Share Data Across Requests Served by OpenResty
This tutorial will demonstrate how to share data across different HTTP requests served by an OpenResty application.
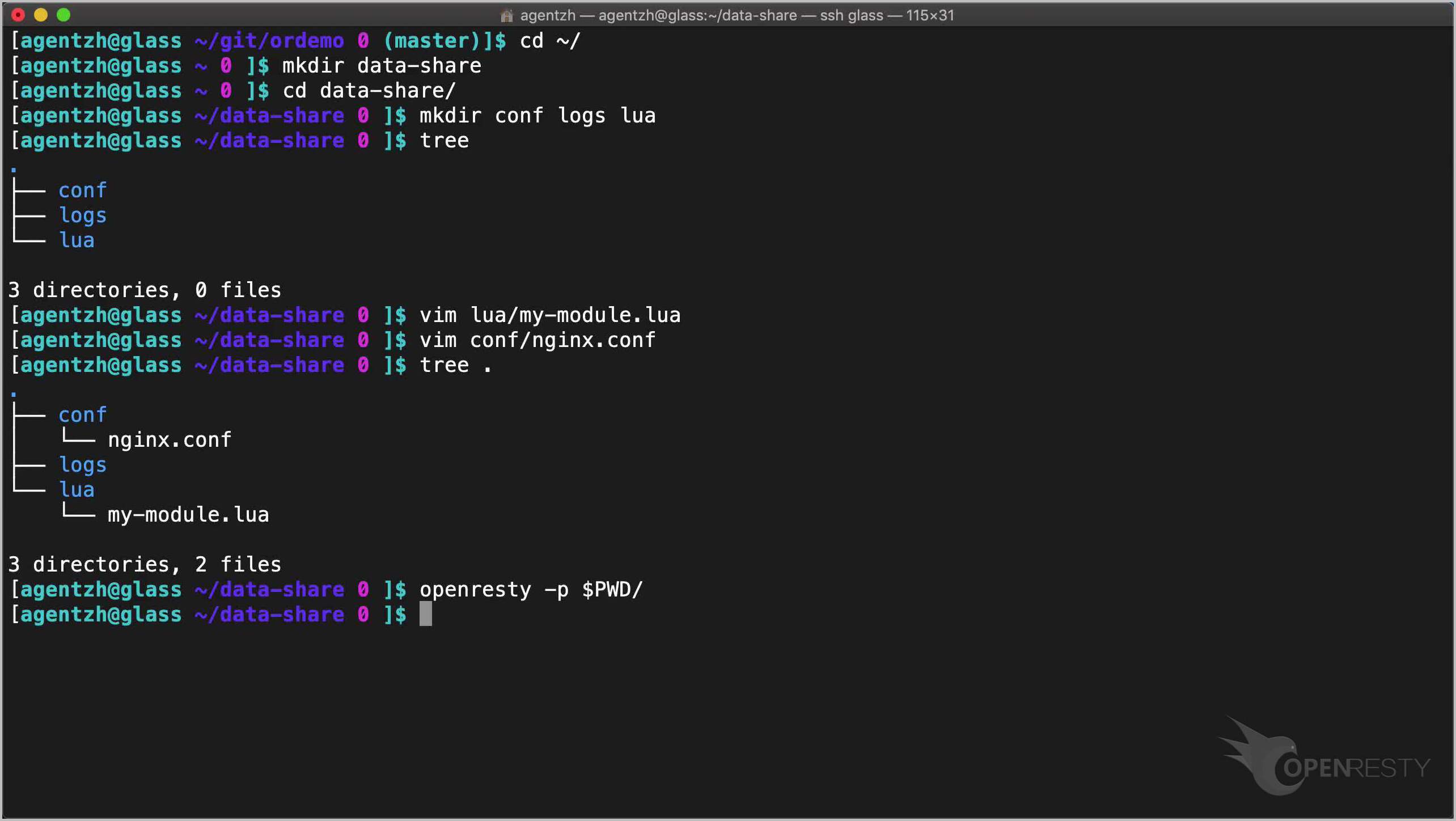
cd ~/
mkdir data-share
cd data-share/
mkdir conf logs lua
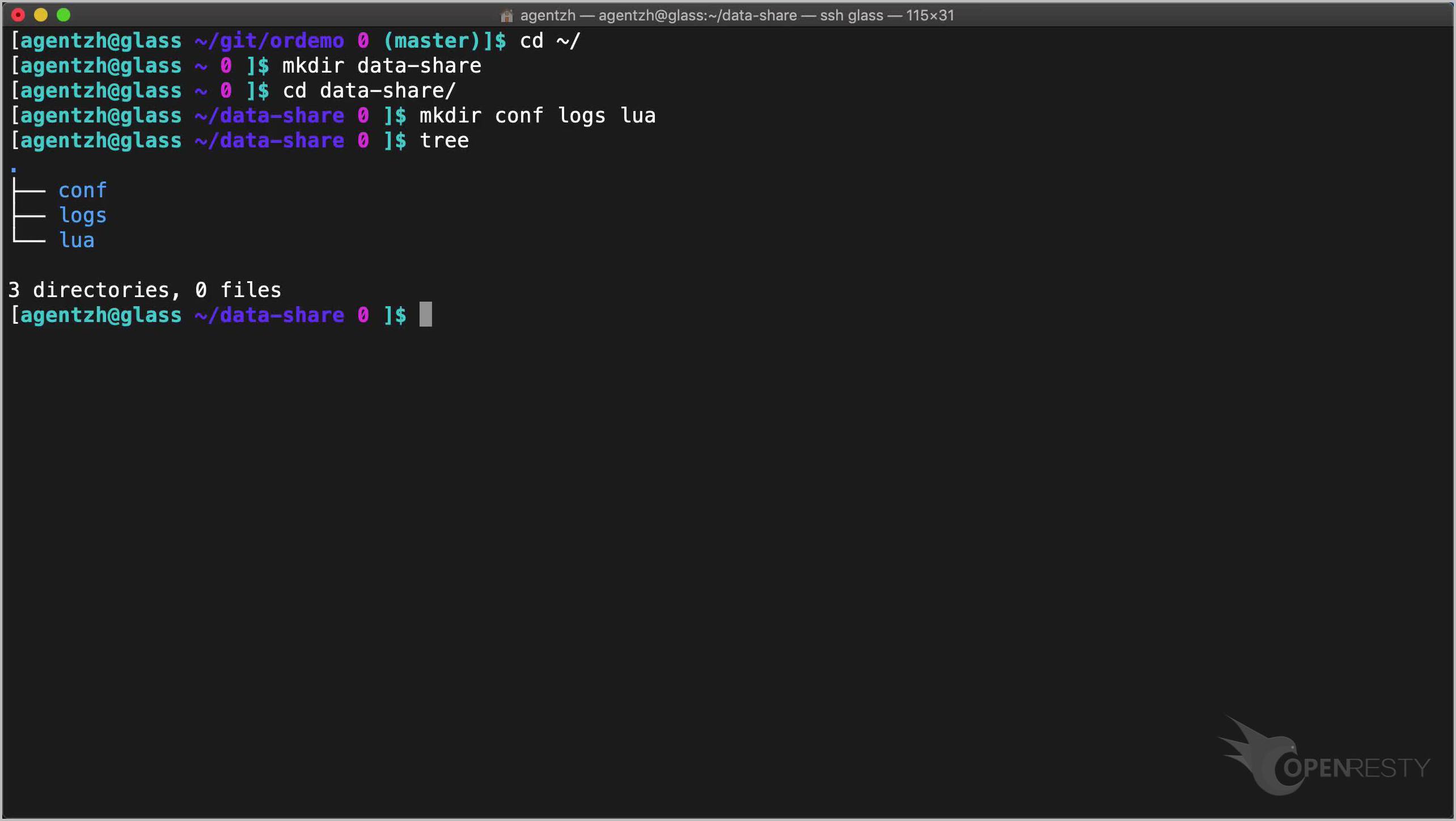
tree
We first prepare our test application’s directory tree.
The easist way to share data among requests is to use a custom Lua module named lua/my-module.lua.
We make the following edits:
- We add a global counter variable on the top-level of this module.
- Then we always increment this counter in a module function named
main. - and return the new counter value.
