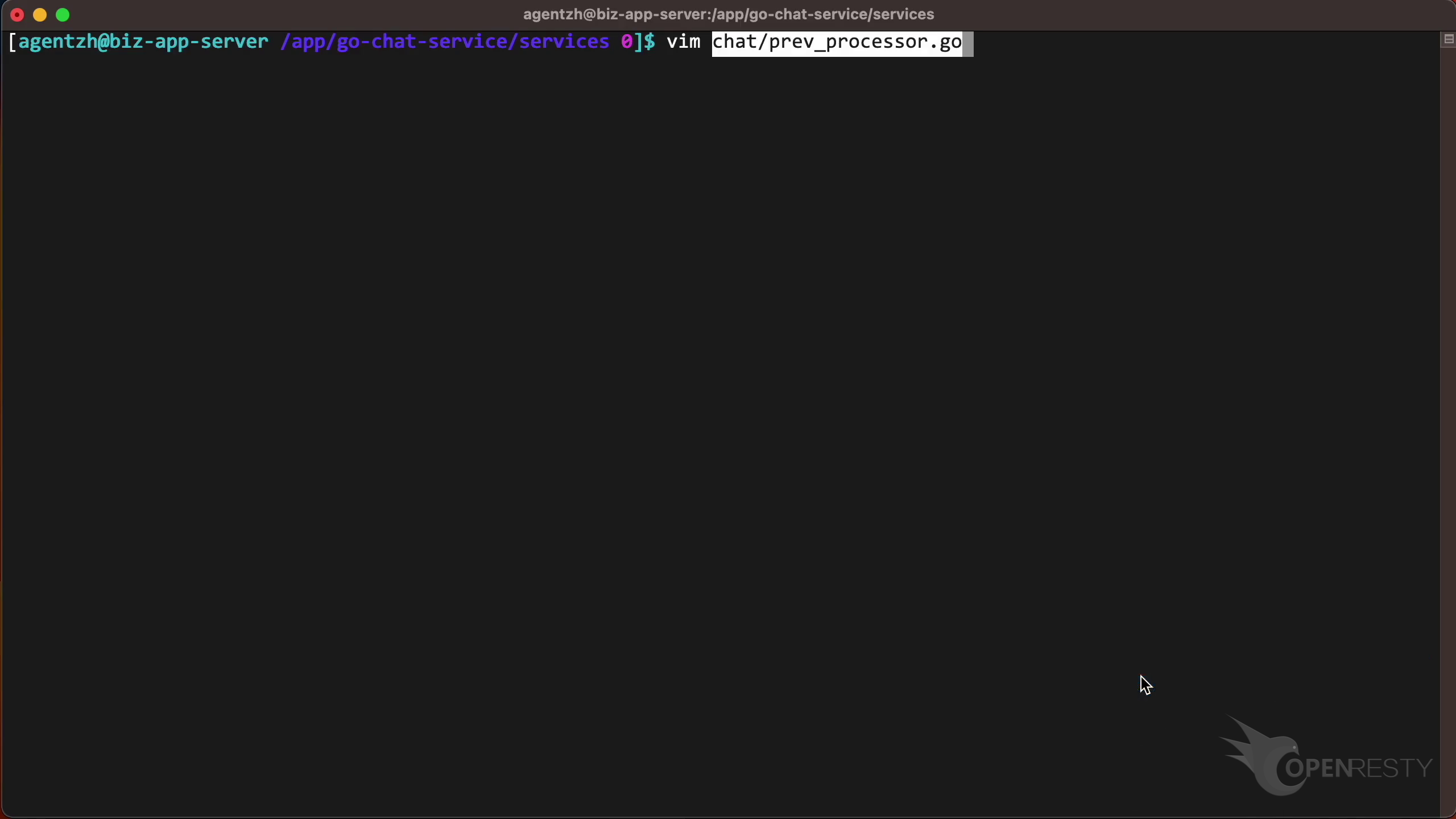
We can see the Go source file of the CheckMessage function. And its full path for the prev_processor.go file in the tooltip.
The Go source line number is 17.
Click the icon to copy the full Go source file path for this function.
Use the vim editor and paste the code path we just copied to look at the corresponding business Go code. You can use any editor you like.