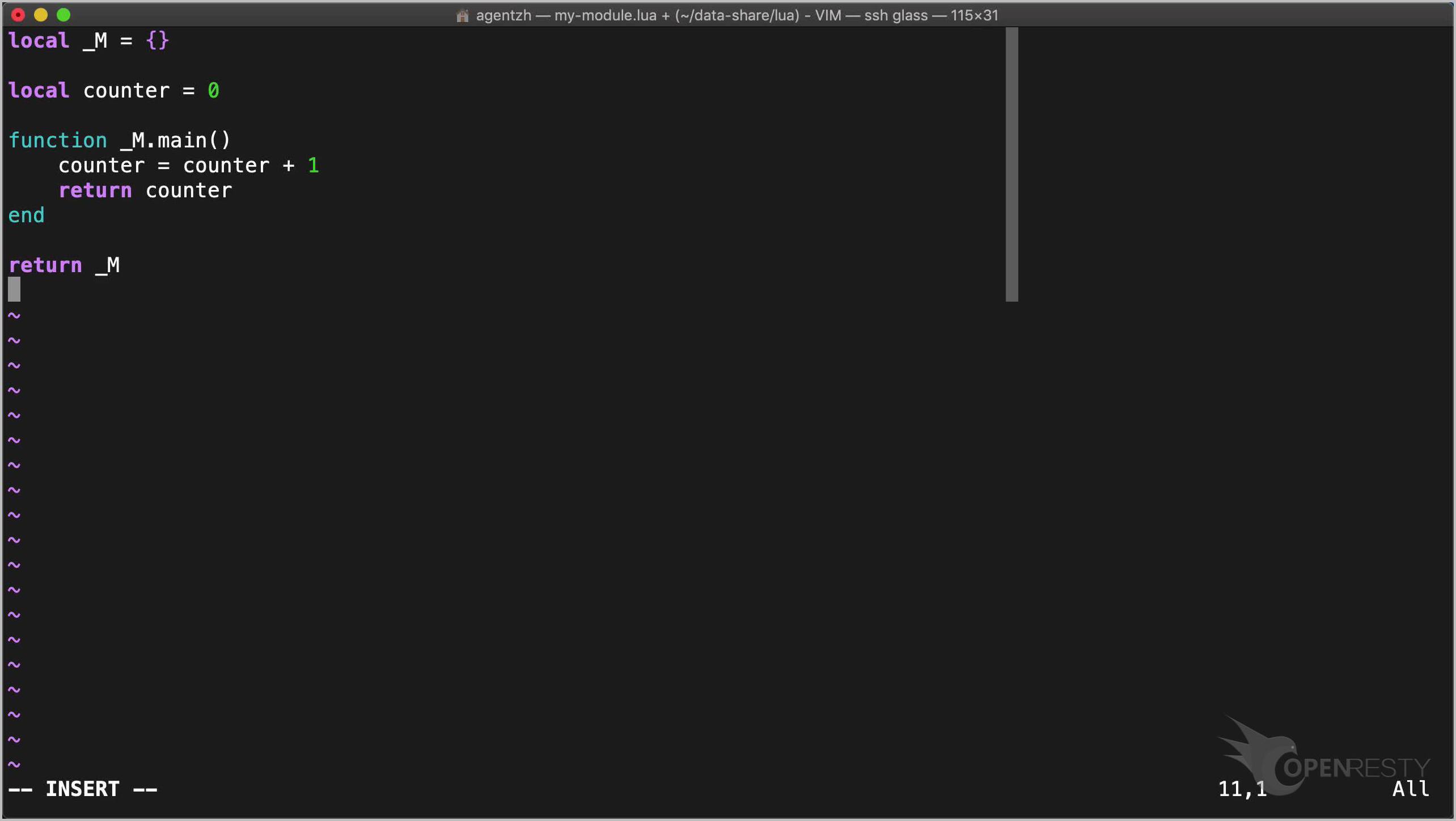
local _M = {}
local counter = 0
function _M.main()
counter = counter + 1
return counter
end
return _M
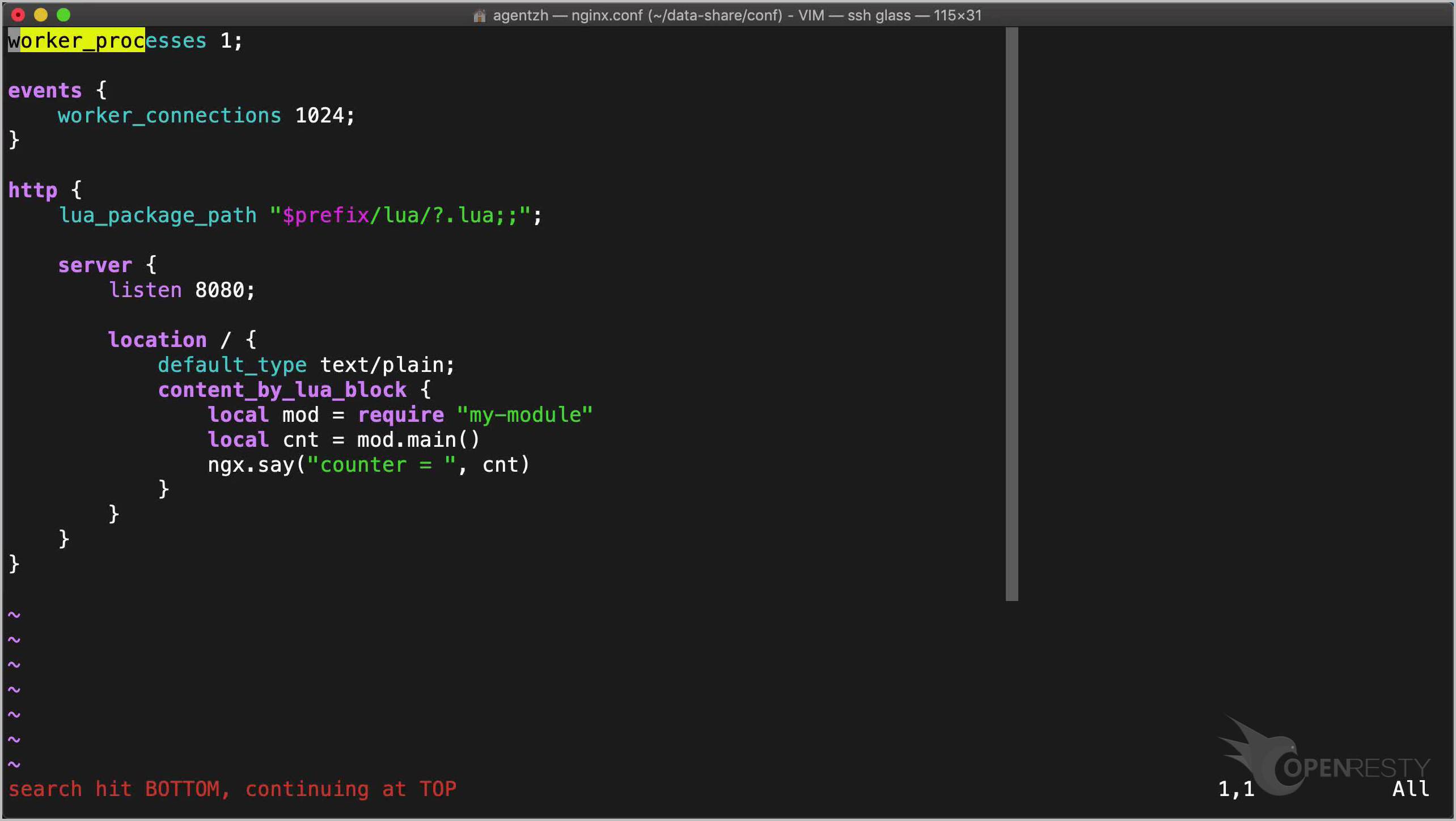
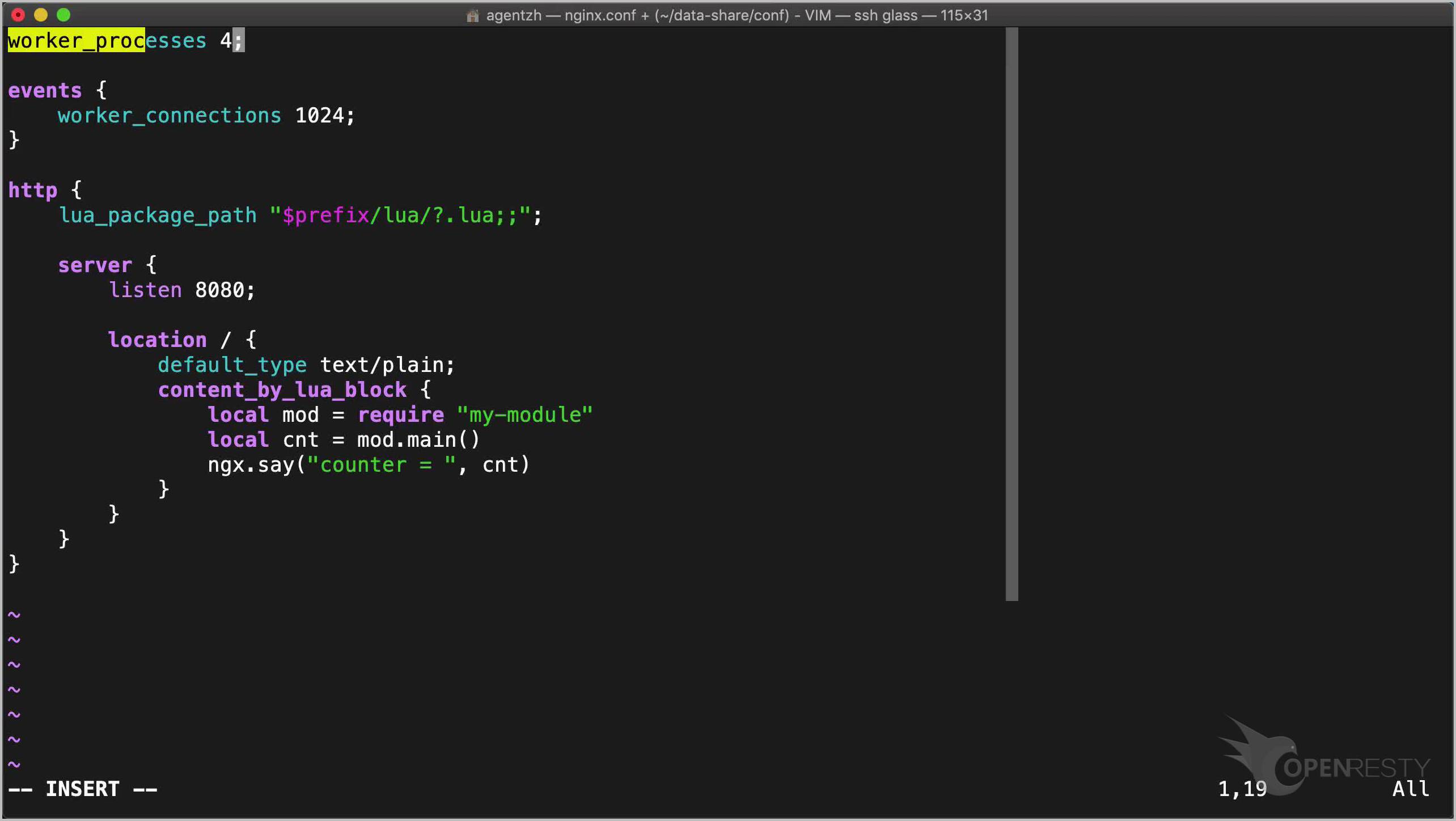
Now let’s quickly craft the nginx configuration file, conf/nginx.conf.
We make the following edits:
- Here we specify where to look for our Lua module.
- Then define a server listening on the local 8080 port.
- And a root location with
content_by_lua_block. - Load up our Lua module and invoke its
mainfunction. - And output the returned counter value as the response body.
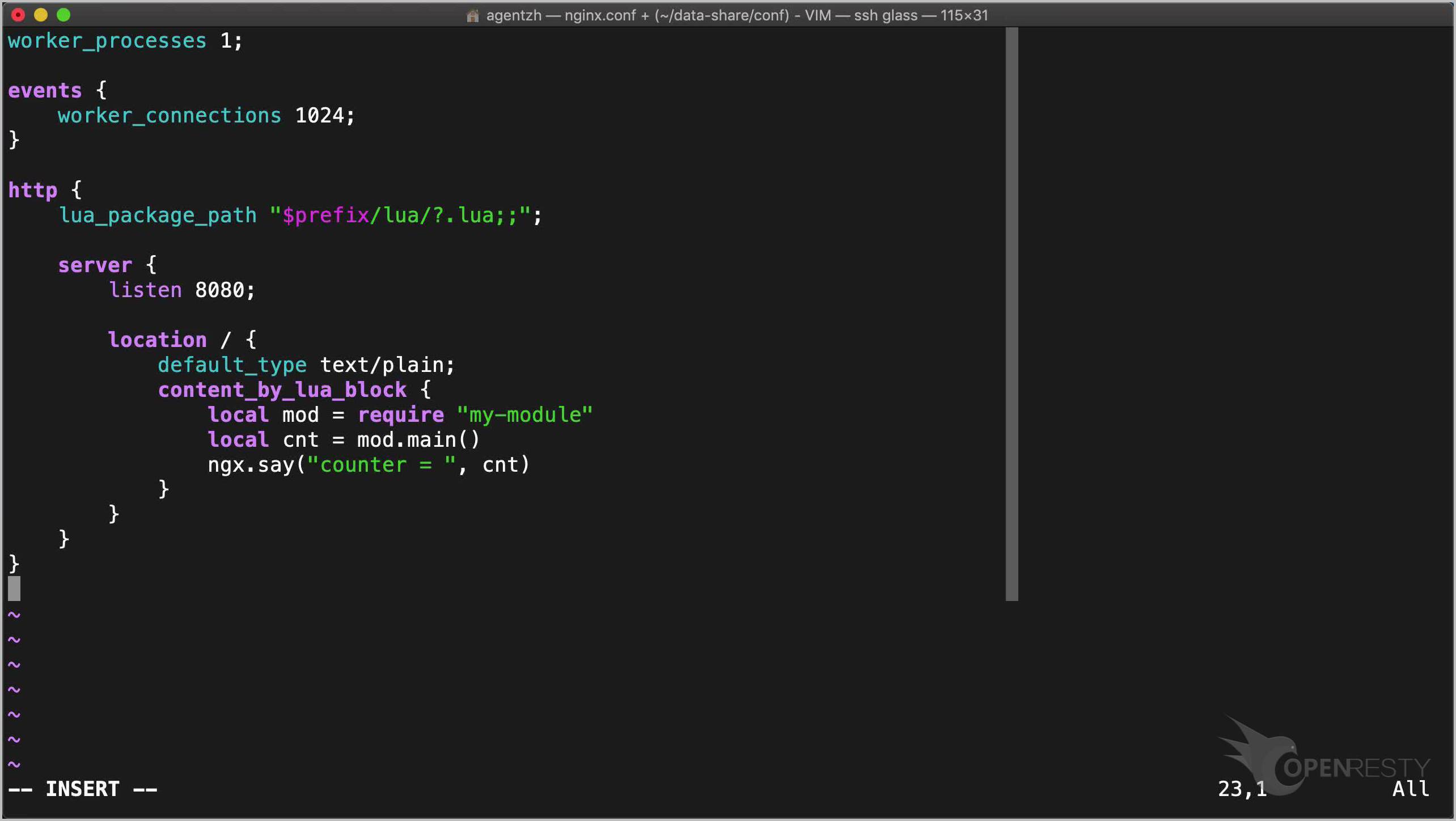
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