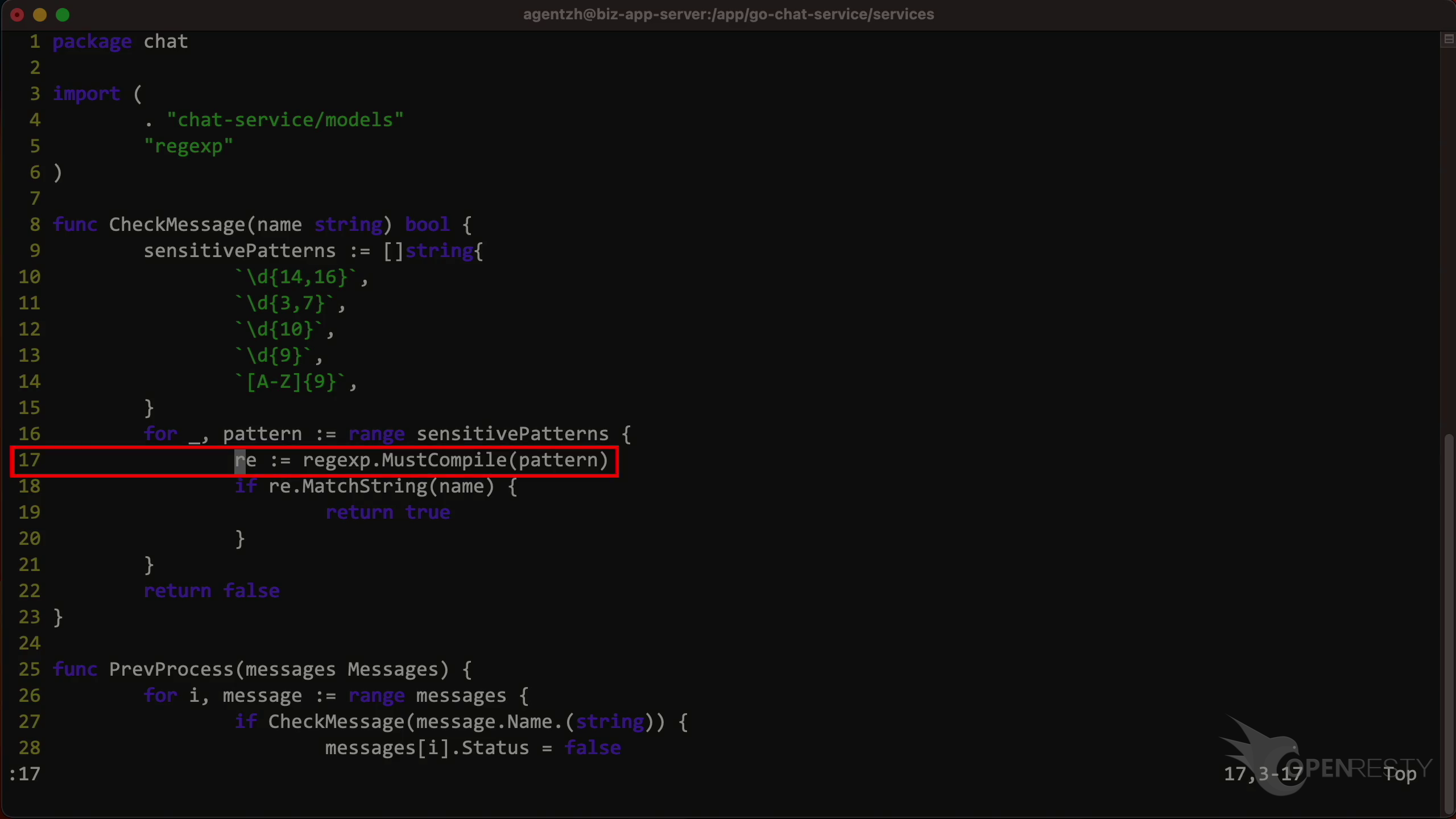
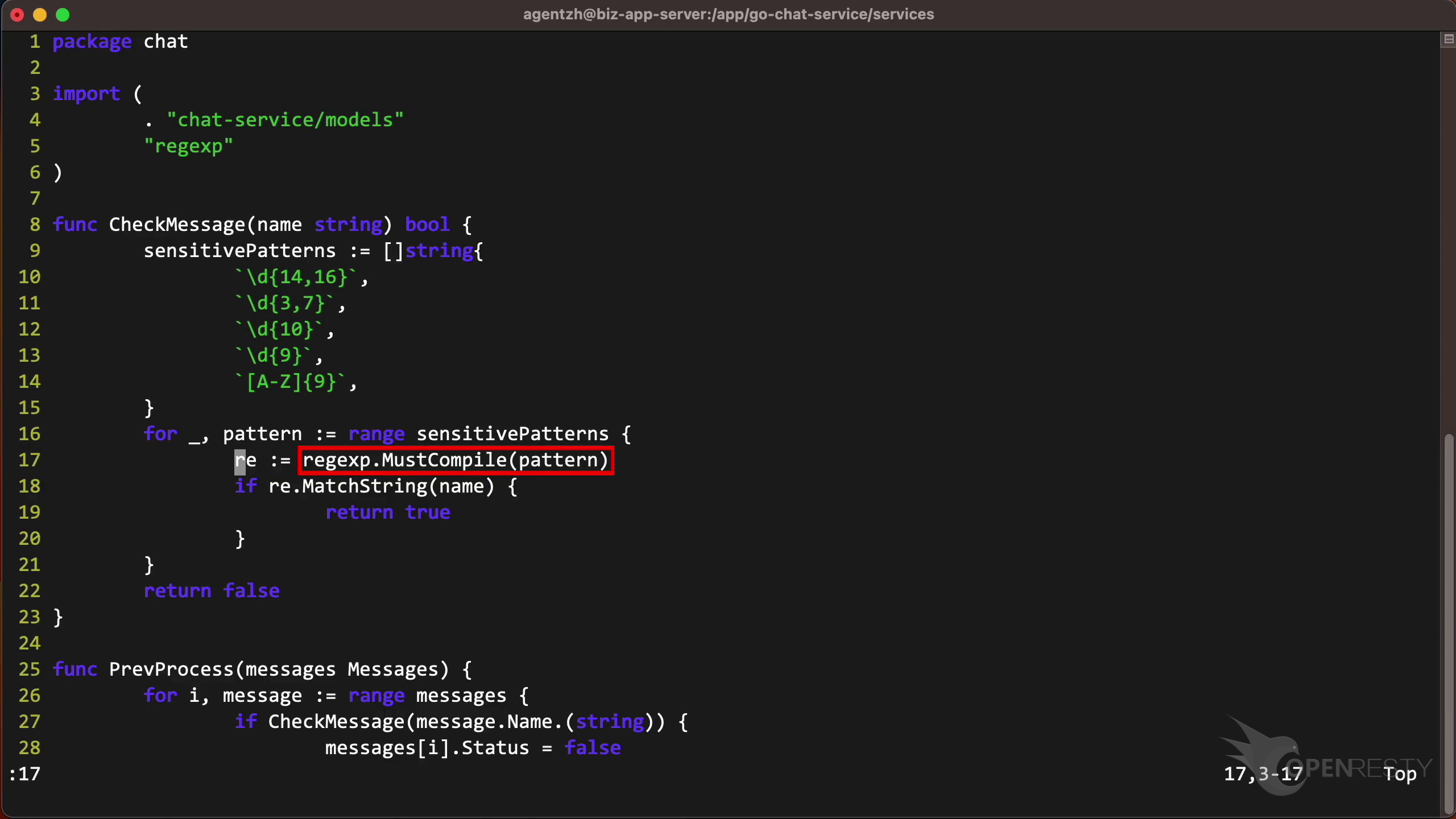
Go to line 17 as shown in the report tooltip.
We can see that It does the regular expression compilation.
It is also in the function CheckMessage as shown in the report. It’s now easy to optimize the Go code!
Automatic analysis and reports
OpenResty XRay can also monitor online processes automatically and show analysis reports. Go to the Insights page.
You can find the reports in the Insights page for daily and weekly periods.
For this reason, you don’t have to use the Guided Analysis feature. Guided analysis is useful for application development and demonstration purposes.
What is OpenResty XRay
OpenResty XRay is a dynamic-tracing product that automatically analyzes your running applications to troubleshoot performance problems, behavioral issues, and security vulnerabilities with actionable suggestions. Under the hood, OpenResty XRay is powered by our Y language targeting various runtimes like Stap+, eBPF+, GDB, and ODB, depending on the contexts.
If you like this tutorial, please subscribe to this blog site and/or our YouTube channel. Thank you!
About The Author
Yichun Zhang (Github handle: agentzh), is the original creator of the OpenResty® open-source project and the CEO of OpenResty Inc..
Yichun is one of the earliest advocates and leaders of “open-source technology”. He worked at many internationally renowned tech companies, such as Cloudflare, Yahoo!. He is a pioneer of “edge computing”, “dynamic tracing” and “machine coding”, with over 22 years of programming and 16 years of open source experience. Yichun is well-known in the open-source space as the project leader of OpenResty®, adopted by more than 40 million global website domains.
OpenResty Inc., the enterprise software start-up founded by Yichun in 2017, has customers from some of the biggest companies in the world. Its flagship product, OpenResty XRay, is a non-invasive profiling and troubleshooting tool that significantly enhances and utilizes dynamic tracing technology. And its OpenResty Edge product is a powerful distributed traffic management and private CDN software product.
As an avid open-source contributor, Yichun has contributed more than a million lines of code to numerous open-source projects, including Linux kernel, Nginx, LuaJIT, GDB, SystemTap, LLVM, Perl, etc. He has also authored more than 60 open-source software libraries.