lua_package_path "$prefix/lua/?.lua;;";
server {
listen 8080;
location / {
default_type text/plain;
content_by_lua_block {
local mod = require "my-module"
local cnt = mod.main()
ngx.say("counter = ", cnt)
}
}
}
}
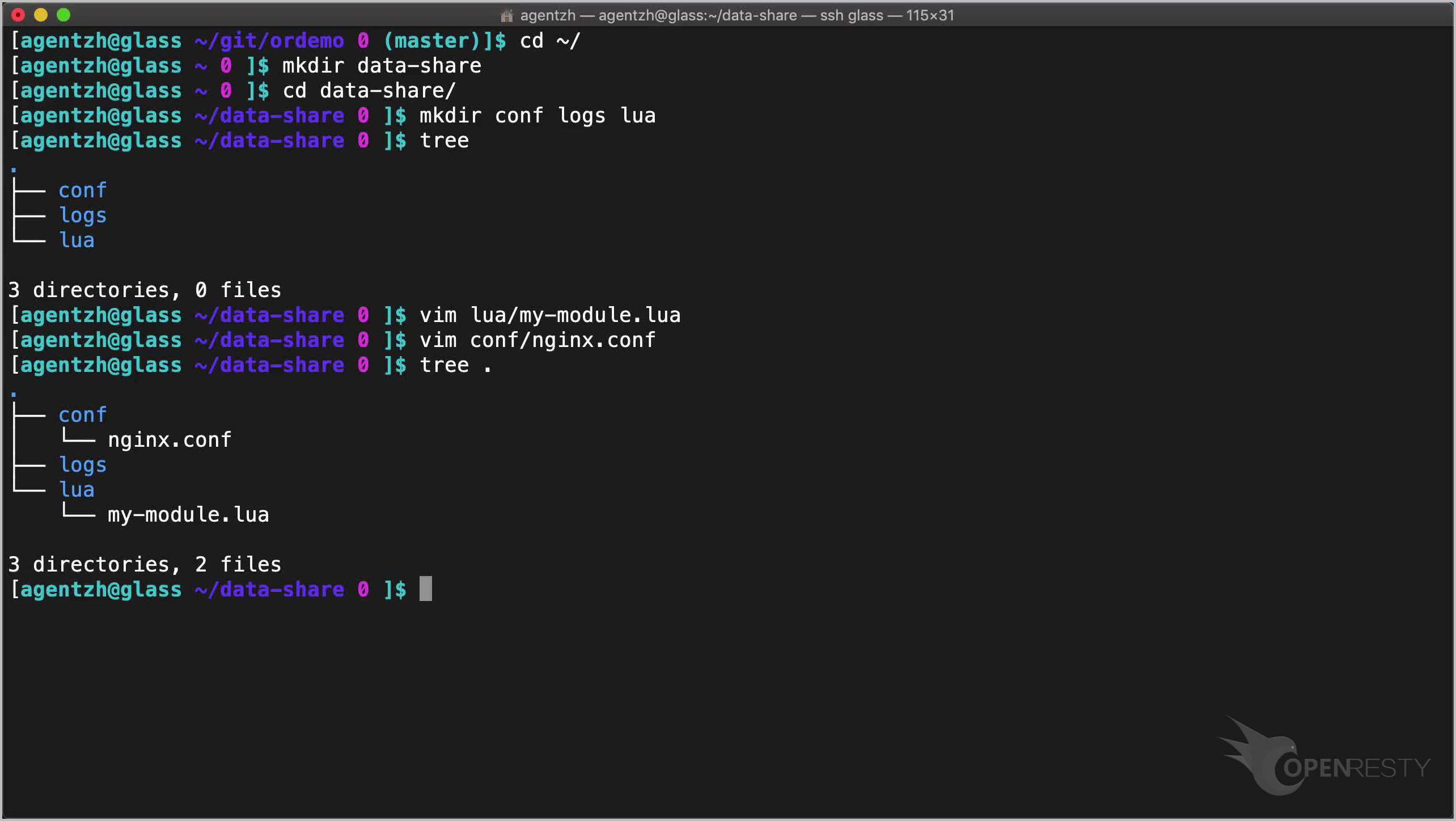
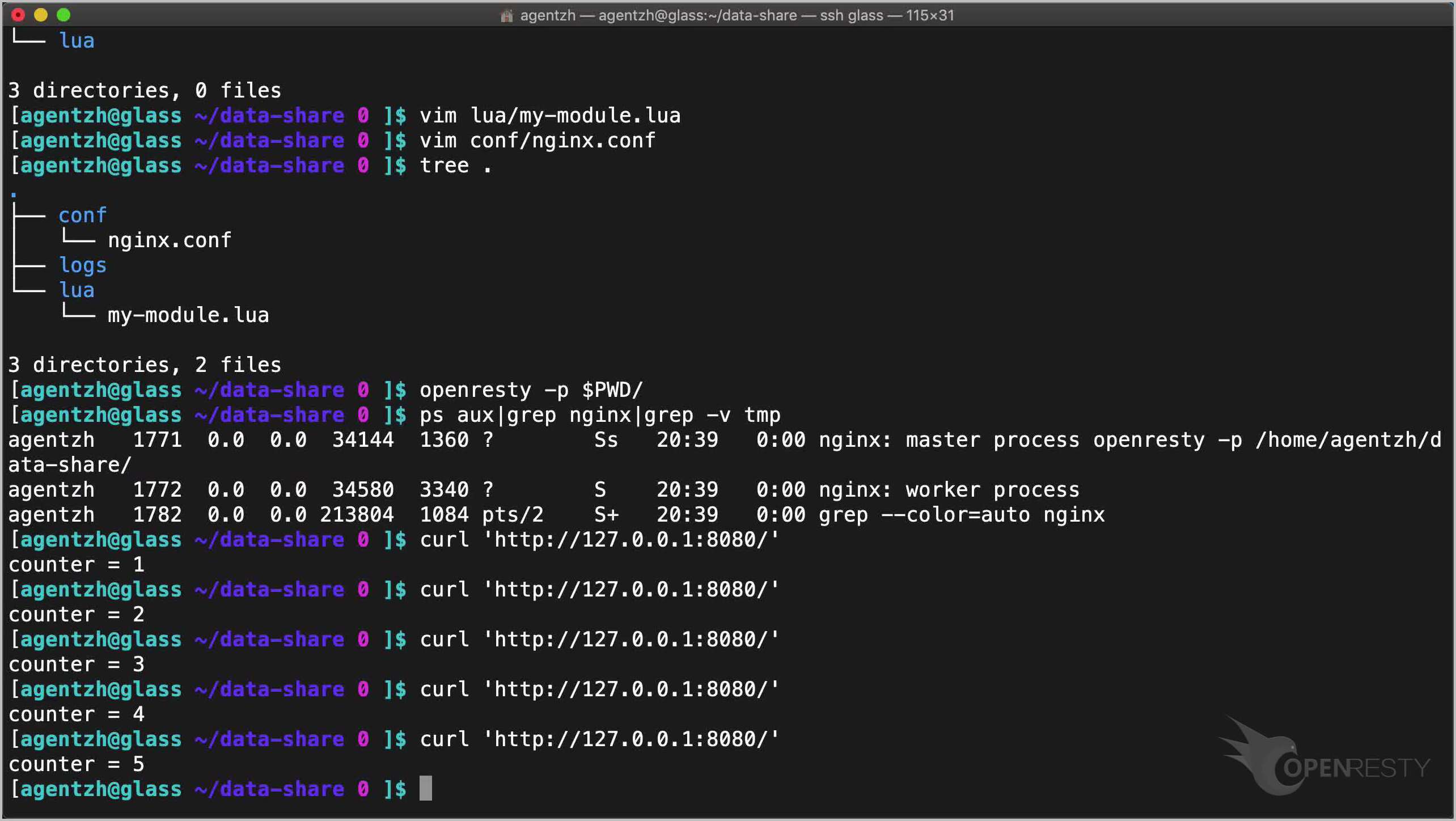
Let’s check the directory tree again.
tree .
Looking good.
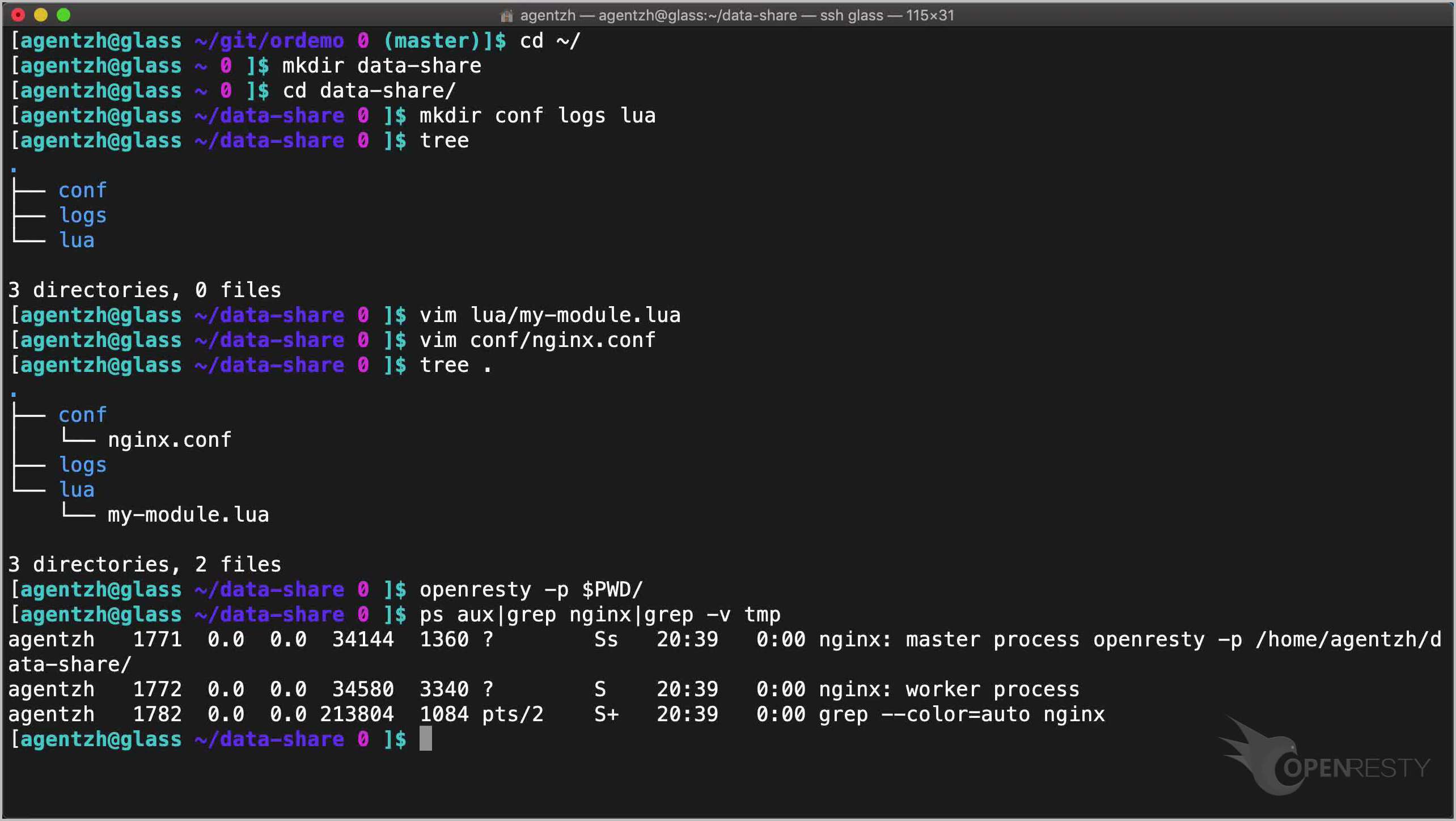
Start this OpenResty application without sudo.
openresty -p $PWD/
Here we only enable a single worker process.
ps aux|grep nginx|grep -v tmp
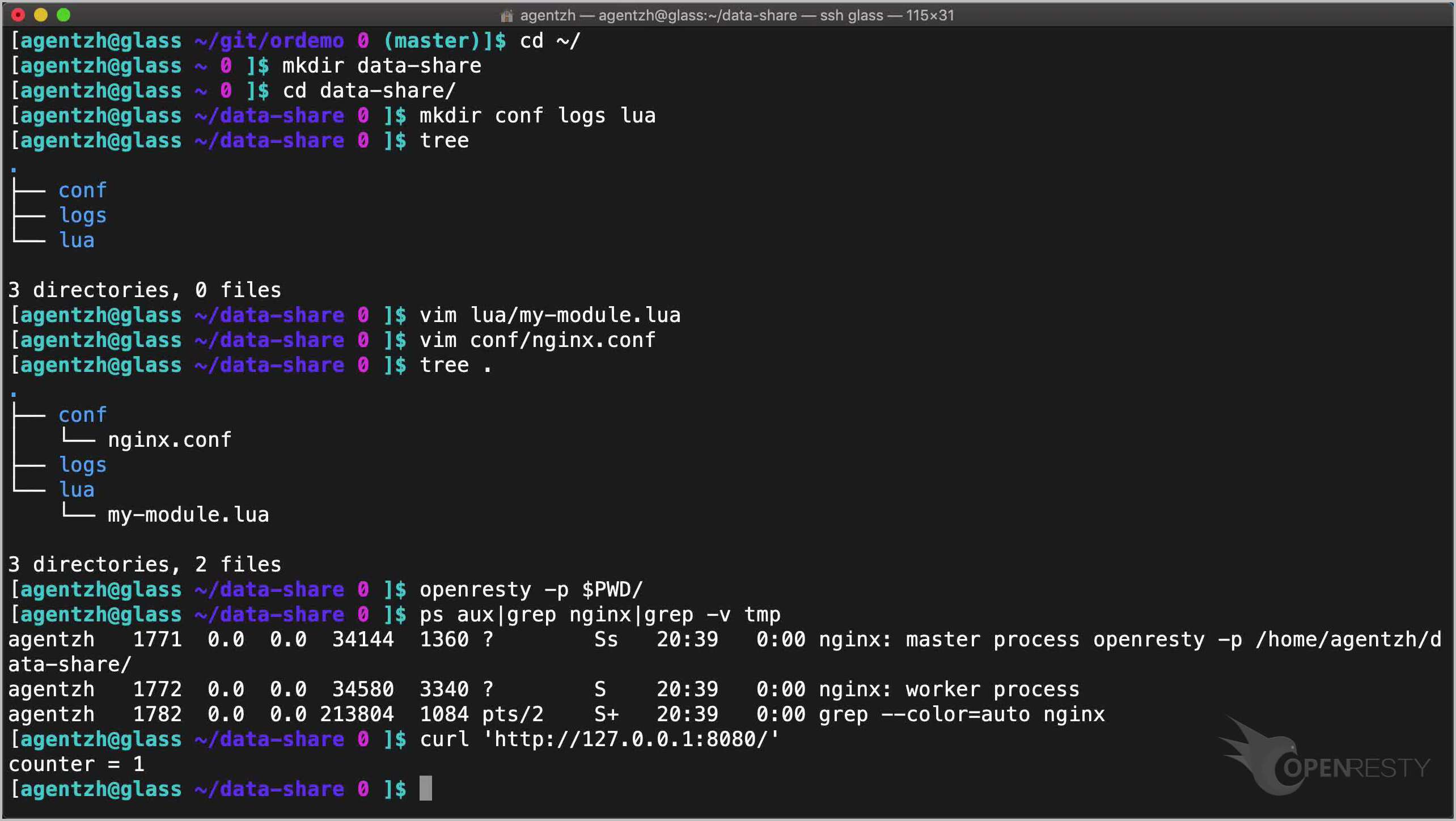
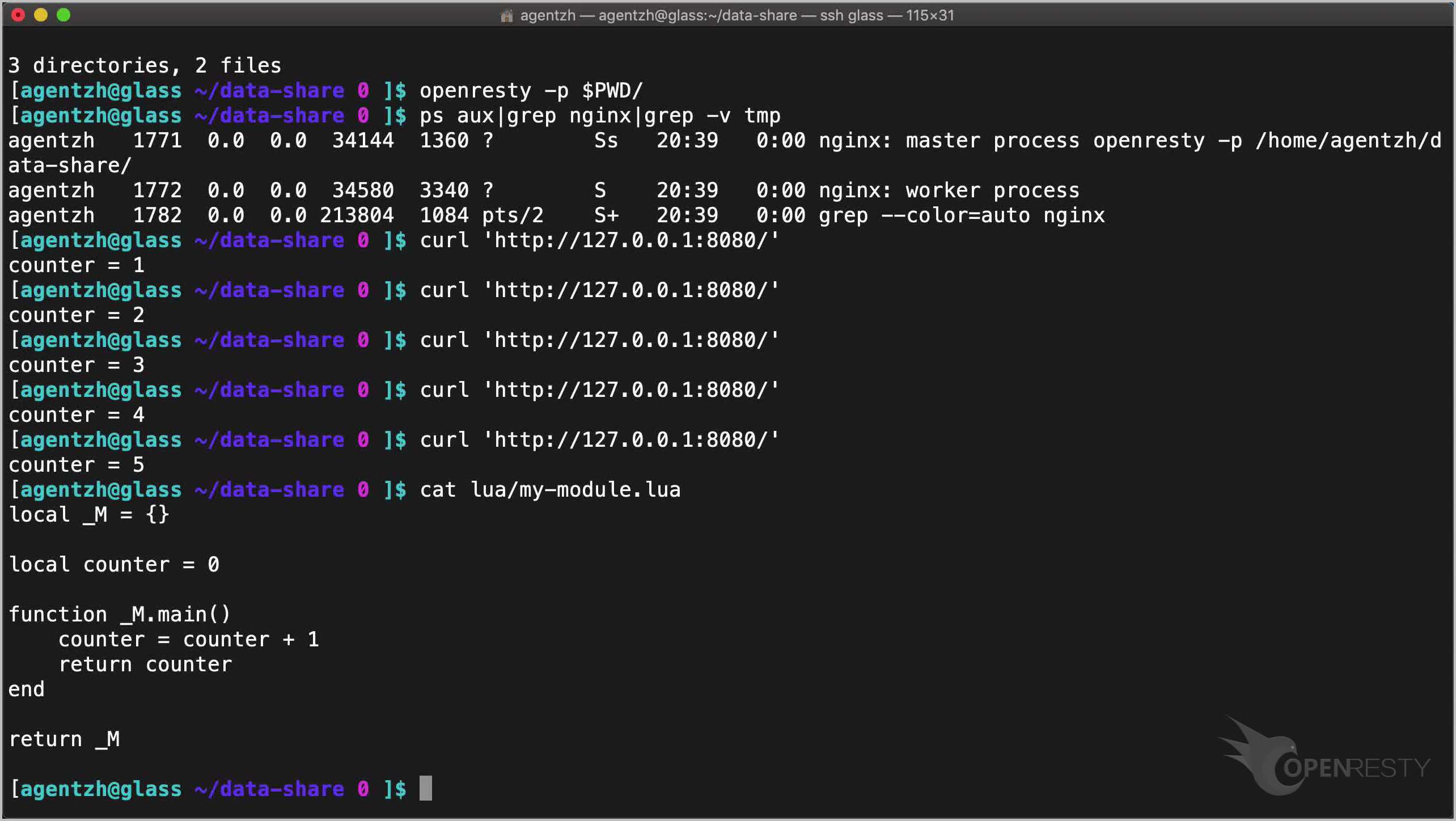
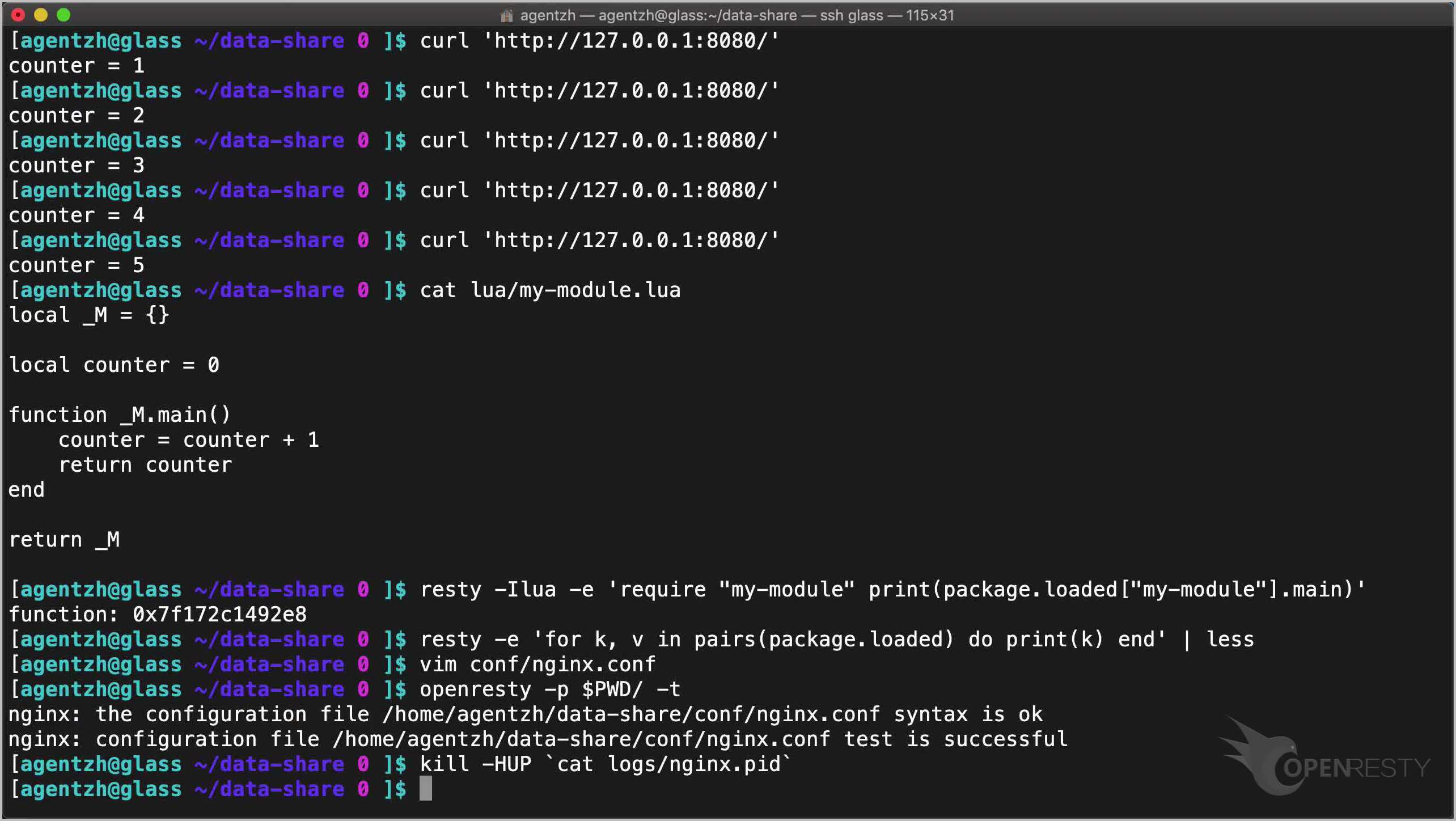
Send an HTTP request to the server using curl:
curl 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/'
The counter value is 1.
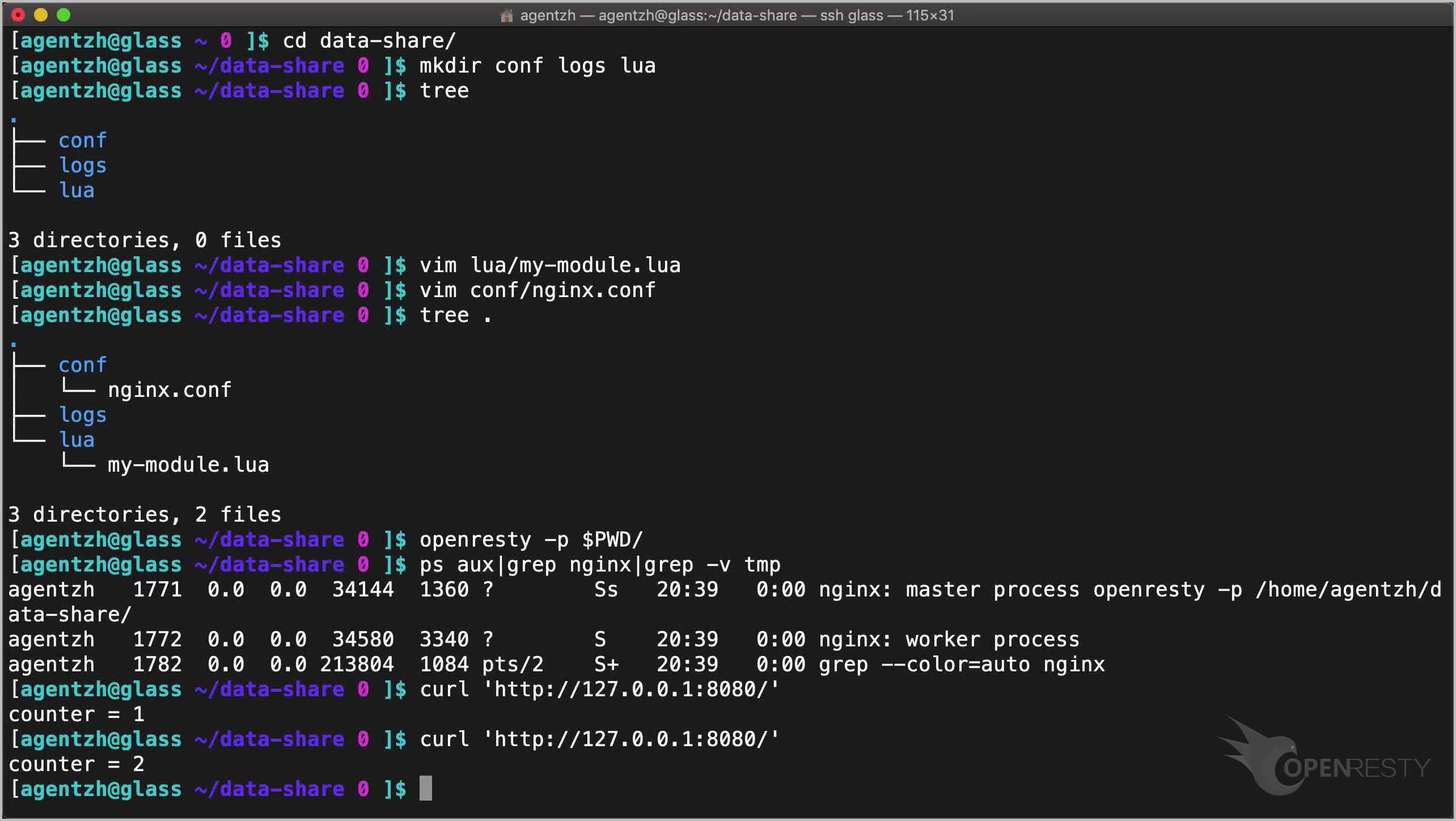
Again.
Cool, it’s 2 now.
It will only keep growing.
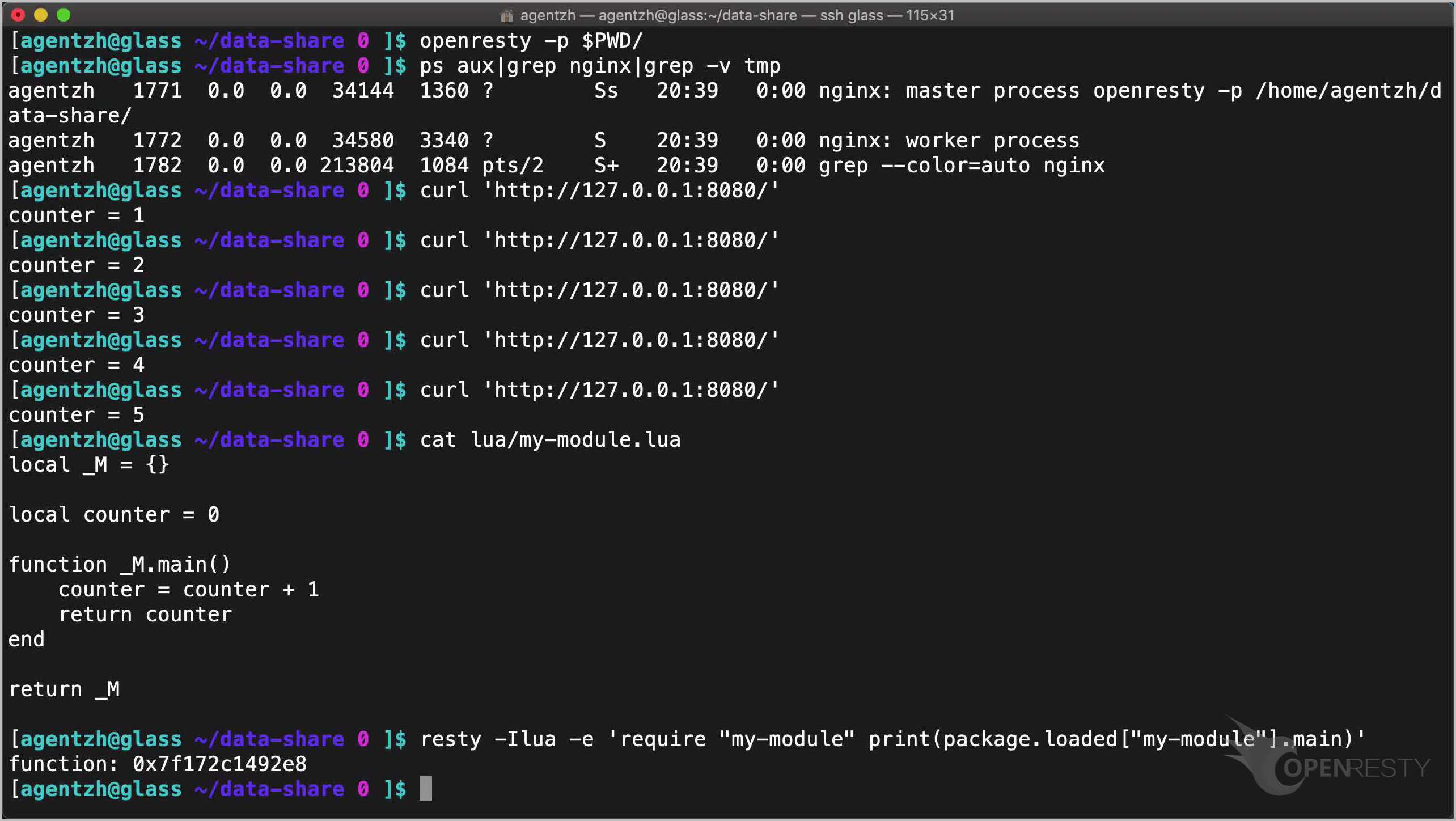
This counter Lua variable is shared because it is an up value (upvalue) of the Lua module function.
cat lua/my-module.lua
And the Lua module is cached and shared in the global LuaJIT virtual machine.
resty -Ilua -e 'require "my-module" print(package.loaded["my-module"].main)'
See? We can also access the cached Lua module directly.
The package.loaded global table holds all the loaded Lua modules.
resty -e 'for k, v in pairs(package.loaded) do print(k) end'
Here, most of the modules are those standard ones.
There is a limitation, however. Such data cannot be shared among different nginx worker processes.
It’s not a problem here because only 1 worker process is configured.
But usually we would utilize multiple CPU cores by enabling multiple worker processes.
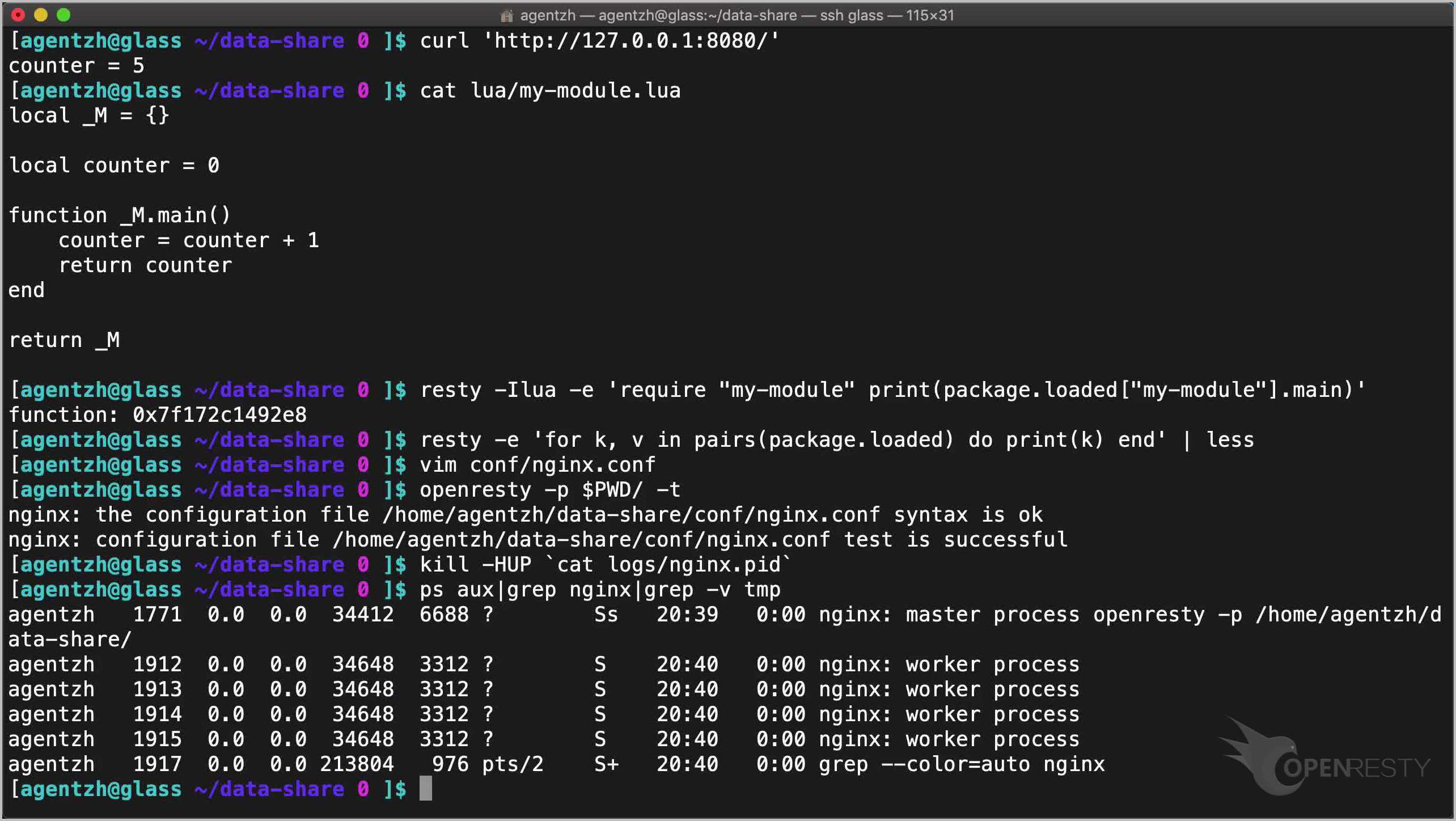
worker_processes 4;
Then each worker process would have its own counter.
Let’s test the configuration and then reload the server.
openresty -p $PWD/ -t
kill -HUP `cat logs/nginx.pid`
Now we should have 4 worker processes.
ps aux|grep nginx|grep -v tmp
So this Lua module data sharing approach is mostly useful for Lua level data caching.
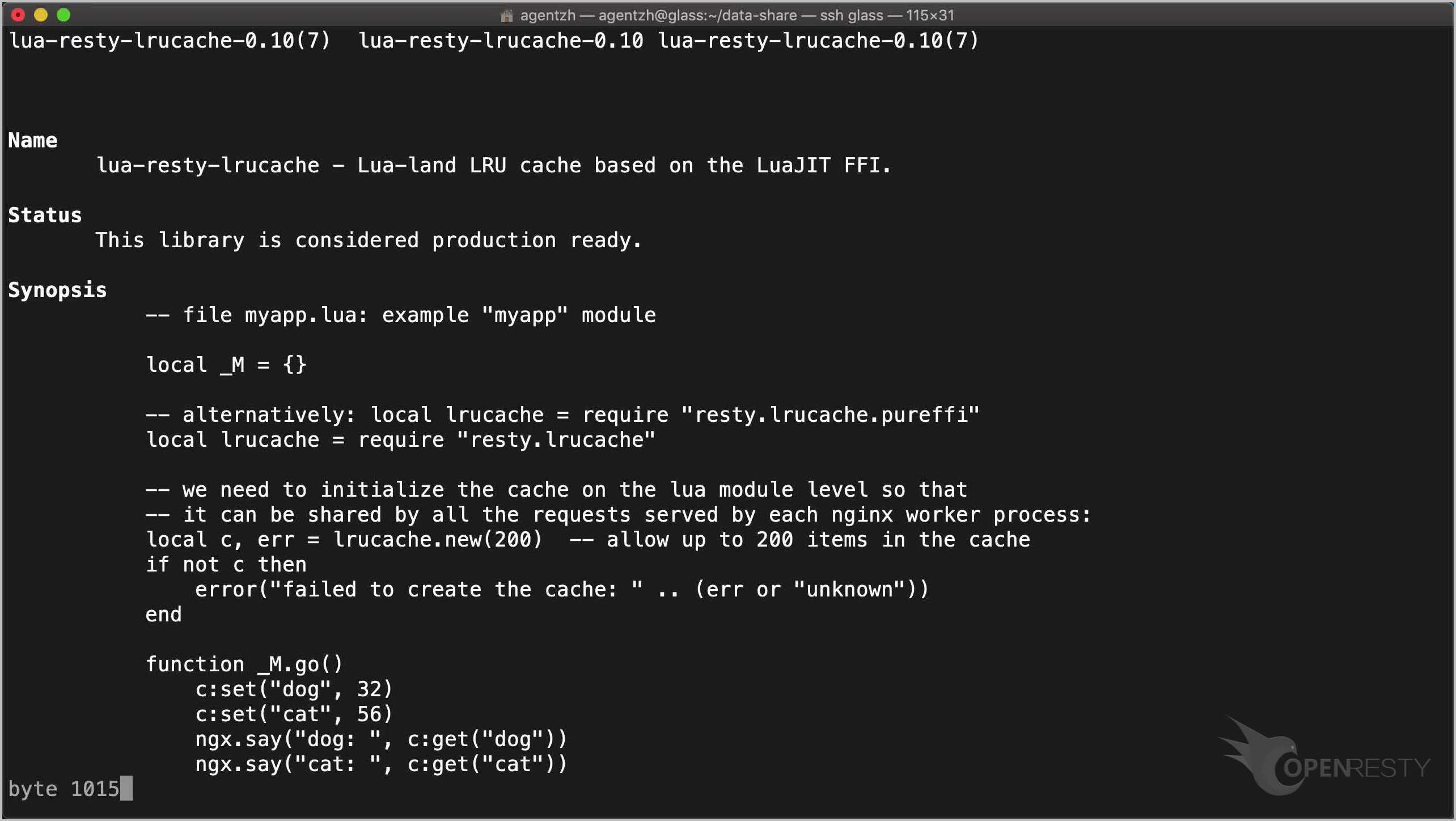
The resty.lrucache Lua module shipped with OpenResty is designed for such use cases.
restydoc resty.lrucache
We will cover this module in a future tutorial.
If we want to share data across all the worker processes, we should use the Lua shared memory dictionaries instead.
restydoc -s lua_shared_dict
restydoc -s ngx.shared.DICT
We will cover this topic in another dedicated tutorial.
That’s all I’d like to cover today. Happy hacking!
If you like this tutorial, please subscribe to this blog site and our YouTube channel. Thank you!
About The Author
Yichun Zhang (Github handle: agentzh), is the original creator of the OpenResty® open-source project and the CEO of OpenResty Inc..
Yichun is one of the earliest advocates and leaders of “open-source technology”. He worked at many internationally renowned tech companies, such as Cloudflare, Yahoo!. He is a pioneer of “edge computing”, “dynamic tracing” and “machine coding”, with over 22 years of programming and 16 years of open source experience. Yichun is well-known in the open-source space as the project leader of OpenResty®, adopted by more than 40 million global website domains.
OpenResty Inc., the enterprise software start-up founded by Yichun in 2017, has customers from some of the biggest companies in the world. Its flagship product, OpenResty XRay, is a non-invasive profiling and troubleshooting tool that significantly enhances and utilizes dynamic tracing technology. And its OpenResty Edge product is a powerful distributed traffic management and private CDN software product.
As an avid open-source contributor, Yichun has contributed more than a million lines of code to numerous open-source projects, including Linux kernel, Nginx, LuaJIT, GDB, SystemTap, LLVM, Perl, etc. He has also authored more than 60 open-source software libraries.